Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.3 Boyle'S Law: Analysis
Uploaded by
malaomarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.3 Boyle'S Law: Analysis
Uploaded by
malaomarCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
3 BOYLES LAW
Option 1: Changing the volume of air to measure pressure
Hypothesis:
When the volume of air decreases, the pressure increases when its mass and temperature is
constant
Aim:
To investigate the relationship between the pressure and volume of air
Variables:
Manipulated: Volume of air within syringe
Responding: Pressure of air
Constant: Mass, temperature of air
3
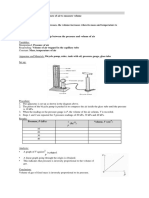
Apparatus and Materials: Rubber hose, Bordon gauge, 100 cm syringe
Set up:
Procedure:
1. Apparatus is set up as per the diagram.
2. The nose of the syringe is fitted with a rubber hose and the piston is adjusted so that air volume of 100
3
cm at atmospheric pressure is trapped in the syringe.
3. The rubber hose is connected to a Bourdon gauge and air pressure is read from the
gauge.
3
4. The piston of the syringe is pushed in until the trapped air volume becomes 90 cm
and the air pressure is read from the Bourdon gauge.
3
5. Step 4 is repeated for air volume values 80, 70, and 60 cm .
Results:
3 Pressure, P (Pa)
Volume, V (cm ) 1 -3
(cm )
V
Analysis:
A graph of P against
Analysis:
A graph of P against 1
is plotted.
V
A linear graph going through the origin is obtained.
This indicates that pressure is inversely proportional to the volume of
gas.
Conclusion:
Gas pressure of fixed mass is inversely proportional to its volume.
You might also like
- Boyles Law 2Document1 pageBoyles Law 2malaomarNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law ExperimentDocument11 pagesBoyle's Law ExperimentDustin VazquezNo ratings yet
- Skema Physics Quiz SPMDocument2 pagesSkema Physics Quiz SPMimposter131No ratings yet
- BOYLE'S, CHARLES'S AND GRAHAM'S LAWSDocument9 pagesBOYLE'S, CHARLES'S AND GRAHAM'S LAWSzulaika fahmiNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation Full ReportDocument6 pagesBernoulli Equation Full ReportChala1989No ratings yet
- Lab Gas FlowmeterDocument7 pagesLab Gas Flowmeterazym94No ratings yet
- Physics Coursework STPMDocument20 pagesPhysics Coursework STPMtarvinraj100% (1)
- Dependence of Pressure On VolumeDocument7 pagesDependence of Pressure On VolumeFranko VujicicNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law - Experiment 2: 0 Comments Lesson PlansDocument8 pagesBoyle's Law - Experiment 2: 0 Comments Lesson PlansArif AzmanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4Document14 pagesLab Report 4zulaika fahmiNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument10 pagesReportapi-272632563No ratings yet
- Frederick Terry's Lab Report Fluid Dynamics - AsdDocument19 pagesFrederick Terry's Lab Report Fluid Dynamics - AsdFreddie TerryNo ratings yet
- Flow Mesurement FinalDocument20 pagesFlow Mesurement FinalMbabazi Jackson CalmaxNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Process ControlDocument51 pagesInstrumentation & Process ControlChiến Phan Công100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Marine Hydrodynamics I - Fluid Statics - Part 2Document20 pagesLecture 3 Marine Hydrodynamics I - Fluid Statics - Part 2Khalid BaragaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 and 4, Week 2. Temperature and Zeroth Law, Pressure Scale CalculationsDocument15 pagesLecture 3 and 4, Week 2. Temperature and Zeroth Law, Pressure Scale CalculationsUmer MajeedNo ratings yet
- Measure Air Viscosity Using a Pipe Flow ApparatusDocument4 pagesMeasure Air Viscosity Using a Pipe Flow ApparatusvishwajitNo ratings yet
- FLUID PRESSURE MEASUREMENT GUIDEDocument23 pagesFLUID PRESSURE MEASUREMENT GUIDEAyoub Al QeamNo ratings yet
- ES 65 Summer 2012-2013 Take Home 3Document2 pagesES 65 Summer 2012-2013 Take Home 3Eddie Balansag MCheavenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Latest JuDocument117 pagesLecture 5 Latest JuSolomon GebremariamNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Basic Mechanical Engineering (Bt-203) UNIT-2 Measurement of Pressure BY J.P.SinghDocument9 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Basic Mechanical Engineering (Bt-203) UNIT-2 Measurement of Pressure BY J.P.SinghDharmendra BelwanshiNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument112 pagesPressureissa sherryNo ratings yet
- Gases Push Water in Shallow WellsDocument112 pagesGases Push Water in Shallow Wellssaxman011No ratings yet
- Bernoulli ReportDocument12 pagesBernoulli ReportNashpreet DhillonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab MannualDocument14 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab MannualAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Fluids Lab Experiment No:3 Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementDocument14 pagesFluids Lab Experiment No:3 Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementDarivan DuhokiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document117 pagesLecture 3gebreslassie gereziherNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Boyle'S Law, Charles' Law and The Ideal Gas LawDocument13 pagesExperiment 5: Boyle'S Law, Charles' Law and The Ideal Gas LawNurul NadyaNo ratings yet
- Speed of Sound LabDocument2 pagesSpeed of Sound LabNWSPhysicsNo ratings yet
- How To Find Partial Pressures: RelatedDocument5 pagesHow To Find Partial Pressures: Relatedsalesy EcNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Pressure Measurementmohammad. 21No ratings yet
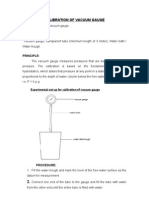
- Calibration of Vacuum GaugeDocument3 pagesCalibration of Vacuum Gaugeapi-197532840% (2)
- Static Fluid and Its ApplicationDocument22 pagesStatic Fluid and Its ApplicationNikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- Experiment Charles LawDocument3 pagesExperiment Charles LawZaiwati Othman0% (1)
- GFM Lab ReportDocument102 pagesGFM Lab ReportÁlvaroDeLaGarza100% (1)
- PK Sir SuggestionsDocument15 pagesPK Sir SuggestionsSanskriti GhisingNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law Lab Report 4Document10 pagesBoyle's Law Lab Report 4Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument12 pagesBernoulli's Equationasfand12345100% (1)
- Pi I Unit 2 Pressure MeasurementDocument41 pagesPi I Unit 2 Pressure MeasurementRahmat ElyasaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter on GasesDocument97 pagesChemistry Chapter on GasesEko Setyo BudiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document5 pagesExperiment 3Ediezel James IlarinaNo ratings yet
- Measure Boyle's Law with a Gas Thermometer (40chDocument24 pagesMeasure Boyle's Law with a Gas Thermometer (40chHakimi100% (1)
- Presuure MeasurmentDocument9 pagesPresuure Measurmenteng.ali.haudear.2004No ratings yet
- PAG 08.3 - Estimating Work Done by A Gas When Temperature IncreasesDocument3 pagesPAG 08.3 - Estimating Work Done by A Gas When Temperature IncreasesjmsonlNo ratings yet
- LO2 - Pressure and Its Measurement For An Incompressible FluidDocument43 pagesLO2 - Pressure and Its Measurement For An Incompressible Fluidsushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Report Velocity Profile PDFDocument12 pagesReport Velocity Profile PDFNoor AlomariNo ratings yet
- Venturi MetersDocument16 pagesVenturi Metersengineer63No ratings yet
- Pressure Physics Form 4Document47 pagesPressure Physics Form 4Hairul Akmal100% (2)
- Sesi-15.PDF Example But Old Nozzle FlowDocument42 pagesSesi-15.PDF Example But Old Nozzle FlowyamakunNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 To Verify The Bernoulli's Theorem For Steady Flow of WaterDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 To Verify The Bernoulli's Theorem For Steady Flow of WaterMHS MHSNo ratings yet
- Calibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugesubyNo ratings yet
- 220s15 ExpB LabManualDocument5 pages220s15 ExpB LabManualMetu Ncc HaberlerNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Pressure Measurement of Water by Using Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge and U-Tube Differential ManometerDocument6 pagesComparative Study of Pressure Measurement of Water by Using Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge and U-Tube Differential ManometerYash PatilNo ratings yet
- Validates Bernoulli's Theorem in Tapered DuctDocument29 pagesValidates Bernoulli's Theorem in Tapered DuctAnonymous NyvKBWNo ratings yet
- Discharge Through Aventuri-MeterDocument8 pagesDischarge Through Aventuri-MeterMohammad KahlaNo ratings yet
- Review Materials in Incompressible FlowDocument42 pagesReview Materials in Incompressible FlowAviation Review MaterialsNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument31 pagesPressureasparagus1996No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2018-19 - MEE1004 - ETH - MB309 - VL2018191003741 - Reference Material I - Fluid Mechanics-2 PDFDocument48 pagesFALLSEM2018-19 - MEE1004 - ETH - MB309 - VL2018191003741 - Reference Material I - Fluid Mechanics-2 PDFSivaram PeramNo ratings yet
- Recommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsFrom EverandRecommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsE. F. G. HeringtonNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Discovery and Half-LifeDocument21 pagesRadioactivity Discovery and Half-LifemalaomarNo ratings yet
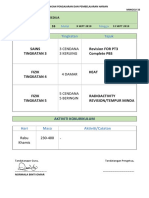
- RANCANGAN PENGAJARAN DAN PEMBELAJARAN HARIAN MINGGU 1Document11 pagesRANCANGAN PENGAJARAN DAN PEMBELAJARAN HARIAN MINGGU 1malaomarNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukDocument15 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Daily lesson plan for science week 31Document15 pagesDaily lesson plan for science week 31malaomarNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision Complete PBSDocument12 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision Complete PBSmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Holiday Package Physics F5 2017 - SoalanDocument2 pagesHoliday Package Physics F5 2017 - SoalanmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision FOR PT3 Complete PBSDocument14 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision FOR PT3 Complete PBSmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukDocument16 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan TajukmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Holiday - Package KIMIA F4Document2 pagesHoliday - Package KIMIA F4malaomarNo ratings yet
- Mata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision FOR PT3 Complete PBSDocument15 pagesMata Pelajaran Tingkatan Tajuk: Sains Tingkatan 3 Revision FOR PT3 Complete PBSmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Script Smksbs Group 2 - Petrosains Science Show Competition 2017Document4 pagesScript Smksbs Group 2 - Petrosains Science Show Competition 2017malaomar0% (1)
- Trial p2 Section C No-11Document4 pagesTrial p2 Section C No-11malaomar0% (1)
- Traspiration Factor WindDocument1 pageTraspiration Factor WindmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 5Document1 pagePhysics Form 5malaomarNo ratings yet
- Determine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellDocument3 pagesDetermine EMF and internal resistance of a dry cellmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Petri Dish 2 Types of Paddy Plant Forcep Paper Bag: Cross PolinationDocument1 pagePetri Dish 2 Types of Paddy Plant Forcep Paper Bag: Cross PolinationmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Important ConceptsDocument12 pagesNutrition: Important ConceptsmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Chap 02 - 2-3Document13 pagesChap 02 - 2-3malaomarNo ratings yet
- Absorption of The Products of DigestionDocument3 pagesAbsorption of The Products of DigestionmalaomarNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument3 pagesLithiummalaomarNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Homework Holiday NotesDocument2 pagesForm 4 Physics Homework Holiday NotesmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Importance of A Balanced DietDocument3 pagesImportance of A Balanced DietmalaomarNo ratings yet
- Pascal HandoutDocument2 pagesPascal HandoutmalaomarNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS FORM 4: Homework Mid Year Holiday Cut and Paste Into Note BookDocument2 pagesPHYSICS FORM 4: Homework Mid Year Holiday Cut and Paste Into Note BookmalaomarNo ratings yet
- SodiumDocument3 pagesSodiummalaomarNo ratings yet
- LithiumDocument3 pagesLithiummalaomarNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Float Into Water With Which It Reacts Instantly To Release Hydrogen, Which Burns With A Lilac FlameDocument2 pagesPotassium: Float Into Water With Which It Reacts Instantly To Release Hydrogen, Which Burns With A Lilac FlamemalaomarNo ratings yet
- Soalan Aechimedes' PrincipleDocument4 pagesSoalan Aechimedes' PrinciplemalaomarNo ratings yet