0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views4 pagesEE 5601 Power System Analysis
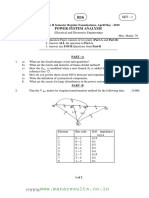
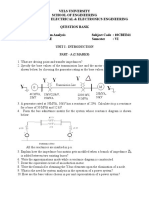
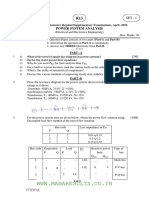
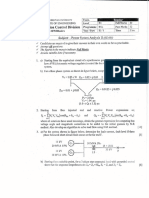
This document outlines the examination structure for the VI Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering course at Anna University, specifically for the Power System Analysis subject. It includes details on the exam format, topics covered, and types of questions, including both theoretical and practical applications related to power systems. The document also specifies the marks distribution and Bloom's Taxonomy levels for each question.
Uploaded by
dhayanithi351Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views4 pagesEE 5601 Power System Analysis
This document outlines the examination structure for the VI Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering course at Anna University, specifically for the Power System Analysis subject. It includes details on the exam format, topics covered, and types of questions, including both theoretical and practical applications related to power systems. The document also specifies the marks distribution and Bloom's Taxonomy levels for each question.
Uploaded by
dhayanithi351Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd