Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-7 Astable Multivibrators: T RC F T
Uploaded by
redberryyesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-7 Astable Multivibrators: T RC F T
Uploaded by
redberryyesCopyright:
Available Formats
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
Chapter-7
Astable Multivibrators
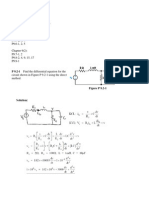
1. For the multivibrator in Fig.7p.1, R
1
= R
2
= R = 47 kO, C
1
= C
2
= C = 0.01 F.
Find the time period and frequency.
Fig.7p
.
1 Un-symmetric astable multivibrator
Solution:
Given R
1
= R
2
= R = 47 k ,C O
1
= C
2
= 0.01 F.
This is a symmetric astable multivibrator.
3 6
1.38 1.38 47 10 0.01 10 0.648 ms T RC
= = =
3
1 1
1.54 kHz.
0.648 10
f
T
= = =
2. For the astable multivibrator in Fig.7p.1, R
1
= 20 kO, R
2
= 30 kO,C
1
= C
2
= C =
0.01 F. Find the time period, duty cycle and the frequency.
Solution:
This is an un-symmetric astable multivibrator.
3 6
2 1 1
0.69 0.69 20 10 0.01 10 0.2 ms T R C
= = =
3 6
1 2 2
0.69 0.69 30 10 0.01 10 0.138 ms T R C
= = =
1 2
0.138 0.2 0.338 ms T T T = + = + =
1
0.138
per cent 100 per cent 100 per cent 59.17 per cent
0338
T
D
T
= = =
3
1 1
2.95 kHz.
0.338 10
f
T
= = =
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 1
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
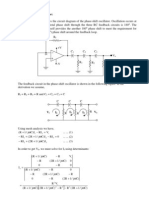
3. For the symmetric astable multivibrator that generates square waves with vertical
edges shown in Fig.7p.3, V
CC
=10 V, R
C
= R
3
= 2 kO, R
1
= R
2
= 20 k , C = 0.1 O F ,
h
FE(min)
= 30. Show that the ON device is in saturation. Also find f. Assume suitable
values for V
CE(sat)
and V
BE(sat).
Si transistors are used.
Fig.7p.3 Astable multivibrator with vertical edges
Solution:
Assume Q
1
is OFF and Q
2
is ON and in saturation. If Q
2
is ON and in saturation, for
silicon transistors, V
C2
=V
CE(sat)
= 0.2 V, V
B2
= = 0.7 V then D
V
2
is ON. The collector
load is R
3
//R
C
.
'
C
R
= R
3
//R
C
=
2 2
1 k
4
=
(sat)
2
' 3
10 0.2 9.8
9.8 mA
1 k 1 10
CC CE
C
C
V V
I
R
= = = =
2
3
10 0.7 9.3
0.465 mA
20 k 20 10
CC
B
V V
I
R
o
= = = =
2
2min
min
9.8 mA
0.326 mA
30
C
B
FE
I
I
h
= = =
I
B2
>> I
B2min
Hence Q
2
is in saturation.
To find f:
For a symmetric astable multivibrator: f =
3 6
0.7 0.7
350 Hz
20 10 0.1 10 RC
= =
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 2
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
4. Design a symmetric collector-coupled astable multivibrator to generate a square wave
of 10 kHz having peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 V where h
FEmin
= 30,
V
CE(sat)
= 0.2 V, I
C(sat)
= 2 mA.
Solution:
Given V
CE(sat)
= 0.2 V, V
BE(sat)
= V
o
= 0.7 V, I
C(sat)
= 2 mA, f = 2 kHz, h
FEmin
= 30.
As the output amplitude is specified as 12 V, choose V
CC
= 12 V.
As f = 2 kHz,
3
1 1
0.1 ms
10 10
T
f
= = =
The astable is symmetric, hence
R
1
= R
2
= R and C
1
= C
2
=C
1 2
0.1
0.05 ms
2 2
T
T T = = = =
To calculate R
C2
:
(sat)
2
3
(sat)
10 0.2
4.9 k
2 10
CC CE
C
C
V V
R
I
= = =
R
C1
= R
C2
= 4.9 k.
To calculate R
2
:
2
2(sat)
CC
B
V V
R
I
o
=
(sat)
2 min
min
2 mA
0.066 mA
30
C
B
FE
I
I
h
= = =
If Q
2
is in saturation
2(sat) 2(min)
1.5
B B
I I =
1.5 0.066 0.099 mA = =
2
3
10 0.7
93.9 k
0.099 10
R
= =
1 2
93.9 k R R = =
As C
1
= C
2
T
1
= 0.69R
2
C
2
3
2
3
0.05 10
771.7 pF
0.69 93.9 10
C
= =
C
1
= C
2
= 771.7 pF
5. Design an un-symmetric astable multivibrator having duty cycle of 40 per cent. It is
required to oscillate at 5 kHz. Ge transistors with h
FE
= 40 are used. The amplitude of the
square wave is required to be 20 V. I
C
= 5 mA, V
CE(sat)
= 0.1 V and V
BE(sat)
= 0.3 V.
Solution:
For Ge transistors, V
CE(sat)
= 0.1 V, V
BE(sat)
= V = 0.3 V
o
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 3
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
Given I
C(sat)
= 5 mA, f = 5 kHz, h
FEmin
= 40, duty cycle = 40 per cent.
As the output amplitude is specified as 20 V, choose V
CC
= 20 V.
As f = 5 kHz,
3
1 1
0.2 ms
5 10
T
f
= = =
The astable is unsymmetric, hence
T
1
T
2
i.e. R
1
C
1
R
2
C
2
choose C
1
= C
2
=C
then R
1
R
2
Duty cycle =
T
T
T T
T
1
2 1
1
=
+
0.4 =
3
1
10 2 . 0
T
3
1
0.4 0.2 10 0.08 ms T
= =
T
2
= T T
1
= 0.2 0.08 = 0.12 ms
To calculate R
C2
:
(sat)
2
(sat)
20 0.1
3.98 k
5 mA
CC CE
C
C
V V
R
I
= = =
Choose R
C1
= R
C2
=3.98 k = R
C
To calculate R
2
:
2
2(sat)
CC
B
V V
R
I
o
=
(sat)
2 min
min
5 mA
0.125 mA
40
C
B
FE
I
I
h
= = =
If Q
2
is in saturation
2(sat) 2(min)
1.5
B B
I I =
1.5 0.125 mA = 0.187 mA =
2
3
20 0.3
105.3 k
0.187 10
R
= =
As C
1
= C
2
= C
T
1
= 0.69R
2
C
2
3
1
2
3
2
0.08 10
1.1 nF
0.69 0.69 105.3 10
T
C
R
= = =
1 2
1.1 nF C C = =
T
2
= 0.69R
1
C
1
9
1
3
10 1 . 1 69 . 0 10 12 . 0
= R
3
1
9
0.12 10
158.1 k
0.69 1.1 10
R
= =
h
FE
R
C
= 40 3.98 k = 159 k
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 4
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
The values R
1
and R
2
are less than h
FE
R
C
. Hence the devices Q
1
and Q
2
are in
saturation, when ON.
6. For an un-symmetric astable multivibratorR
1
= 100 k, R
2
= 100 k, C
1
= 0.02 F,
C
2
= 0.01F. Find the frequency of oscillation and the duty cycle.
Solution:
3 6
2 1 1
0.69 0.69 100 10 0.02 10 1.38 ms T R C
= = =
3 6
1 2 2
0.69 0.69 100 10 0.01 10 0.69 ms T R C
= = =
1 2
0.69 1.38 2.09 ms T T T = + = + =
3
1 1
483 Hz
2.09 10
f
T
= = =
1
3
0.69
per cent 100 per cent 100 per cent 33 per cent
2.09 10
T
D
T
= = =
.
7. Design an unsymmetrical astable multivibrator shown in Fig.7p.1 using silicon n
pn transistors having an output amplitude of 12 V. Given data,
I
C(sat)
= 5 mA, h
FEmin
= 50, f = 5 kHz, duty cycle = 0.6.
Fig.7p.1 Un-symmetric astable multivibrator
Solution:
Assume V
CE(sat)
= 0.2 V
V
BE(sat)
= V = 0.7 V
o
Given I
C(sat)
= 5 mA, f = 2 kHz, h
FEmin
= 50, duty cycle = 0.6.
As the output amplitude is specified as 12 V, choose V
CC
= 12 V.
As f = 2 kHz,
3
1 1
0.5 ms
2 10
T
f
= = =
The astable is unsymmetric, hence
T
1
T
2
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 5
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
i.e. R
1
C
1
R
2
C
2
choose C
1
= C
2
=C
then R
1
R
2
Duty cycle =
T
T
T T
T
1
2 1
1
=
+
0.6 =
T
T
1
1
0.6 0.6 0.5 0.3 ms T T = = =
T
2
= T T
1
= 0.5 0.3 = 0.2 ms
To calculate R
C2
:
(sat )
2
(sat)
12 0.2 11.8
5 mA 5 mA
CC CE
C
C
V V
R
I
= = =
R
C2
= 2.36 k
Choose R
C1
= R
C2
=2.2 k = R
C
.
To calculate R
2
:
2
2(sat)
CC
B
V V
R
I
o
=
(sat )
2min
min
5 mA
50
C
B
FE
I
I
h
= =
=0.1 mA
If Q
2
is in saturation
2(sat ) 2(min)
1.5
B B
I I =
1.5 0.1 0.15 mA = =
2
12 0.7 11.3 V
75.3 k
0.15 0.15 mA
R
= = =
As C
1
= C
2
= C
T
1
= 0.69R
2
C
0.3 ms 0.69 75.3 k C =
3
3
0.3 10
5.77 nF
0.69 75.3 10
C
= =
T
2
= 0.69R
1
C
9
1
3
10 77 . 5 69 . 0 10 2 . 0
= R
3
1
9
0.2 10
50 k
0.69 5.77 10
R
=
=
h
FE
R
C
= 50 2.2 K 110 K =
The values R
1
and R
2
are less than h
FE
R
C
. Hence the devices Q
1
and Q
2
are in saturation,
when ON.
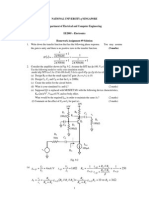
8. A Voltage-to-frequency converter shown in Fig.7p.2 generates oscillations at a
frequency f
1
when V
BB
= V
CC
. Find the ratio of V
CC
/V
BB
at which the frequency f
2
= 4f
1
.
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 6
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
Fig.7p.2 Voltage-to-frequency converter
Solution:
From Eq.(7.30), the expression for the frequency of oscillations is
f =
) 1 ln( 2
1
BB
CC
V
V
+ t
Case1: The frequency of oscillations is f
1
when V
CC
= V
BB
2 ln 2
1
) 1 1 ln( 2
1
1
t t
=
+
= f
Case 2: If a new frequency f
2
= 4f
1
is desired.
) 1 ln( 2
1
2
BB
CC
V
V
f
+
=
t
2 ln
2
2 ln 2
1
4
4
1 2
t t
= =
= f f
) 1 ln( 2
1
2 ln
2
BB
CC
V
V
+
=
t
t
) 1 ln( 4 2 ln
BB
CC
V
V
+ =
2 ln ) 1 ln(
4
= +
BB
CC
V
V
Taking antilog
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 7
Pulse and Digital Circuits Venkata Rao K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Rao G.
Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd 2010 8
2 ) 1 (
4
= +
BB
CC
V
V
414 . 1 2 ) 1 (
2
= = +
BB
CC
V
V
189 . 1 414 . 1 1 = = +
BB
CC
V
V
189 . 0 1 189 . 1 = =
BB
CC
V
V
You might also like
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2DrGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- hw12 PDFDocument9 pageshw12 PDFanisettimanikantaNo ratings yet
- Bistable Multivibrator Design PDFDocument20 pagesBistable Multivibrator Design PDFOmkar Thakur100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (3)
- Common-Emitter Amplifier Frequency Response Example: Function For Calculating Parallel ResistorsDocument6 pagesCommon-Emitter Amplifier Frequency Response Example: Function For Calculating Parallel ResistorsJain DeepakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Oscillator: - Introduction of Oscillator - Linear OscillatorDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Oscillator: - Introduction of Oscillator - Linear Oscillatoraaljuhani123No ratings yet
- Oscillator DesignDocument10 pagesOscillator Designsowmya.mas1542No ratings yet
- Web For Principle of Communication - B. Tech 4th SemDocument36 pagesWeb For Principle of Communication - B. Tech 4th SemFurqan Ali Khan100% (1)
- 3AE Exercises Chap 1 Freq Resp Solutions Aug10Document3 pages3AE Exercises Chap 1 Freq Resp Solutions Aug10Aluwani KhomolaNo ratings yet
- Series RC Circuit: Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesSeries RC Circuit: Electrical and Electronic Engineeringخہٰہٰالہٰد ۦ' ۦ'No ratings yet
- Files-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Document8 pagesFiles-3-Lesson Notes Lecture 31Eyad Abozyd100% (1)
- Solution - Tutorial 3Document11 pagesSolution - Tutorial 3zgalionoooNo ratings yet
- MD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 12Document6 pagesMD Singh Power Electronics Solution Manual To Chapter 12Anoop MathewNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of Mosfet Amplifier Configurations: 2.1 ObjectiveDocument8 pagesPspice Simulation of Mosfet Amplifier Configurations: 2.1 ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapt14Prob41 60Document11 pagesChapt14Prob41 60oriontheoneNo ratings yet
- Problem Solutions: V S SC Ts Vs SC R Ts SRCDocument37 pagesProblem Solutions: V S SC Ts Vs SC R Ts SRCLuis AntonioNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge Oscillators PresentationDocument15 pagesWein Bridge Oscillators PresentationHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- EE236: Experiment No. 1 NGSPICE Simulation of RC and RLC CircuitsDocument15 pagesEE236: Experiment No. 1 NGSPICE Simulation of RC and RLC CircuitsAakanksha JainNo ratings yet
- Detailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'Document12 pagesDetailed Solution of IES 2103 (ECE) Objective Paper - I: Set - A'vijaynarayan guptaNo ratings yet
- EE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionDocument6 pagesEE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionKL ChiangNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio 2014Document2 pagesFormula Rio 2014Alberto García WatsonNo ratings yet
- Transistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Document66 pagesTransistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Adri Muhaimin AfifNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsDocument9 pagesReaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsMiguel Magat Joves100% (1)
- Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDFDocument6 pagesEe115hw+sol03 06 N PDFthinkberry22100% (1)
- CP Phys Web Rev CH 17Document7 pagesCP Phys Web Rev CH 17fathoboNo ratings yet
- Capacitor: Chapter - 31Document22 pagesCapacitor: Chapter - 31Venkatesh BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- MT-CET 2013 PCM Solution - 20.04.2013Document11 pagesMT-CET 2013 PCM Solution - 20.04.2013Ashwin MishraNo ratings yet
- ECE QuestionsDocument12 pagesECE QuestionsSimran SiNo ratings yet
- Problem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgDocument8 pagesProblem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Physics: L B A G 2Document7 pagesPart 1 - Physics: L B A G 2bindaaz301No ratings yet
- Ln-8 Idle Mind Solutions: A 1 E A R 1 T 1 1 T 2Document22 pagesLn-8 Idle Mind Solutions: A 1 E A R 1 T 1 1 T 2aashulhedaNo ratings yet
- 2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFDocument19 pages2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFKD0% (1)
- Test2 - Answer Key - PDF 364Document3 pagesTest2 - Answer Key - PDF 364chhistNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Question 1 (2 Points)Document3 pagesAnswer:: Question 1 (2 Points)oke dmm50% (2)
- Nguyen P Hw2Document7 pagesNguyen P Hw2Phat NguyenNo ratings yet
- SPT - 1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesSPT - 1 SolutionsChristopher NolanNo ratings yet
- Solution Booklet EnglishDocument8 pagesSolution Booklet EnglishVidyakumari RethinavelNo ratings yet
- HW5 Fall 2007 EEE481&581 SolutionDocument10 pagesHW5 Fall 2007 EEE481&581 SolutionUmit GudenNo ratings yet
- Cap 31Document100 pagesCap 31Gilmar FerrettiNo ratings yet
- 3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsDocument2 pages3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsAluwani KhomolaNo ratings yet
- Point: Electric Current in Conductors Chapter - 32Document20 pagesPoint: Electric Current in Conductors Chapter - 32Jaynandan KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceDocument46 pages01 RLC Circuit and ResonanceLatif Nurohman Bayu Nugroho60% (5)
- Sallen-Key Low Pass Filter Design Routine: R C R G VDocument17 pagesSallen-Key Low Pass Filter Design Routine: R C R G VMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises: Chapter 10: 10.1 Use The Chemical Potential of An Ideal Gas in (10.1.9) and Obtain The BarometricDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises: Chapter 10: 10.1 Use The Chemical Potential of An Ideal Gas in (10.1.9) and Obtain The BarometricSalomé TorresNo ratings yet
- TUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Document11 pagesTUGAS ELEKTRONIKA - Kelompok 2Christine SibaraniNo ratings yet
- 05 - Communication All Chapters PDFDocument52 pages05 - Communication All Chapters PDFthumatimadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Phs122Document52 pagesElectric Field Phs122Danika LoavesNo ratings yet
- 350 NC 7Document36 pages350 NC 7Malou Ruiz DenolanNo ratings yet
- Hart Chapter 10 SolutionsDocument8 pagesHart Chapter 10 SolutionsCarolina de MeloNo ratings yet
- R-C and Wien Bridge OscillatorsDocument8 pagesR-C and Wien Bridge Oscillatorsলাজ মাহমুদNo ratings yet
- EEE C364/INSTR C 364 Analog ElectronicsDocument17 pagesEEE C364/INSTR C 364 Analog ElectronicsAngad SehdevNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document108 pagesCH 14SherifNo ratings yet
- Ep 05012Document25 pagesEp 05012vikas_vernekarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microwave EngineeringDocument12 pagesAdvanced Microwave Engineeringkwizera evaNo ratings yet
- Rland RCDocument33 pagesRland RCSyed Muhammad DanishNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- FS3KMDocument5 pagesFS3KMpepe sanchezNo ratings yet
- 10 Mike BrinsonDocument63 pages10 Mike Brinsonjitu_4No ratings yet
- Master Control SwitchingDocument4 pagesMaster Control SwitchingJosé Juan PifanoNo ratings yet
- TMS3705 Transponder Base Station IC: 1 Device OverviewDocument28 pagesTMS3705 Transponder Base Station IC: 1 Device OverviewwillseeseewillNo ratings yet
- 3par StoreServ 7000 Overview PDFDocument272 pages3par StoreServ 7000 Overview PDFpruthivi dasNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix of LGDocument22 pagesBCG Matrix of LGsumancalls71% (14)
- 66 FC 7463 DBD 2 FCCDDocument87 pages66 FC 7463 DBD 2 FCCDfrangky.rengkungNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Limitation of Conventional Tubes:: Lead Inductance and Inter-Electrode Capacitance EffectDocument55 pagesHigh Frequency Limitation of Conventional Tubes:: Lead Inductance and Inter-Electrode Capacitance EffectRaveena GurralaNo ratings yet
- MP803PIT-V2-S1-F3: Modulating Digital ThermostatDocument1 pageMP803PIT-V2-S1-F3: Modulating Digital ThermostatChhomNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ED1052-1CC08-0BA0: DisplayDocument2 pagesData Sheet 6ED1052-1CC08-0BA0: DisplayMamoon RiazNo ratings yet
- Any Any Inverter M Model: Compatible With Al L Models of Inverter ProductsDocument2 pagesAny Any Inverter M Model: Compatible With Al L Models of Inverter Productsmanlu1001565100% (1)
- Dcrust ECE 4th YearDocument16 pagesDcrust ECE 4th YearRahulPoriaNo ratings yet
- Regulador 5 - 3,3V LD1117 Home Sony PDFDocument44 pagesRegulador 5 - 3,3V LD1117 Home Sony PDFErnandesTorresBarbosaNo ratings yet
- Abbreviation BoeingDocument7 pagesAbbreviation BoeingРоман ДяченкоNo ratings yet
- 24C16Document33 pages24C16Jair2808No ratings yet
- ITU Radio Regulations - Vol I - ArticlesDocument428 pagesITU Radio Regulations - Vol I - Articleszzz.ttt6696100% (1)
- ATM Transport (RAN15.0 03)Document180 pagesATM Transport (RAN15.0 03)Zouhir El AllaouiNo ratings yet
- Superheterodyne ReceiverDocument10 pagesSuperheterodyne ReceiverAndhika Kumara DjaffriNo ratings yet
- FH-P4200MP: Connecting The UnitsDocument4 pagesFH-P4200MP: Connecting The UnitsJeremy NordenNo ratings yet
- BC1209IRODVA/28AH: Ir Distance: 30M 2.8-12MM LENSDocument2 pagesBC1209IRODVA/28AH: Ir Distance: 30M 2.8-12MM LENSPedro DazaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Guru Online BrochureDocument3 pagesVLSI Guru Online Brochurerajesh1108kiotNo ratings yet
- Niva Wiring DiagramDocument131 pagesNiva Wiring DiagramSmolovic Srdjan100% (2)
- VIVA Question-RectifierDocument3 pagesVIVA Question-RectifierMaheswariRVNo ratings yet
- Comms 4 Satcom AnswersDocument5 pagesComms 4 Satcom AnswersjobelleNo ratings yet
- Accedian Skylight Performance Element GT DatasheetDocument3 pagesAccedian Skylight Performance Element GT DatasheetEnrique RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Grupos de ConexionDocument13 pagesGrupos de ConexionPedro SanchezNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic System Power Loss Calculator: AssumptionsDocument1 pageFiber Optic System Power Loss Calculator: AssumptionsLeão AmaruNo ratings yet
- HID iCLASS SecurityDocument13 pagesHID iCLASS SecurityMrJohnGalt09No ratings yet
- MTCWEDocument6 pagesMTCWEAnanda Dwi75% (4)
- SD Wan Comparison Guide UpdatedDocument1 pageSD Wan Comparison Guide UpdatedAlberto Ciaffardoni80% (5)