100% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views23 pagesPhysics Measurement and Concepts Guide
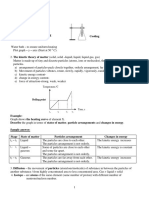
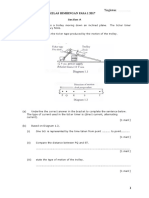
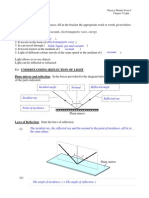
The document contains information about physics concepts taught in Form 4 and Form 5. It discusses chapters on force, motion, pressure, heat, light, waves, electricity, electromagnetism, electronics and radioactivity. It also contains information about measurement tools like vernier calipers and micrometer screw gauges. Concepts around accuracy, consistency, sensitivity, systematic and random errors are defined. Diagrams show motion graphs, barometers, manometers and gas laws. Lenses, mirrors, reflection and refraction are also summarized.
Uploaded by
kamalharmozaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views23 pagesPhysics Measurement and Concepts Guide
The document contains information about physics concepts taught in Form 4 and Form 5. It discusses chapters on force, motion, pressure, heat, light, waves, electricity, electromagnetism, electronics and radioactivity. It also contains information about measurement tools like vernier calipers and micrometer screw gauges. Concepts around accuracy, consistency, sensitivity, systematic and random errors are defined. Diagrams show motion graphs, barometers, manometers and gas laws. Lenses, mirrors, reflection and refraction are also summarized.
Uploaded by
kamalharmozaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd