Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cognitive View of Learning: By: Antonio R. Naing Jr. Joan D. Del Castillo
Uploaded by
Anton Naing0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views19 pagesThe document discusses the cognitive theory of learning. It defines cognition as the process of acquiring knowledge and notes that cognitive theory views thoughts and behaviors as tendencies that should be analyzed. Several cognitivists are discussed, including Paivio who developed the dual coding theory of enhancing recall through visual and verbal information, and Gardner who proposed multiple intelligences that individuals possess to different degrees. The document also discusses classroom implications, such as incorporating different learning styles and challenging students at varying levels of Bloom's taxonomy. It proposes ways to implement cognitive theory both with and without technology, such as using repetition and assessments to reinforce learning.
Original Description:
cognitive
Original Title
cognitive
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the cognitive theory of learning. It defines cognition as the process of acquiring knowledge and notes that cognitive theory views thoughts and behaviors as tendencies that should be analyzed. Several cognitivists are discussed, including Paivio who developed the dual coding theory of enhancing recall through visual and verbal information, and Gardner who proposed multiple intelligences that individuals possess to different degrees. The document also discusses classroom implications, such as incorporating different learning styles and challenging students at varying levels of Bloom's taxonomy. It proposes ways to implement cognitive theory both with and without technology, such as using repetition and assessments to reinforce learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views19 pagesCognitive View of Learning: By: Antonio R. Naing Jr. Joan D. Del Castillo
Uploaded by
Anton NaingThe document discusses the cognitive theory of learning. It defines cognition as the process of acquiring knowledge and notes that cognitive theory views thoughts and behaviors as tendencies that should be analyzed. Several cognitivists are discussed, including Paivio who developed the dual coding theory of enhancing recall through visual and verbal information, and Gardner who proposed multiple intelligences that individuals possess to different degrees. The document also discusses classroom implications, such as incorporating different learning styles and challenging students at varying levels of Bloom's taxonomy. It proposes ways to implement cognitive theory both with and without technology, such as using repetition and assessments to reinforce learning.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
By:
Antonio R. Naing Jr.
Joan D. Del Castillo
Cognitive View of
Learning
The Cognitive Theory:
Defined
Developed after the influence of Behaviorism.
Cognition: literally means knowing, and is the mental act or
process to which knowledge is acquired (Mcleod,S.A.).
Cognitive Theory compared our thoughts and recollections to our
behavior:
Both are tendencies of the individual, and therefore should be
analyzed as such. (Gary, Shelly B. Pg 371).
The human mind and the present day computer have a synergistic
function:
Input, store and retrieve information.
As humans, we hear/see/do certain things which are placed into
our memory for us to use this acquired knowledge in the future.
The Cognitivist
Allan Paivio (1925- Current)
Developed the dual coding theory- information
given visually and verbally enhance recall and
recognition.
believes people process information in
distinctively different ways.
Processing images v. Processing language.
Howard Gardner (1943- Current)
Developed the theory of multiple intelligence-
verbal, mathematical, visual, kinesthetic, musical,
interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalist.
Believes that everyone may have all eleven
intelligences but one or two are more dominate.
Believes the intelligences are influenced by
biological predispositions, learning opportunities,
and the individuals cultural context.
The Cognitivist
Robert Gagne (1916- 2002)
Based on the building block principle.
Five major categories of learning- verbal
information, intellectual skills, cognitive strategies,
motor skills and attitudes.
Incorporated characteristics of behavior
modification theory and performance education
Believed that a variety of internal and external
conditions must be present for learning to occur.
The Cognitivist
Benjamin Bloom (1913- 1999)
Focused on students learning domain
Classified learning into three domains
Cognitive- organization of ideas and thoughts
Affective- emotions, attitude, interests, attention, awareness
Psychomotor- students motor and physical abilities
Blooms Taxonomy
Levels move from simple to complex
Connected to mastered learning
Students continue to learn after they
have already mastered a skill
Classroom Implications
Students need to stray away from lecturing
and get the students to actively participate.
Teachers should understand and incorporate
different learning styles.
Each student has a different type of
intelligence. They should use their dominant
intelligence, while also working to improve
their non dominant intelligences.
Classroom implications
Teachers roles
Using Gagnes Nine Events of Instruction teachers improved
their students internal process of learning.
Using Gagnes building block techniques the students are able to
use technology in a variety of ways: beginning with something
simple, such as searching the web for information to more
demanding tasks like creating a website.
With the knowledge of Garners different intelligences teachers
are able to incorporate a variety of activities that uses a
variation of learning styles.
Blooms Taxonomy allows teachers to actively challenge
students with a variety of questions ranging from recall to
analysis.
Classroom implications
Students roles
Students can learn about the different intelligences they
poses using Gardners different intelligences.
Once the students discover what intelligence(s) is(are)
their strongest they can achieve higher academic goals by
learning with those styles.
The students can challenge themselves by using different
style questions as described by Benjamin Bloom.
Using the idea of dual coding, proposed by Allan Paivio,
the students are able to analyze images and language
separately to create intricate and creative answers.
The Cognitive Theory:
Classroom/Teacher Use
With Technology:
The multimedia principle: states that people
learn more deeply from words and pictures
than from words alone (Mayer, p. 47).
Teachers use technology to help students retain
information.
The principle states that these elements (pictures
and visuals) are selected and organized
dynamically to produce logical mental constructs.
PowerPoint Clip Art
Classroom Implications
Students need to stray away from lecturing
and get the students to actively participate.
Teachers should understand and incorporate
different learning styles.
Each student has a different type of
intelligence. They should use their dominant
intelligence, while also working to improve
their non dominant intelligences.
The Cognitive Theory:
Classroom/Teacher Use
Without Technology:
Teachers in the classroom will teach students
with repetition for the students to input the
information.
Information comes in, is processed, and leads
to certain outcomes.
Using assessments to see these outcomes is how
the teacher implements this theory.
The Cognitive Theory:
Student Use
With Technology:
Students see what the teacher presents as a
visual
They will then start to process and input the
information into their memory
Then they will recall that information when
tested on that particular visual presentation
The Cognitive Theory:
Student Use
Without Technology:
Students will use the thought process to
successfully perform the problem by recalling
information that the instructor lectured about
prior to an assessment.
They use problem solving, analysis, and then
they explain the result.
PowerPoint Clip Art
The Cognitive Theory:
How We Would Implement This
Using a vocabulary curriculum to allow the students to
input new information into their brains.
Giving students formulas to know if in a mathematics-
based classroom.
Showing the students different videos (implementing
technology) and then testing them on what they
learned.
Constantly adding new information for the students to
input into their memory, then reviewing what they
have learned by assessments.
Personal Teaching
Cognitive thinking involves a large amount of student
and teacher participation.
I think this theory would work well in my classroom
because of the different academic challenges in poses.
A wide variety of studies, techniques, and organization
styles are available pertaining to the cognitive theory.
Integrating technology into the lessons would be fairly
easy with the different skill levels assisted.
For example: I could teach the students a lesson and build
on the ideas demonstrated in the lessons. Once the
students have reached the point of mastery learning I will
implement a more difficult lesson with the use of
equipment.
Works Cited
"Cognitive Theories." Learning Theories. Web. 20 Nov.
2011. <http://www.learning-
theories.com/category/cognitive-theories>.
Gary, Shelly B. Boston (2010). 6
th
Edition. Teachers
Discovering Computers; Integrating Technology and
Digital media in the Classroom.
Mayer, R. E.; R. Moreno (1998). A Cognitive Theory of
Multimedia Learning: Implications for Design Principles.
http://www.unm.edu/~moreno/PDFS/chi.pdf.
Mcleod, S. A. (2007). Simply Psychology; Cognitive
Approach in Psychology. Retrieved 20 November 2011,
from http://www.simplypsychology.org/cognitive.html
THANKS FOR LISTENING
You might also like
- Grade 3 (MUSIC 4th Quarter)Document37 pagesGrade 3 (MUSIC 4th Quarter)anon_3805127484% (19)
- Observation Checklist GR 1-4Document4 pagesObservation Checklist GR 1-4norzulidaNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDocument109 pagesK To 12 Pedagogical ApproachesDianne Permejo del Prado100% (3)
- Jot2 Task 2 Attempt 2-YarboroughDocument21 pagesJot2 Task 2 Attempt 2-Yarboroughapi-351961319No ratings yet
- Sample Curriculum Design For A Local ChurchDocument2 pagesSample Curriculum Design For A Local ChurchAna Rica Santiago Navarra-CruzNo ratings yet
- Social ConstructivismDocument12 pagesSocial ConstructivismCentro Studi Villa Montesca100% (3)
- Part Iv: Individual Development Plans: Mica O. Nugal Nimfa P. Balasabas Nimfa P. BalasabasDocument1 pagePart Iv: Individual Development Plans: Mica O. Nugal Nimfa P. Balasabas Nimfa P. BalasabasmicaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Theory and The Classroom: Jess BDocument13 pagesCognitive Theory and The Classroom: Jess BSuperBkKingdomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningEunice FernandezNo ratings yet
- IT Enters A New Learning EnvironmentDocument50 pagesIT Enters A New Learning EnvironmentLulu BritanniaNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Multiple IntelligencesDocument5 pagesLearning Theories Multiple IntelligencesAnonymous AFFiZnNo ratings yet
- Theories Supporting The Teaching of Physical and Health Education For Elementary GradesDocument10 pagesTheories Supporting The Teaching of Physical and Health Education For Elementary GradesBhebz SagalaNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Learning TheoriesDocument30 pagesLec 2 Learning TheoriesShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- EDU Chapter 11 M Learning StrategiesDocument22 pagesEDU Chapter 11 M Learning StrategiesWahab ArfanNo ratings yet
- Artifact 2Document22 pagesArtifact 2api-418762763No ratings yet
- Nur Afiqah Binti Ammar 157386Document19 pagesNur Afiqah Binti Ammar 157386Afiqah AmmarNo ratings yet
- Models of TeachingDocument60 pagesModels of TeachingHidayah Roslee100% (2)
- Teaching and Learning Strategy in ChemistryDocument47 pagesTeaching and Learning Strategy in ChemistryLidya PurwasihNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - H - MTDocument3 pagesGroup 3 - H - MTAura PutriNo ratings yet
- ASSURE Model Ppt-LectureDocument28 pagesASSURE Model Ppt-LectureApril DetorresNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: NEPF + Components of An Effective Lesson HybridDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: NEPF + Components of An Effective Lesson Hybridapi-286246584No ratings yet
- Cognituve TheoryDocument6 pagesCognituve TheoryRosy QuijadaNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Evidence FinalDocument6 pagesSTD 8 Evidence Finalapi-328446016No ratings yet
- FS2 Epi19 PontejosDocument4 pagesFS2 Epi19 PontejosPontejos Princess Dianne G.100% (1)
- Ed Tecth Leson CompleteDocument19 pagesEd Tecth Leson CompleteEva Joy DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Module DevelopmentDocument46 pagesModule DevelopmentNorasyikin OsmanNo ratings yet
- Implications of Cognitive Learning Theory in Teaching and LearningDocument5 pagesImplications of Cognitive Learning Theory in Teaching and LearningOgechi AjaaNo ratings yet
- Selection and Organization of ContentDocument65 pagesSelection and Organization of ContentRuss TyNo ratings yet
- Rekabentuk InstruksiDocument51 pagesRekabentuk InstruksiAmirul SyaqirNo ratings yet
- Educational Technology EDU-203 Fall 2020-2021 Dr. Fouad YehyaDocument37 pagesEducational Technology EDU-203 Fall 2020-2021 Dr. Fouad YehyaLuluAlain TDNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Development: in Order To Proceed, You Should Have The Following in PlaceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Development: in Order To Proceed, You Should Have The Following in PlacebookreaderNo ratings yet
- King Saud University College of Nursing Master ProgramDocument25 pagesKing Saud University College of Nursing Master ProgramAilah MaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Assure ModelDocument33 pagesLecture 6 Assure ModelAlphonse KimoriNo ratings yet
- M2 The 21st Century LearnersDocument8 pagesM2 The 21st Century LearnersRenz E. FerreraNo ratings yet
- 7.rekabentuk InstruksiDocument51 pages7.rekabentuk Instruksibisyarah waniNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1.pptx Theories in TeachingDocument38 pagesTECHNOLOGY FOR TEACHING AND LEARNING 1.pptx Theories in TeachingKim Trishia BrulNo ratings yet
- Constructivism: Regional Mass Training of Grade 9 Esp TeachersDocument29 pagesConstructivism: Regional Mass Training of Grade 9 Esp TeachersPatatas SayoteNo ratings yet
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocument36 pagesStudent Directed Learning Strategiesyhanne100% (17)
- FLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Document10 pagesFLCT Beed - 2a (Daran)Jeanette Fernandez DNo ratings yet
- "Lambaian Malar Hijau": KPP60704: Learning and CognitionDocument21 pages"Lambaian Malar Hijau": KPP60704: Learning and Cognitionsathiah2802No ratings yet
- Teaching Aptitude UGC NetDocument6 pagesTeaching Aptitude UGC NetShubham Sharma100% (1)
- Jot2 Task 2 Lynette Di StasioDocument14 pagesJot2 Task 2 Lynette Di Stasioapi-498856890100% (1)
- Classroom Blog LessonDocument2 pagesClassroom Blog Lessonapi-445888100No ratings yet
- Group 2Document4 pagesGroup 2ewolramnasomitelimusNo ratings yet
- SELECTION and ORGANIZATION of CONTENTDocument29 pagesSELECTION and ORGANIZATION of CONTENTRUVENANo ratings yet
- Traditional Teaching Strategies: Group 1Document34 pagesTraditional Teaching Strategies: Group 1chocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- W2 - Learning and UnderstandingDocument23 pagesW2 - Learning and UnderstandingnidifaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 Student TeachingDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 2 Student Teachingapi-639552475No ratings yet
- Multimedia in EducationDocument29 pagesMultimedia in EducationIrfan FazailNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles Dela Cruz TTL BSE Eng 3Document32 pagesTheories and Principles Dela Cruz TTL BSE Eng 3Allen BercasioNo ratings yet
- TEACHING-STRATEGIES-AND-APPROACHES-FOR-SCIENCE For My Presentation TomDocument50 pagesTEACHING-STRATEGIES-AND-APPROACHES-FOR-SCIENCE For My Presentation Tommarkcarmeloalberto.azorNo ratings yet
- The Ability To Learn Is The Most Significant Activity of Man.Document56 pagesThe Ability To Learn Is The Most Significant Activity of Man.Bernard Vincent Guitan MineroNo ratings yet
- TEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated LearningDocument6 pagesTEEP A4 6pp - Accelerated Learninganand raviNo ratings yet
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocument36 pagesStudent Directed Learning StrategiesSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Pedagogical Approaches-KTDocument88 pagesPedagogical Approaches-KTJhing HeraNo ratings yet
- StateDocument26 pagesStateDiosa ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Effective Instructional Design - Standards-Based Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesEffective Instructional Design - Standards-Based Lesson Planapi-549787754No ratings yet
- General Methods of Teaching 4Document12 pagesGeneral Methods of Teaching 4M.Muneeb -ur-RehmanNo ratings yet
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology: Department of Education Assignment TitleDocument30 pagesMirpur University of Science and Technology: Department of Education Assignment TitleKainat AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wow Science TM-Grade 8Document169 pagesWow Science TM-Grade 8kavitakadam1647No ratings yet
- Smart PedagodyDocument14 pagesSmart PedagodyAudrina Mary JamesNo ratings yet
- Forum NotesDocument10 pagesForum NotesMageswary NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Nepf Collecting ArtifactsDocument2 pagesNepf Collecting Artifactsapi-281965237No ratings yet
- Approaches in Science TeachingDocument39 pagesApproaches in Science TeachingShela Marie De VeraNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Supervisory Monitoring ToolDocument2 pagesCatch Up Supervisory Monitoring ToolAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Spta A Dasco 2023-2024Document1 pageSpta A Dasco 2023-2024Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Name Position: Head Teacher III Official Station Purpose of TravelDocument9 pagesName Position: Head Teacher III Official Station Purpose of TravelAnton NaingNo ratings yet
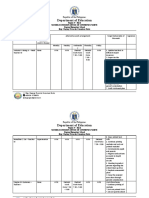
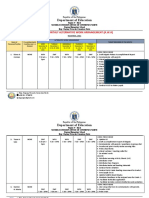
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Research Anton 2021Document10 pagesResearch Anton 2021Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- School Workweek Plan Sept. 1-30Document30 pagesSchool Workweek Plan Sept. 1-30Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Name Position: Head Teacher III Official Station Purpose of TravelDocument9 pagesName Position: Head Teacher III Official Station Purpose of TravelAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: School Monthly Alternative Work Arrangement (A.W.A)Document13 pagesDepartment of Education: School Monthly Alternative Work Arrangement (A.W.A)Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: School Monthly Alternative Work Arrangement (A.W.A)Document13 pagesDepartment of Education: School Monthly Alternative Work Arrangement (A.W.A)Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Integration PaperDocument4 pagesIntegration PaperAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Mount MayonDocument3 pagesMount MayonAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- What Is InnovationDocument6 pagesWhat Is InnovationAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Training Matrix: Time September 27, 2018Document1 pageTraining Matrix: Time September 27, 2018Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- 3 GoldDocument1 page3 GoldAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument19 pagesWorksheetAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- ICT Training 2016 MatrixDocument1 pageICT Training 2016 MatrixAnton NaingNo ratings yet
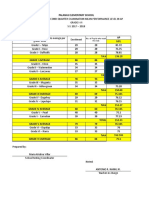
- No. of Pupils Who Took The TestDocument1 pageNo. of Pupils Who Took The TestAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- GRADE 5-6 Summary and General Average For SY 2015-2016Document36 pagesGRADE 5-6 Summary and General Average For SY 2015-2016Anton NaingNo ratings yet
- Specific Reading Difficulties in The Selected Schools of Paracale District FindingsDocument3 pagesSpecific Reading Difficulties in The Selected Schools of Paracale District FindingsAnton NaingNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Policy 4Document40 pagesRecruitment Policy 4anukritibhatNo ratings yet
- Expository Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesExpository Lesson Planapi-265180782100% (1)
- PB 502 ManualDocument16 pagesPB 502 ManualArio FitriantoNo ratings yet
- Parapro PlanDocument6 pagesParapro Planapi-302654941No ratings yet
- CHAPTER ASSESSMENT Module 5 Lessons 1 To 3Document3 pagesCHAPTER ASSESSMENT Module 5 Lessons 1 To 3anjeilinne mae BocalaNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Cebu Province Consolacion Elementary School District of Dalaguete IDocument2 pagesSchools Division of Cebu Province Consolacion Elementary School District of Dalaguete ILilian Laurel CariquitanNo ratings yet
- Reflective EssayDocument3 pagesReflective EssayVivi Ivy LieuNo ratings yet
- Front Covers SBM NewDocument34 pagesFront Covers SBM NewEvangeline San JoseNo ratings yet
- Algebra ConquestDocument10 pagesAlgebra ConquestAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Diploma: The State Senior High SchoolDocument4 pagesDiploma: The State Senior High Schoolhalil ariantoNo ratings yet
- Rvti Women AdmissionDocument1 pageRvti Women AdmissionSwapna Rasal0% (2)
- OliviaflickingerDocument3 pagesOliviaflickingerapi-314651156No ratings yet
- Four Paths of Influence Kenneth LeithwoodDocument28 pagesFour Paths of Influence Kenneth LeithwoodMohamad IskandarNo ratings yet
- University of British Columbia 2009-2010: Yeung - A@surreyschools - CaDocument3 pagesUniversity of British Columbia 2009-2010: Yeung - A@surreyschools - Caapi-414473255No ratings yet
- Implications of The Implementation of The Segak Test in Malaysian Secondary SchoolsDocument14 pagesImplications of The Implementation of The Segak Test in Malaysian Secondary SchoolsGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- or... Amarth - ME - Samarth Verma PDFDocument2 pagesor... Amarth - ME - Samarth Verma PDFAnurag PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Education System KenyaDocument12 pagesEducation System KenyaAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Study Less, Study SmartDocument6 pagesStudy Less, Study SmartBob samuel100% (1)
- Learning Agreement For Studies180416Document3 pagesLearning Agreement For Studies180416Anonymous mCKToU8ONo ratings yet
- 2004 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge Division Orals Grade 6Document3 pages2004 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge Division Orals Grade 6Deped TambayanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Reading Environment of High School Libraries: Megha M. Pawar, Rajesh Kanthe & Rajendra MohiteDocument4 pagesA Study On Reading Environment of High School Libraries: Megha M. Pawar, Rajesh Kanthe & Rajendra MohiteTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Brooks Resume Updated 2019Document2 pagesAubrey Brooks Resume Updated 2019api-459105255No ratings yet
- Idioms Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesIdioms Lesson Planapi-3463025930% (1)
- Classroom Environment ChecklistDocument10 pagesClassroom Environment Checklistapi-213648940No ratings yet
- Active Learning 2Document260 pagesActive Learning 2pterodaktil100% (2)