Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Male Reproductive System: Nur Anisah
Uploaded by
dhiet54Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Male Reproductive System: Nur Anisah
Uploaded by
dhiet54Copyright:
Available Formats
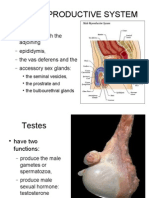
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Nur Anisah
Department of Histology & Cell Biology
Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada University
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Testis
-- Components:
Adventitia (lamina propria or tunica propria)
of seminiferous tubules
Cells: -- Leydig, Sertoli, spermatid,spermatocyte,
spermatogonium, spermatozoan
Mediastinum testis
Rete testis
Tubuli recti
Tunica albuginea
Tunica vaginalis (peritoneum)
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Miscellaneous male tubules
Efferent duct
Epididymis-head and tail
Ductus deferens
Seminal vesicle
Ejaculatory duct
Spermatic cord
Stereocilia
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Penis:
- Corpus cavernosum and
spongiosum
- Gland of Littre
- Tunica albuginea
- Urethra
Prostate:
- Corpora amylacea
- Prostate (young and old)
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
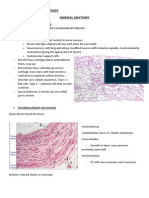
I. Testis and Passages
The tunica albuginea.
The visceral layer of the
tunica vaginalis testis.
The large blood vessel,
and inside of that the
Tunica Vasculosa.
Connective tissue septae
from the Tunica
Vasculosa separate the
seminiferous tubules
from one another.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Pararosanilinetoluidine
blue (PT) stain.
Medium magnification.
Testis :
- seminiferous
tubules
- groups of pale-
stained interstitial
(Leydig) cells
(arrowheads).
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Fig. Epithelium of
seminiferous tubules
surrounded by myoid
cells.
- The spaces between
the tubules :
- connective tissue,
- blood and lymphatic
vessels, and
- interstitial cells.
PT stain.
Medium magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure . Part of a seminiferous tubule with its surrounding tissues.
The seminiferous epithelium is formed by 2 cell populations: the
cells of the spermatogenic lineage and the supporting or Sertoli
cells.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Part of the wall of a
seminiferous tubule.
- Several cells of the
spermatogenic
lineage are present:
* a spermatogonium,
Primary
spermatocytes,
young and late
spermatids.
The approximate limits
of a Sertoli cell holding
several spermatids are
delineated.
H&E stain.
High magnification.
Sistem saluran
A. Tubulus seminifer convolutus lumen
terjadi sejak fetus berusia 7 bulan.
i. epithelium spermatogenicum : -2 jenis sel:
- gonocytus, sel kelamin, membentuk 3 lapis,
dari luar ke dalam/basal kearah lumen
Spermatogonium, dengan gambaran mitosis
Ada 2 jenis:
tipe A, Inti oval
Tipe B, inti berbentuk cakram
Spermatocytus primarius, inti dengan
gambaran meiosis
Spermatocytus secundarius, sel lebih kecil,
terdapat lebih ke arah lumen
Spermatidium, sel memanjang dengan inti
ovoid
Spermatozoon :
di dlm testis dng perantaran caput
terpancang pd epitheliocytus sustentans
(dulu dsbt sel Sertoli) inti berbentuk spt
piramid
pada epididymis terdapat di dlm lumen
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure .
Diagram showing the clonal nature of the germ
cells.
Only the initial spermatogonia divide and produce
separate daughter cells.
Once committed to differentiation, the cells of all
subsequent divisions stay connected by
intercellular cytoplasmic bridges.
Only after they are separated from the residual
bodies can the spermatozoa be considered
isolated cells.
(Modified and reproduced, with permission, from
Bloom W, Fawcett DW: A Textbook of Histology, 10th
ed. Saunders, 1975.)
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Fig. Interstitial cells and cells of the seminiferous
epithelium.
H&E stain. High magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
The Sertoli cells
form
the blood-testis
barrier.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2212. The Sertoli cells form the blood-testis
barrier. Neighbor Sertoli cells are attached by
occluding junctions that divide the seminiferous
tubules into 2 compartments and impede the passage
of substances between both compartments. The basal
compartment comprises the interstitial space and the
spaces occupied by the spermatogonia. The adluminal
compartment comprises the tubule lumen and the
intercellular spaces down to the level of the occluding
junctions (OJ). In this compartment are spermatocytes,
spermatids, and spermatozoa. Cytoplasmic residual
bodies from spermatids undergo phagocytosis by the
Sertoli cells and are digested by lysosomal enzymes.
The myoid cells surround the seminiferous epithelium.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2213. Hypophyseal
control of male reproduction.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) acts
on the Leydig cells, and follicle-
stimulating hormone (FSH) acts
on the seminiferous tubules.
A testicular hormone, inhibin,
inhibits FSH secretion in the
pituitary. ABP, androgen-binding
protein. (Modified and
reproduced, with permission,
from Bloom W, Fawcett DW: A
Textbook of Histology, 10th ed.
Saunders, 1975.)
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Surrounding the
epithelium is a coat of
smooth muscle (that
thickens distally).
At the junction with the
ductus deferens (not
shown), this coat is
trilaminar.
In other words, as one
Human epididymis
- pseudostratified
columnar epithelium
consisting primarily of
tall principal cells
(getting shorter
distally) with
stereocilia (getting
shorter distally) and
basal cells.
In other words, as one moves from
head to tail, the epithelium gets
shorter, the stereocilia get shorter, and
the muscle gets thicker.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2215. The highly
coiled ductus epididymidis,
sectioned several times.
Its wall is made of a
pseudostratified columnar
epithelium surrounded by
connective tissue and smooth
muscle.
PSH stain. Medium
magnification. Inset: Higher
magnification of the epithelial
cells with their long microvilli
(stereocilia).
24/2/09 nur anisah 1
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Ductus deferens, (human)
Note the longitudinal folds in the mucosa, which are lined by
pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
Find the smooth muscle layers and lamina propria.
What is the function of the extremely thick muscular coat?
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2216. Section of
the ductus deferens
showing the mucosa
formed by pseudostratified
columnar epithelium with
stereocilia and a lamina
propria. The thick outer wall
is formed of smooth muscle
(brown) and collagen fibers
(blue). Trichrome stain. Low
magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2217.
Seminal vesicle. A
section of this
tortuous tubular
gland with a much-
folded mucosa gives
the impression that
the gland consists of
many tubules. PSH
stain. Medium
magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2218. Section of prostate showing the
distribution of its glands in 3 zones. The gland
ducts open into the urethra.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure 2219.
Section of the central
region of the prostate
showing the prostatic
urethra and
tubuloalveolar glands
surrounded by
connective tissue and
smooth muscle. PT
stain. Low
magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure .Glands of the prostate surrounded by
connective tissue and smooth muscle. PT stain.
Medium magnification.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
Figure. Transverse section of the penis.
1 nur anisah 24/2/09
1. Pars prostatica:
Tunica mucosa:
Epithelium transitionale,pseudostratificatum
bagian yang terbesar
Lamina propria jar. ikat fibroelastik
Tunicamuscularis:
Stratum longitudinale
Stratum circulare
2. Pars membranacea
3. Pars spongiosa/cavernosa
Urethra
You might also like
- Bradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFDocument514 pagesBradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFJhon Talbot80% (49)
- Thyroid WorkbookDocument17 pagesThyroid Workbookpinkyhead99100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension ExerciseDocument9 pagesReading Comprehension Exercisedewi anggrajeniNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument106 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemRaissa Grace Acebo Carranza100% (3)
- Quiz 1A Hema LecDocument17 pagesQuiz 1A Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Explanations of Criminal BehaviourDocument11 pagesExplanations of Criminal BehaviourLaviniaNo ratings yet
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDocument7 pagesBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- Lab Ex1-2 and Chick OrganogenesisiDocument20 pagesLab Ex1-2 and Chick OrganogenesisiLardel CarayNo ratings yet
- Histology of Urinary SystemDocument36 pagesHistology of Urinary Systemdiraf100% (2)
- Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesReproductive SystemAileen Grace Delima100% (1)
- Organ Reproduksi Laki-Laki: (Organa Genitalia Masculina)Document32 pagesOrgan Reproduksi Laki-Laki: (Organa Genitalia Masculina)Timotius Gatma Buntori PurbaNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument76 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemteklayNo ratings yet
- Med Lec Male Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesMed Lec Male Reproductive Systemmiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- The Male Genital SystemDocument20 pagesThe Male Genital SystemLittleChenaNo ratings yet
- Histologi Sistem Reproduksi Laki-Laki: Ika FidianingsihDocument50 pagesHistologi Sistem Reproduksi Laki-Laki: Ika Fidianingsih'amma' RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Human Micromorphology. Digestive System IIIDocument12 pagesHuman Micromorphology. Digestive System IIIIbrahim dhainyNo ratings yet
- Male R.S. Dr Hekmat هاند اوتDocument15 pagesMale R.S. Dr Hekmat هاند اوتJo adamNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesThe Urinary SystemNayan BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Hist MaleDocument7 pagesHist MalezaidNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument12 pagesReproductive System NotesTanaya PujareNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerDocument111 pagesBio 11 UPD Third Lec Exam ReviewerMedjugorje Beltran DalanNo ratings yet
- Scrotum and OthersDocument10 pagesScrotum and OthersAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesMale Reproductive Systemqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Urinary SystemDocument35 pagesHistology of The Urinary SystemSilvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Physiology 2021Document188 pagesMale Reproductive Physiology 2021Elijah Kihiu18No ratings yet
- The Male Genital SystemDocument5 pagesThe Male Genital SystemDr-AymanBahgatNo ratings yet
- MRS LabDocument6 pagesMRS Lab2012000600No ratings yet
- Male and Female Genital Systems 2Document30 pagesMale and Female Genital Systems 2negmm2226No ratings yet
- Lab. NO. 4: System: ReproductiveDocument10 pagesLab. NO. 4: System: ReproductiveKarrar BassimNo ratings yet
- 7 Hematopoiesis & Circulatory SystemDocument4 pages7 Hematopoiesis & Circulatory SystemNicolePorsueloNo ratings yet
- Li 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologyDocument17 pagesLi 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologysandyaadindaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproduction System - Histology LectureDocument28 pagesMale Reproduction System - Histology LectureAstri Novia RizqiNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesUrinary SystemTalal TariqNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Prostate GlandDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Prostate GlandRao Ghayoor DxNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary Systemراوند اعبيدNo ratings yet
- Micronatomy pt2Document35 pagesMicronatomy pt2poopziNo ratings yet
- PPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesPPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemElvie ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The The Urinary SystemDocument63 pagesHistology of The The Urinary SystemKankomba MuleyaNo ratings yet
- 5 Urinary System Lec5Document8 pages5 Urinary System Lec5Tee bagNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary SystemFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Systems A. B. C. DDocument6 pagesReproductive Systems A. B. C. DJamie BagundolNo ratings yet
- Histology of Urinary System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.Sc. & A.H., RewaDocument35 pagesHistology of Urinary System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.Sc. & A.H., RewaMike AnnisNo ratings yet
- Malereproductive (Author T.globa)Document40 pagesMalereproductive (Author T.globa)Cristina caimac100% (1)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRia Janita RiduanNo ratings yet
- Histology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDocument26 pagesHistology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Rajesh Ranjan Assistant Professor Deptt. of Veterinary Anatomy C.V.SC., RewaDiahNo ratings yet
- CVSDocument58 pagesCVSDoina SvetNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemElaine Eloisa CapilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 General Histology Digestive System Part 2Document7 pagesLecture 10 General Histology Digestive System Part 2Mohammed MNo ratings yet
- Histology Final Exam CoverageDocument19 pagesHistology Final Exam CoverageJAWAD, JAINA A.No ratings yet
- Veterinary Normal HistologyDocument10 pagesVeterinary Normal HistologyIshtar Katherine ChanNo ratings yet
- 15th Proper 1301 SeqDocument21 pages15th Proper 1301 SeqAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- His To LogieDocument10 pagesHis To LogieAhmed Abu AlrobNo ratings yet
- Histology - Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesHistology - Male Reproductive SystemKim AcostaNo ratings yet
- 13 - Male Reproductive SystemDocument60 pages13 - Male Reproductive SystemWai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Histology Work-1Document11 pagesHistology Work-1siddharth.roy26587No ratings yet
- Histo Spotting SlidesDocument31 pagesHisto Spotting Slidessrushtip191No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive SystemNwa OsmanNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulDocument75 pagesIn The Name of God THE Compassionate The MercifulGaziza MaaroofNo ratings yet
- A&p 1Document44 pagesA&p 1HARI KRISHNA G LNo ratings yet
- 6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1Document52 pages6 - Histology Lecture, Structure of The Epithelium 1AMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesHistology of The Urinary SystemOyobolo Blessing Tibike-emiyeNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document25 pagesLab 7202310446No ratings yet
- 2080 Reproductive System of Frog Grade XIDocument1 page2080 Reproductive System of Frog Grade XIkunalkumaryadav086No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- DTM MEDIC-2020 Data RDT LUNGENE-COVID 19 Rapid TestDocument19 pagesDTM MEDIC-2020 Data RDT LUNGENE-COVID 19 Rapid Testdhiet54No ratings yet
- Health Valley HospitalDocument2 pagesHealth Valley Hospitaldhiet54No ratings yet
- Gold 2018Document142 pagesGold 2018histoginoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Abscess: Current Management, J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013Document1 pageDaftar Pustaka: Abscess: Current Management, J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013dhiet54No ratings yet
- PKS DG BidanDocument5 pagesPKS DG Bidandhiet54No ratings yet
- Cara Membuat Kelinci PaskahDocument3 pagesCara Membuat Kelinci Paskahdhiet54No ratings yet
- Islamic Perspective On Stem CellDocument55 pagesIslamic Perspective On Stem CellYunan Syahban MaskatNo ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument1 pageEpidemiologydhiet54No ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar OnkologiDocument63 pagesDasar Dasar Onkologidhiet54No ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument1 pageEpidemiologydhiet54No ratings yet
- Intussusception 1Document9 pagesIntussusception 1dhiet54No ratings yet
- MalariaDocument38 pagesMalariadhiet54No ratings yet
- Alamat Jurnal KedokteranDocument1 pageAlamat Jurnal Kedokterandhiet54No ratings yet
- One H5N1 Paper Finally Goes To Press Second Greenlighted: InfluenzaDocument2 pagesOne H5N1 Paper Finally Goes To Press Second Greenlighted: InfluenzaVera MillerNo ratings yet
- Your Kaplan Medical Timeline PDFDocument6 pagesYour Kaplan Medical Timeline PDFpinkyNo ratings yet
- Liquid CultureDocument30 pagesLiquid CultureSumesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document33 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)nizam ud dinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drug MetabolismDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Drug MetabolismNicole AguilarNo ratings yet
- Kolej Genius@Pintar Negara Research Skill Proposal Form (Cadangan Penyelidikan)Document8 pagesKolej Genius@Pintar Negara Research Skill Proposal Form (Cadangan Penyelidikan)saadhana elangovanNo ratings yet
- Complications of Diabetes 2016Document4 pagesComplications of Diabetes 2016Chan ChanNo ratings yet
- 4092 24437 1 PBDocument13 pages4092 24437 1 PBCloudcynaraaNo ratings yet
- Neuro - Synaptic TransmissionDocument74 pagesNeuro - Synaptic TransmissionSteve BlubaughNo ratings yet
- Scope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWDocument29 pagesScope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWRani SapkotaNo ratings yet
- BioCentury SinSa Labs PDFDocument2 pagesBioCentury SinSa Labs PDFDarren NguyenNo ratings yet
- Submission Guideline Iconic 2018Document6 pagesSubmission Guideline Iconic 2018Riska Awalia LestariNo ratings yet
- ExplanationDocument6 pagesExplanationMoses SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Answers BiostatsDocument2 pagesAnswers BiostatsNitesh67% (3)
- Revtox 29 1 2012Document80 pagesRevtox 29 1 2012Oscar Eduardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Midline DiastemaDocument4 pagesMidline DiastemasmritiNo ratings yet
- Pocket DentistryDocument12 pagesPocket DentistryerinNo ratings yet
- Lupus - Client Brochure Rdramirez v2Document4 pagesLupus - Client Brochure Rdramirez v2api-437843157No ratings yet
- Anti Microbial DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Microbial Drugseyadballas35No ratings yet
- G10 Bio CellsDocument6 pagesG10 Bio CellsswacaneNo ratings yet
- Biacore's SPR Technology and DNA Footprinting For The Discovery and Development of New DNA-targeted Therapeutics and ReagentsDocument4 pagesBiacore's SPR Technology and DNA Footprinting For The Discovery and Development of New DNA-targeted Therapeutics and ReagentsNkem OkonkwoNo ratings yet
- Altitude Adaptation Through Hematocrit Change RevisarDocument8 pagesAltitude Adaptation Through Hematocrit Change RevisarMiguel Angel Santacruz VasquezNo ratings yet
- Precios BiosystemsDocument8 pagesPrecios Biosystemsjoaquin140292No ratings yet
- Infección y Reinfección SARS-Cov-2Document6 pagesInfección y Reinfección SARS-Cov-2lugasalo4996No ratings yet
- 012 Analysis of Reticulocyte Parameters On The Sysmex XEDocument8 pages012 Analysis of Reticulocyte Parameters On The Sysmex XEblanket_thNo ratings yet