Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asme Section Viii Div 2
Uploaded by
nanivenkatgaurav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views17 pagesOriginal Title
asmesecviiidiv2-140726082839-phpapp01.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
358 views17 pagesAsme Section Viii Div 2
Uploaded by
nanivenkatgauravCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
ASME SECTION VIII DIV 2
Article D-4 Welded Joints
AM-400 Welded Joint Categories
Category defines the location of a joint in a vessel
Established for use in specifying joint type and
degree of inspection
Based on service, material and thickness, special
requirements are specified in code
Category A
Category B
Category C
Category D
Article D-4 Welded Joints
Article F-1 General Fabrication Requirements
AF-104 Repair of defective materials
Defect may be removed and material repaired by
vessel manufacturer or unless prohibited by
material specification may also be repaired by
material manufacturer with approval of vessel
manufacturer
Material repair that exceed those permitted by
material specification shall be made to satisfaction
of inspector
Article F-1 General Fabrication Requirements
AM-104.1 Examination of defective area
By MPT (Article 9-1) or by LPT (Article 9-2)
AM-104.2 Repair by welding
Procedure & welds must be qualified in
accordance with Sec IX, including impact testing
Repaired material shall be heat treated when
required
AM-104.3 Examination of finished weld
Article F-1 General Fabrication Requirements
By Radiography (Article I-5) when depth of weld
deposit exceeds 10 mm or one-half material
thickness
Article F-1 General Fabrication Requirements
AF-112 Base metal preparation
AF-112.1 Examination of materials
a Material examination before fabrication for
detecting defects which would affect safety of vessel.
Examination of edges of base materials (including
edges of openings cut through thickness)
b Cut edges of thickness >= 38 mm shall be examined
by MPT or LPT
c For openings, cut edges of all thickness, examination
by MPT or LPT
AF-220 Specific requirements for welded joints
Table AF-241.1
AF-220 Specific requirements for welded joints
AF-228 Liquid Penetrant Examination
All austenitic Cr-Ni alloy steel welds, both butt &
fillet, which exceeds nominal thickness of 19 mm
shall be examined (Article 9-2)
LPT after heat treatment, if performed
All crack shall be eliminated
AF-230 Miscellaneous Welding requirements
AF-235 Identification markings or records for welders
or welding operators
Stamp identifying number, letter or symbol on or
adjacent to and at intervals of not more than 1 m
along the welds in plates >= 6 mm in thickness or
record of welders / WOs employed on each joints
shall be kept
For multiple welds, tube to tube sheet welds
QA system shall have a procedure to identify
welders or welding operators
Welds in each category are of same type and
configuration and are welded with same WPS
Article I-5 Radiographic Examination
AI-510 Acceptance standard for radiographs of welds
AI-511 Unacceptable defects and repair requirements
Imperfections are unacceptable under following
condition
Any crack or incomplete fusion or penetration
Any elongated indication which has length
greater than
6 mm for t upto 19 mm
1/3t for t from 19 mm to 56 mm
19 mm for t over 56 mm
Article I-5 Radiographic Examination
AI-511 Unacceptable defects and repair requirements
Imperfections are unacceptable under following
condition
Any group of aligned indications with aggregate
length greater than t in length of 12t, except
distance between successive imperfections
exceeds 6L where L is length of longest
imperfection in group
Rounded indications in excess of that specified in
Appendix 4
t - thickness of weld excluding any allowable
reinforcement, including throat of fillet if any
Article T-2 Impact testing of welds and vessel test
plates of ferrous materials
AT-203 Impact tests of vessel test plates
When base material is required to be impact tested,
impact testing of weld and HAZ shall be made for
category A & B joints in accordance with AT-201 for
each qualified procedure used in vessel
Test plate shall be from one of heats of vessel or
group of vessels
For category A joint, test plate shall, where
practicable, be welded as an extension to end of
production joint or welded as close to start of
production welding as practicable, utilizing
equipment, welding material and procedures which
are to be used on production joints
Article T-2 Impact testing of welds and vessel test
plates of ferrous materials
AT-203 Impact tests of vessel test plates
For category B joint (welded using different welding
procedure than used on category A joints, test plate
shall be welded under production welding conditions
used for vessel, using same type of equipment and at
same location and using same procedures as used for
joint and it shall be welded concurrently with
production welds or as closed to start of production
welding as practicable
Article T-2 Impact testing of welds and vessel test
plates of ferrous materials
AT-203.1 Number of vessel Impact Plates required
For each vessel, one test plate shall be made for each
welding procedure used for category A & B
In addition, for category A & B joints, following
requirements shall apply
For automatic or semi automatic welding, one
test plate in each position
For manual welding, vertical upward welded test
plate qualify for all position.
AT-203.2 Rejection
If PTC fails to meet the impact requirements, welds
represented shall be unacceptable. Reheat treatment
and retesting or retesting only are permitted.
Article 9-1 MPE Article 9-2 LPE
9-130 Acceptance standard
All surfaces to be examined shall be free of
Relevant linear indications
Relevant rounded indications greater than 5 mm
Four or more relevant rounded indication in a
line separated by 1.5 mm or less, edge to edge
Article 9-3 Ultrasonic Examination of welds
9-320 Acceptance-Rejection standards
Indications characterized as cracks, lack of fusion or
incomplete penetration are unacceptable regardless
of length
Other imperfections are unacceptable if indications
exceed reference level amplitude and have lengths
which exceed
6 mm for t upto 19 mm
1/3t for t from 19 mm to 57 mm
19 mm for t over 57 mm
T-thickness of weld, excluding any allowable
reinforcement
You might also like
- 44AC9100-000-V.02-0105-A4 - Rev B - GENERAL SPECIFICATION FOR WELDED TUBE TO TUBE SHEET JOINTDocument8 pages44AC9100-000-V.02-0105-A4 - Rev B - GENERAL SPECIFICATION FOR WELDED TUBE TO TUBE SHEET JOINTAvinash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sa 672Document7 pagesSa 672lalitaliNo ratings yet
- Technical Delivery Conditions For Seamless Carbon Steel FittingsDocument2 pagesTechnical Delivery Conditions For Seamless Carbon Steel FittingsTanpreet Singh100% (1)
- 0145E16598760151 - 1 - Def - Selecton Internal Floating Roofs v1.1 May 2014Document42 pages0145E16598760151 - 1 - Def - Selecton Internal Floating Roofs v1.1 May 2014Manuel Alejandro González MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Api 650Document4 pagesApi 650arif99pak100% (1)
- WeldDocument3 pagesWeldSenthil SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Anodes in Cooling Water Exchangers PDFDocument12 pagesAnodes in Cooling Water Exchangers PDFcbrittaivNo ratings yet
- Tube To Tube Sheet Mock UpDocument5 pagesTube To Tube Sheet Mock UpKushalNo ratings yet
- Asme Viii - QDocument431 pagesAsme Viii - Qmajdi jerbiNo ratings yet
- ASTM A573 SteelDocument2 pagesASTM A573 SteelneoNo ratings yet
- Ucs 56Document1 pageUcs 56enemesio_85100% (1)
- Saudi Aramco Standards: WeldingDocument12 pagesSaudi Aramco Standards: WeldingGEORGE IVANNo ratings yet
- (1-VI) - Rules For Welding - 2013 PDFDocument302 pages(1-VI) - Rules For Welding - 2013 PDFKhoirulRamadhanNo ratings yet
- Open Book Testing - API 653Document9 pagesOpen Book Testing - API 653EdisonCorderoNo ratings yet
- ASME PipingOffice - Piping CalculatorsDocument5 pagesASME PipingOffice - Piping CalculatorsJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- 510 External C-501 ReportDocument9 pages510 External C-501 ReportBradley Hodges100% (1)
- Highlights-ASME Guides Preheat-PWHT-VIII PDFDocument5 pagesHighlights-ASME Guides Preheat-PWHT-VIII PDFEr Manish JadaunNo ratings yet
- 32 Samss 004Document44 pages32 Samss 004ayubali009No ratings yet
- Difference Between Weld Layer Versus Bead Versus PassDocument6 pagesDifference Between Weld Layer Versus Bead Versus Passlram70No ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Fabrication - Int Dist Training 7-30-09Document41 pagesPressure Vessel Fabrication - Int Dist Training 7-30-09Mostafa Abd El Alem100% (2)
- Introduction To Welding API 577 Capter 7Document12 pagesIntroduction To Welding API 577 Capter 7Edo Destrada100% (1)
- TDC 1150Document3 pagesTDC 1150shazanNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers (API 660 vsTEMA)Document3 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchangers (API 660 vsTEMA)Aravind MadhuNo ratings yet
- Sa 213Document11 pagesSa 213gst ajahNo ratings yet
- 2019 ASME Section VIII Division 1 SynopsisDocument58 pages2019 ASME Section VIII Division 1 SynopsisCristian Xavier Avendaño BelloNo ratings yet
- Astm A358 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm A358 PDFgaminNo ratings yet
- Tilaa Asme BPVC 2015: ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code 2015Document2 pagesTilaa Asme BPVC 2015: ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code 2015CastoriadisNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Plate InspectionDocument5 pagesPressure Vessel Plate InspectionSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- Inspection OF Fired Heaters: For Restricted CirulationDocument59 pagesInspection OF Fired Heaters: For Restricted Cirulationasif rahim100% (1)
- ASME Pressure VesselDocument13 pagesASME Pressure Vesselamechmar5935No ratings yet
- API 653 - 577 Flash Cards - 62 QuestionsDocument8 pagesAPI 653 - 577 Flash Cards - 62 QuestionsSERFORTEC CIA. LTDA.No ratings yet
- API 650-Impact TestDocument4 pagesAPI 650-Impact TestBashu PoudelNo ratings yet
- Scope: PurposeDocument5 pagesScope: Purposezahid_497100% (1)
- Asme Pressure Vessel JoiDocument4 pagesAsme Pressure Vessel JoiliamcsNo ratings yet
- Using s275jr For Asme Div1 Vessel-UnassignedDocument6 pagesUsing s275jr For Asme Div1 Vessel-UnassignedNasrul AdliNo ratings yet
- Pressure Plate MaterialDocument5 pagesPressure Plate MaterialBhavani PrasadNo ratings yet
- This Is Very Common in Tank ConstructionDocument11 pagesThis Is Very Common in Tank ConstructionsbmmlaNo ratings yet
- Astm A181-2001 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm A181-2001 PDFMohammed TariqNo ratings yet
- TBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateDocument4 pagesTBE-Pressure Vessel Standard TemplateSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- SMAW Electrode IdentificationDocument2 pagesSMAW Electrode IdentificationAsim AliNo ratings yet
- Asme-Bpvc Sec IV Int Vol 44Document7 pagesAsme-Bpvc Sec IV Int Vol 44mostafa aliNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel RT TestDocument4 pagesPressure Vessel RT TestalokbdasNo ratings yet
- API 650 12th - 2013Document4 pagesAPI 650 12th - 2013mohamed100% (1)
- WPS-Tube To Tube Sheet (SS-SS)Document2 pagesWPS-Tube To Tube Sheet (SS-SS)suria qaqcNo ratings yet
- Api 602 Forged Steel Valve PDFDocument4 pagesApi 602 Forged Steel Valve PDFThomasFrenchNo ratings yet
- Dished Heads - Head TypesDocument7 pagesDished Heads - Head Typesnaveenbaskaran1989100% (1)
- Interview Type Question Manufacturing PDFDocument4 pagesInterview Type Question Manufacturing PDFSourav KayalNo ratings yet
- Casti Guidebook Pressure VesselDocument3 pagesCasti Guidebook Pressure VesselQuangTiên0% (1)
- General Specification FOR Pressure VesselsDocument13 pagesGeneral Specification FOR Pressure Vesselssumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Acid Storage Tank MaterialDocument2 pagesAcid Storage Tank MaterialOky Andytya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection BOMDocument4 pagesCathodic Protection BOManonymous542No ratings yet
- Asme CCase 1987-2Document2 pagesAsme CCase 1987-2ADAMJSRAONo ratings yet
- FDA and 1935 2004 DoC General Food Contact Regulations BU HFH Rev 008Document15 pagesFDA and 1935 2004 DoC General Food Contact Regulations BU HFH Rev 008Gisela ViskaNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy C-276 WeldingDocument4 pagesHastelloy C-276 WeldingClaudia MmsNo ratings yet
- Weld Weave WidthDocument4 pagesWeld Weave Widthapply19842371No ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan For Pressure Vessel Repair, Modification, AlterationDocument5 pagesInspection and Test Plan For Pressure Vessel Repair, Modification, AlterationMuhammed Abo-Fandood50% (2)
- Steel Pipes Tubes Eng PDFDocument21 pagesSteel Pipes Tubes Eng PDFsintaprisilliaNo ratings yet
- Letterhead (Employer Only) : Tax Borne LetterDocument1 pageLetterhead (Employer Only) : Tax Borne Letternanivenkatgaurav100% (2)
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitlednanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Letterhead (Employer Only) : Indemnity LetterDocument1 pageLetterhead (Employer Only) : Indemnity Letternanivenkatgaurav100% (1)
- Personnel Time Sheet Month:: Work Activity Total HrsDocument3 pagesPersonnel Time Sheet Month:: Work Activity Total HrsnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitlednanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Total Procedure NDT Procedure (Ut For Steel Structure) - 1Document35 pagesTotal Procedure NDT Procedure (Ut For Steel Structure) - 1nanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Total Procedure NDT Procedure (Ut For Steel Structure) - 1Document35 pagesTotal Procedure NDT Procedure (Ut For Steel Structure) - 1nanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- EN ISO 15609-1: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormDocument10 pagesEN ISO 15609-1: European Standard Norme Européenne Europäische NormnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Inspection ReportDocument2 pagesStructural Steel Inspection ReportnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
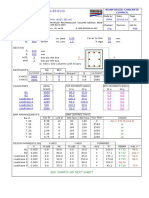
- RCC53 Column DesignDocument15 pagesRCC53 Column DesignnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document2 pagesIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)nanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- NDT (Ut) - Twi - Part (4) .Document31 pagesNDT (Ut) - Twi - Part (4) .nanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- 3 Welding Imperfections and Materials InspectionDocument31 pages3 Welding Imperfections and Materials InspectionnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Symbol of PipingDocument4 pagesSymbol of PipingnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- StainlessSelection PDFDocument1 pageStainlessSelection PDFnanivenkatgauravNo ratings yet
- Defects in Gtaw or Tig WeldingDocument13 pagesDefects in Gtaw or Tig WeldingRamesh R80% (5)
- Hardenability LauraliceDocument87 pagesHardenability LauraliceApun Rian RamadanNo ratings yet
- KITZ SteelBallValvesGraphiteMetalSeatE 204 12Document48 pagesKITZ SteelBallValvesGraphiteMetalSeatE 204 12pt tabNo ratings yet
- Limitations of The Use of Grossman Quench Severity FactorsDocument12 pagesLimitations of The Use of Grossman Quench Severity FactorsPedro Polastri PatriotaNo ratings yet
- Draw-Peeling Improves Wire Quality: Surface TreatmentDocument1 pageDraw-Peeling Improves Wire Quality: Surface TreatmentYahyaMoummouNo ratings yet
- BAB IV Materi IntiDocument19 pagesBAB IV Materi Intidwi sandhaNo ratings yet
- API 571 Damage MechanismsDocument42 pagesAPI 571 Damage MechanismsIsmail Jamaluddin100% (1)
- CSWIP 3.1 Theory ExamDocument13 pagesCSWIP 3.1 Theory ExamAhmed Tajelsir67% (12)
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Document7 pagesWelding Procedure Specification (WPS)Aamer MohammedNo ratings yet
- NIIR List of BooksDocument15 pagesNIIR List of BooksRakeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Engineer'S Report: Company CodeDocument2 pagesEngineer'S Report: Company CodeCAT CYLINDERNo ratings yet
- Joints (Qw-402) DetailsDocument3 pagesJoints (Qw-402) DetailsNaqqash SajidNo ratings yet
- Military-Grade Steel: What It Is & How It's Used - Federal Steel SupplyDocument1 pageMilitary-Grade Steel: What It Is & How It's Used - Federal Steel SupplyYanyan2009No ratings yet
- Report of Jaminy End Quench TestDocument92 pagesReport of Jaminy End Quench TestBharathi K 2018100% (1)
- DeclarationDocument65 pagesDeclarationbhawana guptaNo ratings yet
- Sluice Gate ValveDocument15 pagesSluice Gate ValveRinia DurrsakeNo ratings yet
- Additional Requirements For Pressure Vessels For Applications in H2S Containing EnvironmentsDocument21 pagesAdditional Requirements For Pressure Vessels For Applications in H2S Containing Environmentshalim_kaNo ratings yet
- IG 76 MESC 14d - 2021Document3 pagesIG 76 MESC 14d - 2021bmanojkumar16No ratings yet
- General3 AnswerDocument4 pagesGeneral3 AnswerAnonymous 8bH7sXpcEHNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel Corrosion in A MEA Based CO2 Removal PlantDocument8 pagesInvestigation of Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel Corrosion in A MEA Based CO2 Removal PlantBenedict LimNo ratings yet
- AMACS Corrugated Grid Packing Web2Document1 pageAMACS Corrugated Grid Packing Web2ValiNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Welding - JapanDocument6 pagesGas Pressure Welding - Japanscchung100% (1)
- As 2003-1991 Carbon and Low Alloy Steel - Measurement of DecarburizationDocument6 pagesAs 2003-1991 Carbon and Low Alloy Steel - Measurement of DecarburizationSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- PDF ST Konverter e 3 2019.en.26Document6 pagesPDF ST Konverter e 3 2019.en.26Henry SunarkoNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of MetalsDocument134 pagesWelding Metallurgy and Weldability of MetalsAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Extraction of MetalsDocument57 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Extraction of MetalsJuman AlbuhaisiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus WELDING TECHNOLOGY R2017Document2 pagesSyllabus WELDING TECHNOLOGY R2017CHANDRAPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Specs Pre-Cast Segment LiningsDocument8 pagesSpecs Pre-Cast Segment Liningssatan007No ratings yet
- BH Curve FormulaDocument5 pagesBH Curve Formulabitconcepts9781No ratings yet
- PW CAT Product Catalog enDocument116 pagesPW CAT Product Catalog enTymoteoNo ratings yet