0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views15 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functions
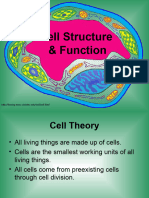
The document summarizes the parts of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and their functions. It describes the major organelles common to both types of cells including the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, and vacuoles. It notes that eukaryotic cells also contain chloroplasts and have a cell wall made of cellulose, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The organelles each perform specialized functions that allow the cell to carry out its required activities.
Uploaded by
Ychel P. YapCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views15 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functions
The document summarizes the parts of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and their functions. It describes the major organelles common to both types of cells including the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, and vacuoles. It notes that eukaryotic cells also contain chloroplasts and have a cell wall made of cellulose, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The organelles each perform specialized functions that allow the cell to carry out its required activities.
Uploaded by
Ychel P. YapCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd