Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structures
Uploaded by
STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structures
Uploaded by
STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoCopyright:
Available Formats
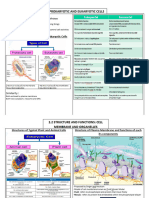
CELL STRUCTURES &
FUNCTIONS
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
CELL – Structural unit and
- Made a simple and
functional unit of life and
single – lens
performs all life processes
microscope
EXAMPLES OF CELL - With magnification
about 275X
ROBERT HOOKE
- DISCOVERED THE CELL
- COINED THE NAME
“CELL”
- USED CORK OF PLANT
- OBSERVED TINY BOXES
THAT LOOK LIKE THE
ROOMS IN
MONASTERY
2 BASIC CELL TYPES
PROKARYOTIC VS
EUKARYOTIC CELL
DISCOVERY OF THE CELL
Also called protoplasm inside of the
cell
Living substance – contains the
organelles that perform all the
physiological properties of the cell
Gel-like Material
- Sol: semi-liquid
3 BASIC PARTS OF THE CELL - Gel: semi-solid
- PLASMA Cytosol
MEMBRANE
- CYTOPLASM - 70% of the cytoplasm
- NUCLEUS - Mixture of cytoskeleton
filaments, dissolved
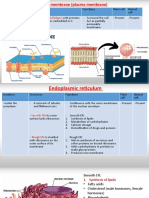
CELL MEMBRANE – Also called materials and water
Plasma Membrane separates the cell
from its external environment ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Envelope - System of membranous
tubules and sacs
- Covers and protects the cell
- Gives shape to the cell Circulatory System of the Cell
Bilayer Phospholipid - Internal transport system
- Allows molecules in the cell
- Phosphate layers: polar to move from one part to
heads; hydrophilic another
- Lipid layers: non-polar tails;
Rough ER (rER)
hydrophobic
Semi-permeable - Lined with ribosomes
- For protein synthesis and
- Selects materials that pass transport
through it
- Regulates the movement of Smooth ER (Ser)
materials - No ribosomes
Fluid Mosaic Model - Transports other materials
other than protein
- Contains various materials or
molecules RIBOSOMES
- Phospholipids - Most common organells in
- Cholesterol almost all cells not
- Proteins surrounded by a membrane
CYTOPLASM
Protein Micro-machines produce energy rich
molecules
- Sites for protein synthesis
DOUBLE-MEMBRANE
FREE RIBOSOMES ORGANELLES
- Floating in the cytoplasm - Smooth outer membrane
- Size 70S - Folded inner membrane
- In prokaryotes - Cristae: infoldings
Polysome / Polyribosome GOLGI APPARATUS
- Group of 80s ribosomes - Also called Golgi complex or
working together translating Golgi body processing and
mRNA to polypeptides packaging plant, and
secretory vesicle
Attached Ribosomes
Cisternae
- Line the membranes of
endoplasmic reticulum - Fused flattened sacs or folds
- Size 80S - Also called dictyosome
- In eukaryotes
Transport Agent
MITOCHONDIA
- Involved in the distribution
- Powerhouse of the cell of lipids around the cell
Large organelles second to nucleus and Protein Collector & Dispatcher
chloroplasts
- Protein synthesized in the ER
ATP MANUFACTURER packed into the vesicles and
fused with the Golgi body for
- Manufacture energy
secretion via exocytosis
In the form of ATP
- Metabolize carbohydrate and LYSOSOME BUILDER
fatty acid to generate energy
- Lysosomes are vesicles with
SEMI-AUTONOMOUS protein enzymes pinched off
ORGANELLES by Golgi body to the
cytoplasm
- Have own DNA, so can
produce by itself by dividing CENTRIOLES
AEROBIC RESPIRATION - Organizing centers for
microtubule contain 2
- Mitochondria act like a bundles of microtubules at
digestive system to right angle to each other
breakdown nutrients to
CELL DIVISION
- Form the spindle fibers for cause cellular damage and
the separation of cell death
chromosomes
VACUOLE
CENTROSOMES
- Storage bubbles found in the
- House the centrioles cells membrane bound fluid
sac
LYSOSOME
Storage Sac
- Tiny sac produced by Golgi
body - Stores large amount of
various materials, like
Digestive Plant organic and inorganic
molecules
- Contains digestive enzyme to
help in the process of Subordinate Role
digestion
- Assisting in exocytosis and
Suicide Sac endocytosis
- When the cell is damaged, Transporting Agent
the lysosomes bursts,
releases enzyme and digests - Transports needed materials
own cell into the cell via endocytosis,
and waste materials out of
Keeps the cell clean the cell via exocytosis
- Also digest excess and worn- CYTOSKELETON
out organelles and engulfed
bacteria or viruses. - Complex network of
interlinking filaments or
PEROXISOME tubules Cell Skeleton
- Formerly known as a 3 Structures:
microbody
1. Microfilaments:
Oxidative Organelle - Contractile: made of actin
- For cell movement and
- Contains enzymes that
cytokinesis
oxidizes fatty acids and
2. Microtubules:
amino acids
- Rigid, hollow tubes: made of
- By product is hydrogen
tubulin
peroxide
- Maintain cell shape
Chemical Detoxification - Form the centrioles (spindle
fibers)
- Oversees reactions that 3. Intermediate Filaments
neutralize free radicals which - Provide strength and support
CHLOROPLASTS - Hereditary material: contains
instructions for traits and
- None in animal cells sites of characteristics
photosynthesis
Nucleolus
Thylakoids
- Spherical body in the nucleus
- Flattened membranous sacs for the synthesis of protein
that contain chlorophyll
Grana
- Pile of thylakoids
Stroma
- Spaces in grana for the
exchange of materials
FLAGELLA AND CILIA
- For cell movement
Cilia – short, Hair-like, numerous in
number
Flagella
- Long
- Thread-like
- Fewer in number
NUCLEUS
- Normally the largest
organelle Brain of the cell.
Nuclear Envelope
- Double membrane with
many pores
- Controls the movement of
material in and out the
nucleus.
Chromosomes
- Houses the genes (DNA)
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2Document10 pagesCell Structures 2STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Microscopy 1Document14 pagesBiology Cells Microscopy 1Andrea Trish NicolasNo ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Parts of The CellDocument3 pagesParts of The CellMa Claire TumboconNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio ReviewerElla ReeveNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant CellDocument6 pagesCell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant Celljean magallonesNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- Sunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenDocument4 pagesSunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- (Zoolone) Animal CellDocument5 pages(Zoolone) Animal CellRenee Margarette GrapilonNo ratings yet
- Cell Mol REVIEWERDocument9 pagesCell Mol REVIEWERRodelio ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Simple or Complex CellsDocument2 pagesCells: Simple or Complex CellsMary Jean BoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsLea IoaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJoyce GuintoNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document10 pagesCell 3OscarNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Bab 2Document31 pagesBio F4 Bab 2Alwani FarahiNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1590 - Invented Primitive Microscope 1665 - 1665-1676 Cell Theory - Complete Cell TheoryDocument4 pages1590 - Invented Primitive Microscope 1665 - 1665-1676 Cell Theory - Complete Cell TheoryjaysparklesNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaDocument7 pagesBiology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaPaolo JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument13 pagesMicropara ReviewerEmhnaly Kae AggalutNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument4 pagesCell Theory and StructureKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- Histonotes 1Document3 pagesHistonotes 1mayumi takagiNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of Cells (A) Diagram of Prokaryotes (B) Diagram of EukaryotesDocument3 pagesInternal Structure of Cells (A) Diagram of Prokaryotes (B) Diagram of EukaryotesKim Angelica AbongNo ratings yet
- Microtubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane SurfacesDocument3 pagesMicrotubules Which Occur On Exposed Membrane Surfacesprettyfriends 05No ratings yet
- Microana Prelim ReviewerDocument17 pagesMicroana Prelim ReviewerjerlerositaNo ratings yet
- Biology: /duringDocument15 pagesBiology: /duringBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 1Valerie HermenegildoNo ratings yet
- 2.01 - Cell Organelles and MacromoleculesDocument2 pages2.01 - Cell Organelles and MacromoleculesJuan Miguel SalvadorNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Pro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDocument5 pagesPro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesWEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Bot 1Document16 pagesBot 1Lawrence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cell/Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesCell/Plasma MembraneKrizsharei Cerrado CerradoNo ratings yet
- The Cell StructureDocument7 pagesThe Cell StructureAbcedef Wyn Grey AbrasadoNo ratings yet
- BiosciDocument10 pagesBiosciBriones, Rozen M.No ratings yet
- CELLS AND TISSUES Notes (Anaphy)Document2 pagesCELLS AND TISSUES Notes (Anaphy)Lanette Liana A. LocaylocayNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellGalvez Glaiza ElaineNo ratings yet
- H2 BIO Cell Structure NotesDocument15 pagesH2 BIO Cell Structure NotesEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 pagesGen Bio Reviewerexceeyel2406zaionNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lec Module 3Document6 pagesZoology Lec Module 3Camille AlzolaNo ratings yet
- CELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESDocument6 pagesCELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESHarry ParconNo ratings yet
- CELL CYTOLOGY AND CYCLE (Inc)Document4 pagesCELL CYTOLOGY AND CYCLE (Inc)ARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument41 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationKaesaav SelvamanikamNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its BeginningDocument6 pagesThe Cell and Its BeginningZarc VenturaNo ratings yet
- HR1Document6 pagesHR1Rose CitcoNo ratings yet
- Nmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesNmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cellssavina100% (1)
- The Cells: Cella - Small RoomDocument5 pagesThe Cells: Cella - Small RoomSarah Grace CajucomNo ratings yet
- Structure and TaxonomyDocument4 pagesStructure and Taxonomymhiee maaaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationDocument8 pagesCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- Genbio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio ReviewerAnne Carmel PinoNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- BIO C2 @notastpm04Document35 pagesBIO C2 @notastpm04Aprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- A Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellDocument2 pagesA Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellLerr Real RelleNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of CellDocument4 pagesThe Beginning of CellTrishia Lynn MaldiaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Cell StructureDocument3 pagesBiology: Cell StructureFernanda AntonialliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- PV Power To Methane: Draft Assignment 2Document13 pagesPV Power To Methane: Draft Assignment 2Ardiansyah ARNo ratings yet
- NauseaDocument12 pagesNauseakazakom100% (2)
- Ass AsDocument23 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- 03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaDocument48 pages03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaSudarshan GadalkarNo ratings yet
- RS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerDocument25 pagesRS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerromanNo ratings yet
- DC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFDocument1 pageDC Generator - Construction, Working Principle, Types, and Applications PDFGokul GokulNo ratings yet
- 2021 Individual 20546 (Lawrence, Stephen R. and Bette F.) ClientDocument18 pages2021 Individual 20546 (Lawrence, Stephen R. and Bette F.) ClientVANDA MOORENo ratings yet
- DIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionDocument168 pagesDIY Toolkit Arabic Web VersionAyda AlshamsiNo ratings yet
- SANDWICH Elisa (Procedure) - Immunology Virtual Lab I - Biotechnology and Biomedical Engineering - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument2 pagesSANDWICH Elisa (Procedure) - Immunology Virtual Lab I - Biotechnology and Biomedical Engineering - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabsantonuNo ratings yet
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDocument196 pages(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66No ratings yet
- Innocent Words That Make Her HornyDocument14 pagesInnocent Words That Make Her HornyH69% (13)
- Writing About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsDocument68 pagesWriting About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsLangers BastasaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I Lesson II Seven Environmental PrinciplesDocument17 pagesCHAPTER I Lesson II Seven Environmental PrinciplesTrixie jade DumotNo ratings yet
- ANTINEOPLASTICSDocument21 pagesANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- (Ebook - Antroposofia - EnG) - Rudolf Steiner - Fundamentals of TheraphyDocument58 pages(Ebook - Antroposofia - EnG) - Rudolf Steiner - Fundamentals of Theraphyblueyes247No ratings yet
- AN44061A Panasonic Electronic Components Product DetailsDocument3 pagesAN44061A Panasonic Electronic Components Product DetailsAdam StariusNo ratings yet
- Arc Hydro - Identifying and Managing SinksDocument35 pagesArc Hydro - Identifying and Managing SinkskbalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyDocument17 pagesLesson 1 Concepts About Educational TechnologyMarvin ContigaNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Radio Access OverviewDocument8 pagesWCDMA Radio Access OverviewDocMasterNo ratings yet
- Yu ZbornikDocument511 pagesYu ZbornikВладимирРакоњацNo ratings yet
- Task of ProjectDocument14 pagesTask of ProjectAbdul Wafiy NaqiuddinNo ratings yet
- Training Design SprintDocument11 pagesTraining Design Sprintardi wiantoNo ratings yet
- Book Chapter 11 SubmissionDocument18 pagesBook Chapter 11 Submissioncristine_2006_g5590No ratings yet
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraNo ratings yet
- 00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentDocument4 pages00022443the Application of A Continuous Leak Detection System To Pipelines and Associated EquipmentFaizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Kursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014Document12 pagesKursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014ihsanyusoffNo ratings yet
- Krishna TejaDocument71 pagesKrishna TejaHimanshu GaurNo ratings yet
- DADTCO Presentation PDFDocument34 pagesDADTCO Presentation PDFIngeniería Industrias Alimentarias Itsm100% (1)
- Antenatal Care (ANC)Document77 pagesAntenatal Care (ANC)tareNo ratings yet
- Zillah P. Curato: ObjectiveDocument1 pageZillah P. Curato: ObjectiveZillah CuratoNo ratings yet