Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 3-5,6 Keys and Couplings
Uploaded by
Raghavendra Kilari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views9 pagesThis document discusses keys and couplings. It provides equations to calculate the shear stress and bearing stress on keys to determine the appropriate key size based on the tangential force and material properties. It also briefly mentions stress concentration and different types of couplings, including universal joint couplings. The key purpose is to transmit torque between a shaft and mounted component using a properly sized key based on simplified stress equations.
Original Description:
Keys
Original Title
Keys and Coupling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses keys and couplings. It provides equations to calculate the shear stress and bearing stress on keys to determine the appropriate key size based on the tangential force and material properties. It also briefly mentions stress concentration and different types of couplings, including universal joint couplings. The key purpose is to transmit torque between a shaft and mounted component using a properly sized key based on simplified stress equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views9 pagesSection 3-5,6 Keys and Couplings
Uploaded by
Raghavendra KilariThis document discusses keys and couplings. It provides equations to calculate the shear stress and bearing stress on keys to determine the appropriate key size based on the tangential force and material properties. It also briefly mentions stress concentration and different types of couplings, including universal joint couplings. The key purpose is to transmit torque between a shaft and mounted component using a properly sized key based on simplified stress equations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Section 3-5,6
Keys and Couplings
MET 301
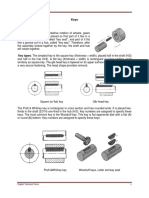
Keys
Key is used to transmit torque
between shaft and the component
mounted on the shaft.
Square and flat keys are most
common.
Other types of keys
Key size
Actual stresses acting on keys are difficult to
determine
Simplified mechanical stresses equations for
shear and compression
Tangential Force at shaft diameter: F= T/(D/2) = 2T/D
Average shear stress t in Key, should not exceed allowable shear stress tw =typ/Nfs
t = F/(W*L) < typ/Nfs
or, F/(W*L) < syp/(2Nfs) ..(1)
Average bearing (compressive) stress s in Key, should not exceed compressive stress sw
=syp/Nfs
s = F/[(H/2)*L] < syp/Nfs
or, s = F/(H*L) < syp/(2Nfs)..(2)
For square key, W=H, Equation (1) and (2) are essentially same, i.e., shear or bearing
stress will produce the same key length.
Stress concentration
Coupling
Universal Joint Coupling
You might also like
- Keys and CouplingDocument9 pagesKeys and CouplingRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Keys and CouplingDocument9 pagesKeys and CouplingSomnath SomadderNo ratings yet
- Keys and CouplingDocument9 pagesKeys and CouplingAbdisalaam mohamudNo ratings yet
- Keys and CouplingDocument9 pagesKeys and CouplingvishnusankarNo ratings yet
- Keys and CouplingDocument9 pagesKeys and CouplingJesriel AlsonadoNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Keys and CouplingsDocument8 pagesUnit-2 Keys and CouplingsCHANDRASEKARANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.0 (Design For Strength) - Introduction & FastenersDocument24 pagesChapter 4.0 (Design For Strength) - Introduction & FastenersPeter SamuelNo ratings yet
- Bending, Torsion, and StressDocument18 pagesBending, Torsion, and StressnasirfahimNo ratings yet
- ELE 301: Signals and Systems: Prof. Paul CuffDocument35 pagesELE 301: Signals and Systems: Prof. Paul Cuffnawinnawmu1026No ratings yet
- Keys LectureDocument4 pagesKeys LectureellyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Target Torque For Bolts (Asme Pcc-1)Document1 pageCalculation of Target Torque For Bolts (Asme Pcc-1)daniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Keys & CouplingsDocument24 pagesKeys & Couplingsrahulbachute100% (9)
- MODULE 3 - Keys and CouplingsDocument10 pagesMODULE 3 - Keys and CouplingsBoris PalaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document25 pagesLecture 2Balaji KannanNo ratings yet
- Keys and KeywaysDocument39 pagesKeys and KeywaysInnocent J MathonsiNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series and Integrals With Applications To Signal AnalysisDocument116 pagesFourier Series and Integrals With Applications To Signal AnalysisislaNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: A B C Xy XyDocument5 pagesObjectives:: A B C Xy XyWaseem Al-khawajaNo ratings yet
- Clutches and BrakesDocument77 pagesClutches and BrakesKaushikUpadyaNo ratings yet
- Clutches and BrakesDocument77 pagesClutches and BrakesVenu Gopal100% (1)
- Unit5 Design of KeysDocument32 pagesUnit5 Design of Keyssuswagat75% (4)
- Mohr Circle State Of-StressDocument30 pagesMohr Circle State Of-StressdocsdownforfreeNo ratings yet
- Full Design of Flange CouplingDocument10 pagesFull Design of Flange CouplingSamara AyubNo ratings yet
- Transmission 1Document16 pagesTransmission 1bilal elgeddawyNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase AC Circuits: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument13 pagesSingle-Phase AC Circuits: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurSai SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- UnitDocument40 pagesUnitvarshasdm1987No ratings yet
- KeysDocument2 pagesKeysZàkaria DjellouliNo ratings yet
- Full BridgeDocument7 pagesFull Bridgebryan eduardo villegas carrascoNo ratings yet
- Metal Fatigue SpreadsheetsDocument94 pagesMetal Fatigue Spreadsheetsfsijest100% (1)
- Maximum Width-To-Thickness Ratios For Compression PDFDocument3 pagesMaximum Width-To-Thickness Ratios For Compression PDFtoliveira80No ratings yet
- Introduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- European Normal Black ScholesDocument14 pagesEuropean Normal Black ScholesrahiminatorNo ratings yet
- 4 Noise in Communication SystemsDocument34 pages4 Noise in Communication SystemsyuliNo ratings yet
- Kolkl Asd Asd Asda SfwerqweweDocument3 pagesKolkl Asd Asd Asda SfwerqweweDamodar S PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Signals Are Variables That Carry Information - Systems Process Input Signals To Produce Output SignalsDocument10 pagesSignals Are Variables That Carry Information - Systems Process Input Signals To Produce Output Signalsking_hhhNo ratings yet
- 02 Classification of SignalsDocument5 pages02 Classification of SignalsPravat KarkiNo ratings yet
- Signal and SystemDocument15 pagesSignal and Systemswap_k007100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Power Density Spectrum: EE420/500 Class Notes 7/27/2011 John StensbyDocument18 pagesChapter 8 - Power Density Spectrum: EE420/500 Class Notes 7/27/2011 John StensbyMahmoud NaguibNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Keys - Types, Selection of Square and Flat Keys PDFDocument25 pages2.4 Keys - Types, Selection of Square and Flat Keys PDFManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- Springs PDFDocument7 pagesSprings PDFanimeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Transformer CodeDocument14 pagesTransformer Codevidhisuthar1162No ratings yet
- Thin and Thick CylinderDocument8 pagesThin and Thick CylinderBala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Decoding: DTMF Telephone Touch Tone SignalsDocument30 pagesDecoding: DTMF Telephone Touch Tone SignalsCharlie WolfendenNo ratings yet
- Safety Valve CalcDocument12 pagesSafety Valve CalcArjun CharanNo ratings yet
- UG-37 F FactorDocument7 pagesUG-37 F FactorjamesNo ratings yet
- ELE 301: Signals and Systems: Prof. Paul CuffDocument45 pagesELE 301: Signals and Systems: Prof. Paul CuffTe NgNo ratings yet
- 3 Mohr CircleDocument8 pages3 Mohr CircleSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Huffman ExampleDocument19 pagesDynamic Huffman Exampleoureducation.inNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 MatlabDocument13 pagesLab 8 MatlabSher EjazNo ratings yet
- 1200 Uncertainty Analysis PDFDocument23 pages1200 Uncertainty Analysis PDFLalo MejiaNo ratings yet
- Triangular Norms. Position Paper IIDocument28 pagesTriangular Norms. Position Paper IIvlady120489No ratings yet
- Metal Fatigue SpreadsheetsDocument73 pagesMetal Fatigue SpreadsheetsKishore BhatNo ratings yet
- Model-2900-Uncertainty-Analysis-Rev-3 ThunderDocument44 pagesModel-2900-Uncertainty-Analysis-Rev-3 Thunderanil nsNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Huffman Coding: Computer Networks AssignmentDocument19 pagesDynamic Huffman Coding: Computer Networks Assignmentsumeetgothwal8688No ratings yet
- 15 Cutches & Brakes SDocument17 pages15 Cutches & Brakes SSara Ahmed100% (1)
- Fourier SeriesDocument12 pagesFourier SeriesAnshu ManNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesDocument19 pagesStrength of MaterialFormulas Short NotesRavindra DevireddyNo ratings yet
- Trunnion Stress ValidationDocument3 pagesTrunnion Stress ValidationGaye Kanal100% (1)
- Unit 1 Introduction 130404060314 Phpapp01Document55 pagesUnit 1 Introduction 130404060314 Phpapp01Raghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Limits Fits and Tolerances MetrologyDocument24 pagesLimits Fits and Tolerances MetrologyAnkushNo ratings yet
- Autocollimator Angle Dekkor: Mechanical Measurement and Metrology Prof. Naman M. DaveDocument24 pagesAutocollimator Angle Dekkor: Mechanical Measurement and Metrology Prof. Naman M. DaveRaghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Weld DesignDocument26 pagesWeld DesignRaghavendra Kilari100% (1)
- Limits Fits and Tolerances MetrologyDocument24 pagesLimits Fits and Tolerances MetrologyAnkushNo ratings yet
- Dial GaugeDocument21 pagesDial GaugeRaghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9e FatigueDocument20 pagesChapter 9e FatigueavenashaNo ratings yet
- Fits and Tolerences - AEDocument65 pagesFits and Tolerences - AERaghavendra Kilari100% (1)
- 2 CentrifugalPumpTheory InviscidFLuid SinglePhaseDocument45 pages2 CentrifugalPumpTheory InviscidFLuid SinglePhasekingcobra008No ratings yet
- 6 CouplingsDocument11 pages6 CouplingsKHAJANo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0301679X12002538 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0301679X12002538 MainRaghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection FormulaeDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection Formulae7575757575100% (6)
- JNTUK - List of Ratified Principals & Faculty - 14th, 15th & 17th Sept, 2016Document40 pagesJNTUK - List of Ratified Principals & Faculty - 14th, 15th & 17th Sept, 2016Raghavendra Kilari50% (2)
- JNTUK - List of Ratified Principals & Faculty - Covering Letter 19.09.2016Document2 pagesJNTUK - List of Ratified Principals & Faculty - Covering Letter 19.09.2016Raghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Lec16 SynthesisDocument27 pagesLec16 SynthesisvinaykumaryadavNo ratings yet
- KomDocument2 pagesKomRaghavendra KilariNo ratings yet
- Som NotesDocument54 pagesSom Notesmeetvinayak2007No ratings yet
- Unit18 Surface Finish MeasurementDocument14 pagesUnit18 Surface Finish Measurementirfanajai100% (1)