0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views23 pagesIndustrial Mathematics: Functions & Applications
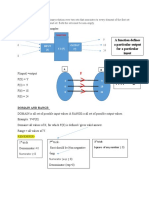
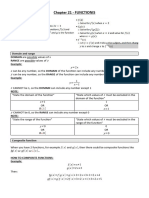
This document contains notes from an Industrial Mathematics - 2 course. It covers various topics in functions, including the definition of a function, function graphs, limits, continuity, derivatives, integrals, and their applications. It provides examples and explanations of key concepts like domain, codomain, range, operations of functions, composite functions, and inverse functions. It also includes practice problems applying these concepts and rules for assessments, including allowing devices, drinking, and a zero score for cheating.
Uploaded by
restuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
98 views23 pagesIndustrial Mathematics: Functions & Applications
This document contains notes from an Industrial Mathematics - 2 course. It covers various topics in functions, including the definition of a function, function graphs, limits, continuity, derivatives, integrals, and their applications. It provides examples and explanations of key concepts like domain, codomain, range, operations of functions, composite functions, and inverse functions. It also includes practice problems applying these concepts and rules for assessments, including allowing devices, drinking, and a zero score for cheating.
Uploaded by
restuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd