Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WEEK 9 - Reading Comprehension
Uploaded by
hchee_80 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views23 pages-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views23 pagesWEEK 9 - Reading Comprehension
Uploaded by
hchee_8-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
3.
1 Reading comprehension
skimming for main ideas
scanning for specific information
locating main ideas and supporting
details
Learning Objectives:
Elicit information from a variety of written
text types using appropriate
comprehension skills
In this lesson we will...
Discuss the skills of skimming and
scanning, locating main ideas and
supporting details based on reading
texts .
We use different styles of reading for
different purposes.
Among the reading techniques that we
use for high speed reading is skimming
and scanning.
Skimming and scanning do not require us
to read all the material in a text.
SKIMMING
Skimming technique is used to get the
gist or an overview of a text.
It helps us to read a text 3 to 4 times
faster than normal reading
We usually skim when we have limited
time to read
Skimming helps us to review major ideas
after we have studied a topic
To skim a text effectively, we must
read the title
read any heading, subheading or
illustrations
read only the main ideas – ignore all
other details
look for topic sentences – usually the first
or last sentence in a paragraph/passage
In skimming we ask questions beginning
with who, what, when, where to find out
what the text is mainly about.
Example:
Skim through the short extract below in
five seconds
Read only the heading, subheading and
the words in bold
The Cheetah
The cheetah which has its home in the
grasslands of Africa is the world’s fastest
runner. It can run up to 70 miles per
hour. Because of its speed it is able to
catch its prey with ease. It can go from
a stationary position to a speed of 45
miles per hour within two seconds.
By reading the heading, subheading
and the words in bold we can say that
the text is about the cheetah from Africa
is the world’s fastest runner.
Other information supports the general
idea that it is an animal which moves
with great speed
Refer to Handout 1 (pp 52 – 58)
SCANNING
Scanning is a technique used to search
for a particular fact or a specific detail to
answer a question
Scanning is looking for and not reading
When scanning we don’t have to read
every word
We usually scan when we are looking for
meaning of words in a dictionary, the
names and telephone numbers or
looking for schedules, tables, charts or
classified ads.
To scan effectively we must;
Know exactly what we are looking for
Search for key words or ideas by moving
your eyes quickly down the page until
you find what you need – do not read
any further
Use headings and subheadings to help
us to identify the sections we need to
locate quickly for the information
needed
Refer to Handout 2 (pp 41 – 46)
1. Topic of a text:
The topic of a text is what you are reading
about or the general idea
2. Topic Sentence:
A topic sentence is a complete sentence
that states the essential point of the
paragraph. It contains controlling ideas
3. Main Idea:
The main idea is the summary of essential
points of the paragraph
The main idea can often be substituted
with a topic sentence with controlling
ideas
The main idea can either be clearly
stated or can sometimes be implied
4. Supporting details are other sentences
that come after the topic sentence.
Usually there will be sentences that help
to explain, support, illustrate or describe
the main idea in a paragraph
Usually comes after the topic sentence –
developed from the controlling words
found in the topic sentence
It can be reasons or details, particular
facts and ideas that prove, explain,
support or give examples of controlling
ideas
To find supporting details developed
from the controlling ideas of the topic,
you may ask question words like; What,
who, whose, when, where, why, how…
Finding main idea and supporting details
is helpful because it;
Is the key to understanding a paragraph
or a passage
helps you to identify the general point
the author is making
Helps you to perceive the relationship
between the main idea and what is said
about the idea
Refer to Handout 3 (pp 65 – 66)
Source for passages and present the
main ideas, specific information and
supporting details in them.
You might also like
- Lecture No.1 Effective Reading Strategies: 1. SkimmingDocument5 pagesLecture No.1 Effective Reading Strategies: 1. Skimmingsalman majeedNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - FH - Reading SkillsDocument7 pagesWeek 2 - FH - Reading SkillskrdloblcNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - PWKDocument8 pagesWeek 2 - PWKhalo akufikaNo ratings yet
- Reading Styles: Unit I-Lsrw SkillsDocument6 pagesReading Styles: Unit I-Lsrw SkillsKalpit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Skimming and Identifying Main PointsDocument3 pagesSkimming and Identifying Main PointsTo NyNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument20 pagesCommunication Skillspeter charlesNo ratings yet
- Reading Strategies: 1. Previewing The Text To Get An OverviewDocument5 pagesReading Strategies: 1. Previewing The Text To Get An OverviewTomas Monge100% (1)
- Critical Reading PDFDocument46 pagesCritical Reading PDFVero Jonell Franz100% (1)
- MCS GCUF NotesDocument17 pagesMCS GCUF NotesMuhammad MussawarNo ratings yet
- 2 Reading MaterialDocument17 pages2 Reading MaterialRicky FegianNo ratings yet
- Finding Topic and Main Idea in The Reading Material: By: Irma SufianingsihDocument20 pagesFinding Topic and Main Idea in The Reading Material: By: Irma SufianingsihIrma SufianingsihNo ratings yet
- Critical ReadingDocument10 pagesCritical ReadingMuhammad NomiNo ratings yet
- Reading TechniquesDocument11 pagesReading TechniquesHuzaifa CHNo ratings yet
- Reading ToeflDocument4 pagesReading ToeflMari BoniattiNo ratings yet
- 1-What Is Skimming and Scanning?Document4 pages1-What Is Skimming and Scanning?nathalyNo ratings yet
- Reading SkillDocument3 pagesReading SkillGary Dennis DavidNo ratings yet
- KINDS-OF-READING For ClassmatesDocument4 pagesKINDS-OF-READING For ClassmatesKim Postrero PorrasNo ratings yet
- Finding The Main Idea: Where Are Main Ideas Found?Document85 pagesFinding The Main Idea: Where Are Main Ideas Found?Jemuel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Reading Strategies and SkillsDocument6 pagesReading Strategies and SkillsDesnitaNo ratings yet
- What Is Book ReviewDocument12 pagesWhat Is Book ReviewTanzil SarkarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Paragraph ComponentsDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Paragraph ComponentsULFATUN NUFUS. PNo ratings yet
- Reading TechniquesDocument4 pagesReading TechniquesAngelou HernandezNo ratings yet
- TSLB3073 Week 3Document39 pagesTSLB3073 Week 3Bryan AndrewNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 3 Reading Acad TextDocument39 pagesEapp Lesson 3 Reading Acad TextKathleenNo ratings yet
- Reading StrategiesDocument4 pagesReading StrategiesLUISA MARIA LOPEZ GOMEZ100% (1)
- Reading Techniques: The Four Main Types of Reading Techniques Are The FollowingDocument5 pagesReading Techniques: The Four Main Types of Reading Techniques Are The FollowingGayatri ManralNo ratings yet
- Reading Techniques Reading Techniques: Skimming ScanningDocument2 pagesReading Techniques Reading Techniques: Skimming ScanningDiana Bermas PagalingNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris - Alridho - 2012111003Document7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris - Alridho - 2012111003myname isridhoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Skimming The Reading TextDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Skimming The Reading TextMeila Khaerasar'iNo ratings yet
- Identifying Topics, Main Ideas, and Supporting (B)Document12 pagesIdentifying Topics, Main Ideas, and Supporting (B)HANITH ISKANDAR100% (1)
- Scanning, Skimming and Summarizing TechniquesDocument2 pagesScanning, Skimming and Summarizing TechniquesRahma NdityaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension and Redaction 1Document6 pagesReading Comprehension and Redaction 1Maria F VallesNo ratings yet
- Reading Review: How to Summarize Complex Texts in Under 15 WordsDocument7 pagesReading Review: How to Summarize Complex Texts in Under 15 WordsSeerat JavaidNo ratings yet
- Reading: Follow These Steps As You Skim A ReadingDocument4 pagesReading: Follow These Steps As You Skim A ReadingJohn Christian MacanNo ratings yet
- Esl2O: 2.4 Reading Strategies: Informational TextsDocument41 pagesEsl2O: 2.4 Reading Strategies: Informational Textsjannica yzabelNo ratings yet
- Reading SkillsDocument7 pagesReading SkillsAfra AfifahNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Developing Reading SkillsDocument8 pagesModule 2. Developing Reading SkillsJigz VasquezNo ratings yet
- 4 Reading SkillsDocument16 pages4 Reading SkillsRishabh RazdanNo ratings yet
- L3 - How To Read and Write in Health Sciences - Lessons 3 and 4 (With Suggested Answers)Document16 pagesL3 - How To Read and Write in Health Sciences - Lessons 3 and 4 (With Suggested Answers)Valiant CheungNo ratings yet
- Reading Techniques for Effective CommunicationDocument10 pagesReading Techniques for Effective CommunicationQamir Ullah Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- L1B116037 - Putra Fajar Erlangga - Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesL1B116037 - Putra Fajar Erlangga - Bahasa InggrisPutra Fajar ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Part One: Reading For PleasureDocument3 pagesPart One: Reading For Pleasuremelanie adilia jodieNo ratings yet
- Reading, Note Taking and Summarization SkillsDocument15 pagesReading, Note Taking and Summarization SkillsIsaack MohamedNo ratings yet
- PreviewingDocument1 pagePreviewingKenny Alvarez OcandoNo ratings yet
- Professional Communication Unit 2Document9 pagesProfessional Communication Unit 2pankajkushwaha956571No ratings yet
- CAEL 204 Study NotesDocument13 pagesCAEL 204 Study Notesggelasoud.razaviNo ratings yet
- What Are Academic Texts?Document5 pagesWhat Are Academic Texts?peerlesscucumber100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension SkillDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension SkillPuReNo ratings yet
- EFFECTIVE & CRITICAL READING by DR - BUDHIDocument24 pagesEFFECTIVE & CRITICAL READING by DR - BUDHIMunawir SyamNo ratings yet
- Active ReaderDocument4 pagesActive Readershazila100% (1)
- English Notes LLB Part 2Document2 pagesEnglish Notes LLB Part 2Fahad amin AminNo ratings yet
- To Acquire Information and Knowledge C) As A Means of PreparingDocument10 pagesTo Acquire Information and Knowledge C) As A Means of PreparingIbrahim Mohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A. DescriptionDocument5 pagesA. DescriptionVan QionaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Reading SkillsDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Reading SkillskennedyNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Skimming and Scanning PDFDocument4 pagesHandouts For Skimming and Scanning PDFUdoy PaulNo ratings yet
- BAB 1 Introduction of ReadingnessDocument6 pagesBAB 1 Introduction of ReadingnessJinganNo ratings yet
- Reading SkillsDocument28 pagesReading SkillsBaseer AhmadNo ratings yet
- RefrenceDocument1 pageRefrencehchee_8No ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionhchee_8No ratings yet
- EssayDocument4 pagesEssayhchee_8No ratings yet
- How Important Is Cultural Diversity at Your SchoolDocument4 pagesHow Important Is Cultural Diversity at Your Schoolhchee_8No ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument1 pageAcknowledgementhchee_8No ratings yet
- 8 Benefits of Cultural Diversity in The Workplace: Katie Reynolds, 2016Document7 pages8 Benefits of Cultural Diversity in The Workplace: Katie Reynolds, 2016hchee_8No ratings yet
- GO 7 Benefits of Cultural Diversity in The WorkplaceDocument1 pageGO 7 Benefits of Cultural Diversity in The Workplacehchee_8No ratings yet
- Promoting Respect For Cultural Diversity in The ClassroomDocument3 pagesPromoting Respect For Cultural Diversity in The Classroomhchee_8No ratings yet
- 可爱卡通小动物幻灯片模板Document27 pages可爱卡通小动物幻灯片模板hchee_8No ratings yet
- 13 Benefits and Challenges of Cultural Diversity in the WorkplaceDocument2 pages13 Benefits and Challenges of Cultural Diversity in the Workplacehchee_8No ratings yet
- EssayDocument4 pagesEssayhchee_8No ratings yet
- WEEK 9 - Reading ComprehensionDocument23 pagesWEEK 9 - Reading Comprehensionhchee_8No ratings yet
- Promote Respect for Culture DiversityDocument1 pagePromote Respect for Culture Diversityhchee_8No ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionhchee_8No ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense ExplainedDocument8 pagesSimple Present Tense Explainedhchee_8No ratings yet
- AdverbDocument10 pagesAdverbhchee_8No ratings yet
- Introduction to History: Defining the PastDocument26 pagesIntroduction to History: Defining the PastYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document16 pagesModule 6api-3807600No ratings yet
- NVision Manual 2019Document593 pagesNVision Manual 2019Alpha MNo ratings yet
- ABOO DIL HOSSAIN V MR SHEIK FAROOK BOODHOO and ANOR 2017 SCJ 142Document7 pagesABOO DIL HOSSAIN V MR SHEIK FAROOK BOODHOO and ANOR 2017 SCJ 142Jonathan BruneauNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Rosetta Stone (CALL) Software On ESL Students Proficiency in English Language 1Document10 pagesThe Impact of Rosetta Stone (CALL) Software On ESL Students Proficiency in English Language 1Delyana EbNo ratings yet
- Philippines Criminal Law Review - Illegal Firearm PossessionDocument2 pagesPhilippines Criminal Law Review - Illegal Firearm Possessionvincent nifasNo ratings yet
- BASIC SKILLS IN CONSTRUCTIVE COMMUNICATIONDocument3 pagesBASIC SKILLS IN CONSTRUCTIVE COMMUNICATIONraja naiduNo ratings yet
- Search Business Management Course ExamsDocument1 pageSearch Business Management Course Examsashley100% (2)
- Risk Assessment For Generator EquipmentDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment For Generator Equipmentabou bakar0% (1)
- Conversation Questions GenerationDocument3 pagesConversation Questions GenerationRania KuraaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Risk Management for Stora EnsoDocument11 pagesEnterprise Risk Management for Stora EnsoHarsh Vardhan0% (3)
- Cellulose Imports Data - India Imports Data of Cellulose - India Imports Data of HS 39123919Document2 pagesCellulose Imports Data - India Imports Data of Cellulose - India Imports Data of HS 39123919TayyabNo ratings yet
- Citizen's Charter for Batac City Government ServicesDocument395 pagesCitizen's Charter for Batac City Government ServicesMark GermanNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of NIA Act AmendmentsDocument8 pagesCritical Analysis of NIA Act AmendmentsAadhitya NarayananNo ratings yet
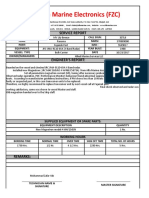
- Alfa Marine Electronics services JRC JMA-9110-6XA radar on MV Lily BreezeDocument2 pagesAlfa Marine Electronics services JRC JMA-9110-6XA radar on MV Lily BreezeZafar YabNo ratings yet
- Migration CaseDocument244 pagesMigration CaseMihai EpureNo ratings yet
- Evidence: I. Search For Truth A. As A Continuing Human Endeavor To Seek Answers For The Purpose of Knowledge ofDocument53 pagesEvidence: I. Search For Truth A. As A Continuing Human Endeavor To Seek Answers For The Purpose of Knowledge ofJoseph Santos GacayanNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Salary Taxation in IndiaDocument36 pagesNature and Scope of Salary Taxation in IndiamaheshNo ratings yet
- Bio DataDocument4 pagesBio DatakamalgkNo ratings yet
- Dramaturgy of Sound in The Avant-Garde ADocument360 pagesDramaturgy of Sound in The Avant-Garde AFromZero FromZeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Non-Verbal Communication: Speaking Without Words OutlineDocument31 pagesLesson 4: Non-Verbal Communication: Speaking Without Words OutlineTâm TâmNo ratings yet
- Education of Children in Rural Areas ofDocument72 pagesEducation of Children in Rural Areas ofJheuz DumaopNo ratings yet
- After Sales ServiceDocument6 pagesAfter Sales ServiceEdsel Jay RaperNo ratings yet
- Impact of Perceived Stress On General Health: A Study On Engineering StudentsDocument17 pagesImpact of Perceived Stress On General Health: A Study On Engineering StudentsGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- C_TADM70_74 Exam Guide: SAP OS/DB Migration Certification PrepDocument6 pagesC_TADM70_74 Exam Guide: SAP OS/DB Migration Certification PrepAdemir SouzaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: From: Shikhar VermaDocument1 pageCurriculum Vitae: From: Shikhar Vermaशिखर वर्माNo ratings yet
- Industry & Competitive Landscape Analysis: Session 6Document16 pagesIndustry & Competitive Landscape Analysis: Session 6SHIVAM VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Answer Sheet Lessons 7 & 8Document4 pagesPersonal Development Answer Sheet Lessons 7 & 8Johaimah MacatanongNo ratings yet
- Project Pre-Initiation and InitiationDocument9 pagesProject Pre-Initiation and InitiationAnh Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Psy4v90.002.09f Taught by Cathie Alexander (Csa033000)Document9 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Psy4v90.002.09f Taught by Cathie Alexander (Csa033000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet