Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Division of A Line-Segment
Uploaded by
Parvez Alam Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views13 pagesThis document provides instructions for dividing a line segment into equal parts and constructing regular polygons like pentagons, hexagons, and heptagons. It explains how to:
1) Divide a line segment into a given number of equal parts by drawing parallel lines through points set off at equal intervals.
2) Construct regular polygons by drawing circles with radii equal to the polygon's sides and locating intersection points to form the sides.
3) Specifically, it outlines different methods for constructing a regular pentagon, such as using angle or distance relationships between the sides and diagonals.
Original Description:
Original Title
Geometrical Construction
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides instructions for dividing a line segment into equal parts and constructing regular polygons like pentagons, hexagons, and heptagons. It explains how to:
1) Divide a line segment into a given number of equal parts by drawing parallel lines through points set off at equal intervals.
2) Construct regular polygons by drawing circles with radii equal to the polygon's sides and locating intersection points to form the sides.
3) Specifically, it outlines different methods for constructing a regular pentagon, such as using angle or distance relationships between the sides and diagonals.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views13 pagesDivision of A Line-Segment
Uploaded by
Parvez Alam KhanThis document provides instructions for dividing a line segment into equal parts and constructing regular polygons like pentagons, hexagons, and heptagons. It explains how to:
1) Divide a line segment into a given number of equal parts by drawing parallel lines through points set off at equal intervals.
2) Construct regular polygons by drawing circles with radii equal to the polygon's sides and locating intersection points to form the sides.
3) Specifically, it outlines different methods for constructing a regular pentagon, such as using angle or distance relationships between the sides and diagonals.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
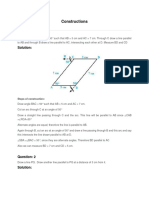
Division of a Line-segment
To divide a given straight
line-segment into any
numbers of equal parts
Let AB be a given line-
segment to be divided into,
say, seven equal parts.
A line-segment AC of any
length is drawn inclined at
any convenient angle to the
line-segment AB
(preferably an acute angle).
From point A and along the
line-segment AC, set-off
with a divider seven equal
divisions of any
7convenient length
Draw a line joining B and 7.
Division of a Line-segment
• Now with the aid of the
two set squares or
alternatively, by setting
the angle of the mini-
drafter equal to the
A7B, draw lines through
1, 2, 3, etc, parallel to B7
and intersecting the line-
segment AB at points 1’,
2’, 3’, etc., thus dividing it
into 7 equal parts.
Division of a Line-segment
Lines parallel to a
given line can be
drawn by constructing
angles equal to
A7B at points 1, 2, 3,
etc. with the aid of
compass.
Drawing Regular Polygons
Draw a line AB equal
to the given length.
At B, draw a line BP
perpendicular and
equal to AB.
Draw a line joining A
with P.
With centre B abd
radius AB, draw the
quadrant AP.
Drawing Regular Polygons
Draw the
perpendicular bisector
of AB to intersect the
straight line AP in
point 4 and the arc
AP in point 6.
A square of a side
equal to AB can be
inscribed in the circle
drawn with center 4
and radius A4.
Drawing Regular Polygons
A regular hexagon of a
side equal to AB can be
inscribed in a circle drawn
with centre 6 and radius
A6.
The mid-point 5 of the
line 4-6 is the centre of
the circle of radius A5 in
which a regular pentagon
of side equal to AB can
be inscribed.
Drawing Regular Polygons
To locate centre 7 of a
regular heptagon of side
AB, step-off a division 6-7
equal to the division 5-6.
With centre 7 and radius
equal to A7, draw a circle.
Starting from B, cut it in
seven equal divisions
with radius equal to AB.
Draw lines BC, CD, etc.
to complete the
heptagon.
Regular polygons of any
number of sides can be
drawn be drawn by this
method.
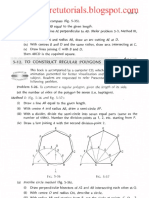
Drawing Regular Pentagon
Draw a line AB equal to
the given length.
Bisect AB in point C.
Draw a line BD
perpendicular and equal
to AB.
With centre C and radius
CD, draw an arc to
intersect the line AB-
produced at E.
AE is the length of the
diagonal of the pentagon
Drawing Regular Pentagon
Therefore, with A as
centre and radius AB,
draw an arc
intersecting the arc
drawn with centre B
and radius AE at R.
Again, with centre A
and radius AE, draw
an arc intersecting the
arc drawn with centre
B and radius AB at P.
Drawing Regular Pentagon
With centres A and B
and radius AE, draw
arcs intersecting each
other at Q.
Draw lines BP, PQ,
QR and RA, thus
completing the
regular pentagon.
Drawing Regular Pentagon
Draw a line AB equal to
the given length.
With centre A and radius
AB, describe a circle-1.
With centre B and the
same radius; describe a
circle-2 cutting circle-1 at
C and D.
With centre C and the
same radius, draw an arc
to cut circle-1 at E and
circle-2 at F respectively.
Drawing Regular Pentagon
Draw a perpendicular
bisector of line AB to cut
arc EF at G.
Draw a line EG and
produce it to cut circle-2
at P.
Draw a line FG and
produce it to cut the
circle-1 at R.
With P and R as centres
and AB as radius, draw
arcs intersecting each
other at Q.
Drawing Regular Pentagon
Draw lines BP, PQ,
QR and RA, thus
completing the
regular pentagon.
You might also like
- Construction of Plane ShapesDocument17 pagesConstruction of Plane Shapesblankfail75% (4)
- Chapter 3 Geometric ConstructionDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Geometric ConstructionYohannis Reta100% (1)
- Drafting: Geometric Construction: Straight LinesDocument25 pagesDrafting: Geometric Construction: Straight LinesVeena ReddyNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Constructions Ppt2Document18 pagesGeometrical Constructions Ppt2coolba442No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Geometric ConstructionsDocument26 pagesLecture 3 - Geometric Constructionsjmensah67No ratings yet
- MCE 101 Lesson 1Document18 pagesMCE 101 Lesson 1Adebanjo AbdulbasitNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drowing Chapter 4Document33 pagesEngineering Drowing Chapter 4DT artNo ratings yet
- Excercise 1Document4 pagesExcercise 1kevs balacanaoNo ratings yet
- Week 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Document4 pagesWeek 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Muhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Geometric Construction - LinesDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Geometric Construction - LinesMat HarzickNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering DrawingDocument4 pagesBasic Engineering DrawingAldrean TinayaNo ratings yet
- Ce 100: Civil Engineering Drawing: Lecture - 2Document58 pagesCe 100: Civil Engineering Drawing: Lecture - 2Muhammad Ridwanul IslamNo ratings yet
- Geometrical DrawingDocument31 pagesGeometrical Drawingnormanjames966No ratings yet
- GRE Lecture 3 Geometric ConstructionDocument12 pagesGRE Lecture 3 Geometric ConstructionPrecious SundayNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument34 pagesConstructionsMohammed RamadanNo ratings yet
- Construction VisitDocument5 pagesConstruction VisitVino PrabaNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionDocument73 pagesGeometric Constructionmauvitz.alfoughreNo ratings yet
- And Eb Are Divided Into Two Equal Parts in The Same Manner, The Straight Line AB Thus BeingDocument10 pagesAnd Eb Are Divided Into Two Equal Parts in The Same Manner, The Straight Line AB Thus BeingtutuoluNo ratings yet
- Basic Geometric ConstructionsDocument48 pagesBasic Geometric ConstructionsMuhammad Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document4 pagesLecture 5abdul raoufNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Geometrical ConstructionDocument16 pagesTopic 2: Geometrical ConstructionEmir Emir SyaminNo ratings yet
- Engg DrawingDocument29 pagesEngg DrawingKarthik CruiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Mec132Document23 pagesChapter 2 - Mec132Hakimi MohdNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Construction: AE EB ABDocument2 pagesGeometrical Construction: AE EB ABKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 1Document65 pagesGeometric Construction 1Pao YapNo ratings yet
- Level 3 FinalDocument274 pagesLevel 3 FinalRas RNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument11 pagesConstructionsSripriyan DandayuthapaniNo ratings yet
- Cam-And-Follower ppt-40-48Document9 pagesCam-And-Follower ppt-40-48Lakshmi Narayana SNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionDocument60 pagesGeometric ConstructionKim Kenneth AsiaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Solution For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 PDFDocument8 pagesNcert Exemplar Solution For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 PDFYashawanth am Yashawanth amNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8.1 Geometric ConstructionDocument26 pagesLecture 8.1 Geometric ConstructionIriama RobertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 ContructionsDocument25 pagesChapter 17 ContructionsNasir SohailNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 11 ConstructionDocument11 pagesCBSE Test Paper 01 Chapter 11 Constructionrai venugopalNo ratings yet
- A NGLEDocument8 pagesA NGLEYashita JainNo ratings yet
- ES 1 04 - How To Draw Regular Polygons PDFDocument6 pagesES 1 04 - How To Draw Regular Polygons PDFchristie MerloinNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Constructions WatermarkedDocument26 pagesExercise Solution of Constructions WatermarkediTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- JSS2 Second Term Basic Technology NoteDocument17 pagesJSS2 Second Term Basic Technology NoteJohn EgbongNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 2Document84 pagesGeometric Construction 2juncos0729100% (1)
- Geometric Construction 1Document78 pagesGeometric Construction 1juncos0729No ratings yet
- Circumference of CircleDocument3 pagesCircumference of Circlefazal ahmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 ConstructionDocument20 pagesChapter 17 ConstructionMann GosarNo ratings yet
- Geometrical ConstructionDocument16 pagesGeometrical ConstructionYaminNo ratings yet
- ConstructionsDocument3 pagesConstructionsQSQFNo ratings yet
- Angle - Chasing J y - Guo Dec21Document4 pagesAngle - Chasing J y - Guo Dec21Jason Wenxuan MIAONo ratings yet
- Jeep 210Document6 pagesJeep 210BHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- X CLASS-Similar Triangles ConstructionsDocument5 pagesX CLASS-Similar Triangles ConstructionstetalichanduNo ratings yet
- Latitude and DepartureDocument2 pagesLatitude and DeparturearuncivilengineerNo ratings yet
- Constructions PDFDocument5 pagesConstructions PDFshafee ul ahmed soudagarNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)Document25 pagesSolution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)rai venugopalNo ratings yet
- Unit D Geometric Construction PowerpointDocument34 pagesUnit D Geometric Construction PowerpointShiela Fherl S. BudionganNo ratings yet
- Geometric ConstructionsDocument9 pagesGeometric Constructionsapi-262621710No ratings yet
- Geometric Construction 1Document18 pagesGeometric Construction 1aryanNo ratings yet
- Simple Geometrical Constructions (Part 1)Document19 pagesSimple Geometrical Constructions (Part 1)SundayNo ratings yet
- ME 111 Engineering Drawing: Geometric Construction-IDocument53 pagesME 111 Engineering Drawing: Geometric Construction-IAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Geometrical ConstractionDocument38 pagesLecture 2 - Geometrical Constractionmmarybenson11No ratings yet
- 13 Ellipse3 130518104245 Phpapp02Document9 pages13 Ellipse3 130518104245 Phpapp02Chand RajNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01-Feb-2021Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 01-Feb-2021Shyam Shankar DasNo ratings yet
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- Chap - TrigonometryDocument64 pagesChap - TrigonometrybinzakerzawadNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.1: AnswersDocument16 pagesExercise 1.1: AnswersNICKOLAJNo ratings yet
- 30-1-3 Maths StandardDocument11 pages30-1-3 Maths StandardMurliNo ratings yet
- X - Cbse - Maths - Material - Unit Test - IVDocument14 pagesX - Cbse - Maths - Material - Unit Test - IVanzhiaxbNo ratings yet
- Presentation Output: Learning Task 7: Photo Conic SectionsDocument28 pagesPresentation Output: Learning Task 7: Photo Conic Sectionsjaypee sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Formula Matematik PMRDocument4 pagesFormula Matematik PMRWaheeda WaheeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsRanjitha SabapathyNo ratings yet
- Area Extension QuestionsDocument10 pagesArea Extension QuestionsBob CrossNo ratings yet
- Geometry Unit Study GuideDocument5 pagesGeometry Unit Study Guidemishi19No ratings yet
- S Puiching01 f3Document7 pagesS Puiching01 f3Llosemi LsNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRIA - FormularioDocument5 pagesGEOMETRIA - FormularioGaspare CiaccioNo ratings yet
- IB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8Document62 pagesIB Grade 9 Math Book-Chapter8aa1cc2100% (3)
- EASA Part 66 Module 1 MathematicsDocument14 pagesEASA Part 66 Module 1 MathematicsHussainAhmed100% (1)
- Arthur L.loeb - Space StructuresDocument201 pagesArthur L.loeb - Space Structureslazar_50100% (1)
- Review: ME 119: Engineering Graphics Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument30 pagesReview: ME 119: Engineering Graphics Department of Mechanical Engineeringamar BaroniaNo ratings yet
- UPSEE Sample Papers 4 (UPSEE Maths Question Paper 2)Document6 pagesUPSEE Sample Papers 4 (UPSEE Maths Question Paper 2)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras WorksheetDocument4 pagesPythagoras Worksheetdelta charlieNo ratings yet
- Maths TrianglesDocument20 pagesMaths TrianglesRajesh BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Vector PracticeDocument14 pagesVector Practicecookie1414No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020 - 2021 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument11 pagesMathematics: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020 - 2021 Surface Areas and VolumesDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- BOLYAI Non-Euclidean GeometryDocument9 pagesBOLYAI Non-Euclidean GeometryBiro Imre LeventeNo ratings yet
- Railway Recruitment Board Arithmatic Model Question and Answer No 1Document7 pagesRailway Recruitment Board Arithmatic Model Question and Answer No 1shibdutt1No ratings yet
- Math-9 LAS Q3 Week-1Document7 pagesMath-9 LAS Q3 Week-1Bern BeybieNo ratings yet
- Volume of A CylinderDocument8 pagesVolume of A CylinderAyeola RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Level - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 15 Time: 25 Min.: o RC FDL Izdkj DK GKSXKDocument7 pagesLevel - 2 & 3 Questions: 25 Exercise - 15 Time: 25 Min.: o RC FDL Izdkj DK GKSXKNaga Chalapathi AripakaNo ratings yet
- Soal MathDocument3 pagesSoal MathNemsi Prisda TampubolonNo ratings yet
- 15 November 2020 SSC CGL MAINS MATHS ALL QUESTIONSDocument9 pages15 November 2020 SSC CGL MAINS MATHS ALL QUESTIONSNITINNo ratings yet
- Waverley College Year 7 Mathematics Yearly Examination Term 4 - 2013 (Past Paper)Document22 pagesWaverley College Year 7 Mathematics Yearly Examination Term 4 - 2013 (Past Paper)AstraX EducationNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Proving Quadrilateral PropertiesDocument27 pages4.5 Proving Quadrilateral PropertiesHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet