Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rapid Prototyping Definition and Process Chain
Uploaded by
Pawan Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views10 pagesRP Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRP Introduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
144 views10 pagesRapid Prototyping Definition and Process Chain
Uploaded by
Pawan SharmaRP Introduction
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Lecture :Rapid prototyping
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 1
Dr. Pawan Sharma
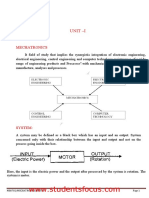
Prototyping
A general definition of a prototype
Prototyping or model making is one of the important steps to finalize
a product design. It helps in conceptualization of a design. Before the
start of full production a prototype is usually fabricated and tested.
Manual prototyping by a skilled craftsman has been an age-old
practice for many centuries.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 2
Dr. Pawan Sharma
Second phase of prototyping started around mid-1970s, when a soft
prototype modeled by 3D curves and surfaces could be stressed in
virtual environment, simulated and tested with exact material and
other properties.
Third and the latest trend of prototyping, i.e., Rapid Prototyping (RP)
by layer-by-layer material deposition, started during early 1980s with
the enormous growth in Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing
(CAD/CAM) technologies.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 3
Dr. Pawan Sharma
Types of Prototypes
The general definition of the
prototype contains three aspects
of interests:
(1) the implementation of the
prototype; from the entire
product (or system) itself to its
subassemblies and
components,
(2) The form of the prototype;
from a virtual prototype to a
physical prototype and
(3) The degree of the
approximation of the
prototype; from very rough
representation to exact
replication of the product.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 4
Dr. Pawan Sharma
What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping (RP) is a term encompassing a variety of
processes used to fabricate models and prototype parts for
products using CAD data from computer models.
RP most commonly refers to a set of processes that utilize 3D
CAD data to create three-dimensional prototype parts, but the
term can also refer to automated processes that utilize 2D CAD
data to create prototype parts from sheet materials.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 5
Dr. Pawan Sharma
The importance of being Rapid
The term ‘rapid’ is used to describe these processes for several
reasons:
They are able to fabricate prototype parts in hours, rather than the
days or weeks required using traditional processes.
They facilitate the rapid production of prototyping tooling for use
with more traditional prototype-making processes.
For certain applications, they can also be used for the
manufacture of parts, bypassing the tooling processes required
for some conventional manufacturing processes.
The benefits of RP include potential cost and time savings during
product development, the physical evaluation of parts, improved
quality control, earlier discovery of errors during product
development, reduced requirement for changes to production
tooling and, for certain materials and applications, even the
potential to remove the need for tooling altogether.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 6
Dr. Pawan Sharma
The RP wheel depicting the four major aspects of RP
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 7
Dr. Pawan Sharma
Time-Compression technique
Time-Compression Engineering (TCE) is also known as
Concurrent Engineering.
The main enabling technology behind TCE is 3D CAD
modelling.
Concurrency in performing different design and
manufacturing activities presents an opportunity to compress
the overall product development time whilst opening up
possibilities to be creative by providing more time for design
iterations
Concurrent engineering environments have evolved
considerably during the last few years to integrate 3-D
modelling with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM),
computer-aided engineering (CAE), rapid prototyping and
manufacturing, and a number of other applications.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 8
Dr. Pawan Sharma
The 3-D model becomes a central component of the whole
product or project information base, so that in all design, analysis
and manufacturing activities the same data are utilized.
There is no duplication or possibility for misunderstanding.
Product information captured in this way can be copied and re-
used; it is readily available for different downstream applications.
Three-dimensional models and virtual prototypes allow most
problems with fitting to become obvious early in the product
development process.
Assemblies can be verified for interference.
Structural and thermal analysis can be performed on the same
models, employing CAE applications as well as simulating
downstream manufacturing processes.
Ultimately, these very accurate and data-rich models can be taken
directly to RP and CAM applications, speeding up process
planning and in some cases eliminating the need for drawings.
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 9
Dr. Pawan Sharma
Rapid prototyping Basics and process chain By
06-09-2019 10
Dr. Pawan Sharma
You might also like
- Mech Rapid Prototyping Report PDFDocument16 pagesMech Rapid Prototyping Report PDFAthisayaraj RajNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Rapid Prototyping For Product DevelopmentDocument15 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Rapid Prototyping For Product DevelopmentAlain GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem Rapid Prototype MANUAL.... 1Document4 pages7th Sem Rapid Prototype MANUAL.... 1Utsaw PandyaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping Technical Paper on Additive Manufacturing MethodsDocument16 pagesRapid Prototyping Technical Paper on Additive Manufacturing MethodsAmey NaikNo ratings yet
- Rapid PrototypingDocument17 pagesRapid PrototypingAnkitNo ratings yet
- A Virtual Prototyping System For Rapid Product Development: S.H. Choi, A.M.M. ChanDocument12 pagesA Virtual Prototyping System For Rapid Product Development: S.H. Choi, A.M.M. Chanbonmarche28No ratings yet
- Product Manufacturing and Cost Estimating using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesFrom EverandProduct Manufacturing and Cost Estimating using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Prototyping and Rapid PrototypingDocument5 pagesPrototyping and Rapid Prototypingatma_namasteNo ratings yet
- Future of Manufacturing Technology RapidDocument10 pagesFuture of Manufacturing Technology Rapidsreedhara g pNo ratings yet
- Rapid PrototypingDocument21 pagesRapid Prototypingapi-3758470100% (1)
- Selected Engineering ProblemsDocument6 pagesSelected Engineering ProblemsDiscord YtNo ratings yet
- Capd Course AllDocument352 pagesCapd Course Allankitjoiya123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Rapid Prototyping: Unit 4Document26 pagesIntroduction To Rapid Prototyping: Unit 4Joeb DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Protoyping Techinques and Advancement in Biomedical ApplicationsDocument1 pageRapid Protoyping Techinques and Advancement in Biomedical Applicationskunadeep samantroyNo ratings yet
- Guide to Rapid Prototyping for Product DevelopmentDocument13 pagesGuide to Rapid Prototyping for Product Developmentspiblu100% (1)
- Rapid PrototypingDocument17 pagesRapid PrototypingRafael Mena FredesNo ratings yet
- Seminar SawDocument36 pagesSeminar SawNimesh C SNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document44 pagesUnit - 1rajeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RPDDocument6 pagesIntroduction To RPDAmeya BandekarNo ratings yet
- Application of CAD/CAE & Rapid Prototyping Technology in Medical FieldDocument5 pagesApplication of CAD/CAE & Rapid Prototyping Technology in Medical FieldRizwanNo ratings yet
- Model Based Environment: A Practical Guide for Data Model Implementation with Examples in PowerdesignerFrom EverandModel Based Environment: A Practical Guide for Data Model Implementation with Examples in PowerdesignerNo ratings yet
- Software Prototyping - WikipediaDocument14 pagesSoftware Prototyping - WikipediaTrữ LưuNo ratings yet
- Does Prototyping Help or Hinder Good Requirements? What Are the Best Practices for Using This Method?From EverandDoes Prototyping Help or Hinder Good Requirements? What Are the Best Practices for Using This Method?No ratings yet
- Rapid PrototypingDocument22 pagesRapid PrototypingMohammed SameelNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering New Approach (Traditional and Agile Methodologies)From EverandSoftware Engineering New Approach (Traditional and Agile Methodologies)No ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering Semester 2 Session 2012/2013 PrototypingDocument4 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering Semester 2 Session 2012/2013 Prototypingdanish91No ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping Technology GuideDocument17 pagesRapid Prototyping Technology GuideJoinal Hussain TapadarNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Rapid PrototypingDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Rapid Prototypingafnhbijlzdufjj100% (1)
- Reading - Types of PrototypesDocument4 pagesReading - Types of Prototypesme.alsiriNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Student NotesDocument90 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Student NotesUdayaKumar100% (1)
- The Development of A Process Map For The Construction SectorDocument11 pagesThe Development of A Process Map For The Construction SectorMICHAEL TADESSENo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument26 pagesAdditive ManufacturingSonia rajpuroitNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Approach For Predictive Maintenance Using Digital TwinDocument7 pagesHybrid Approach For Predictive Maintenance Using Digital TwinSheron SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Product Performance Evaluation using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesFrom EverandProduct Performance Evaluation using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesNo ratings yet
- Implementing the Stakeholder Based Goal-Question-Metric (Gqm) Measurement Model for Software ProjectsFrom EverandImplementing the Stakeholder Based Goal-Question-Metric (Gqm) Measurement Model for Software ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping Reduces Healthcare CostsDocument6 pagesRapid Prototyping Reduces Healthcare CostsMoheb HannaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Rapid PrototypingDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Rapid Prototypingc9qb8gy7100% (1)
- Aeb4101 Engineering and Design: Module - 3Document14 pagesAeb4101 Engineering and Design: Module - 3saiNo ratings yet
- Prototyping: Prototyping Is The Process of Quickly Putting Together A Working Model (ADocument37 pagesPrototyping: Prototyping Is The Process of Quickly Putting Together A Working Model (ATawanda Joe MamhizaNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Unit 1Document37 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Unit 1micotay599No ratings yet
- Center of ExcellenceDocument10 pagesCenter of ExcellencekhayatNo ratings yet
- Preface: Freeform Fabrication, Desktop Manufacturing or Layer Manufacturing TechnologiesDocument3 pagesPreface: Freeform Fabrication, Desktop Manufacturing or Layer Manufacturing TechnologiesZaheer AhamedNo ratings yet
- SRS For Online Pizza StoreDocument49 pagesSRS For Online Pizza StoreR_Arpan60% (10)
- Software PrototypingDocument13 pagesSoftware PrototypingQuốc Thịnh UngNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Rapid PrototypingDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Rapid Prototypingea59j0hq100% (1)
- Presentation On FDocument9 pagesPresentation On FVijay EsportsNo ratings yet
- Research Process On Software Development ModelDocument9 pagesResearch Process On Software Development ModelRuth amelia GNo ratings yet
- System Lifecycle Management: Engineering Digitalization (Engineering 4.0)From EverandSystem Lifecycle Management: Engineering Digitalization (Engineering 4.0)No ratings yet
- RPDocument22 pagesRPshubhamukey628No ratings yet
- The Rapid Tooling Testbed: A Distributed Design-For-Manufacturing SystemDocument11 pagesThe Rapid Tooling Testbed: A Distributed Design-For-Manufacturing SystemDiscord YtNo ratings yet
- Software Pro To TypingDocument19 pagesSoftware Pro To TypingGodwin Rose Samuel WNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Approach For Predictive Maintenance Using Digital TwinDocument7 pagesHybrid Approach For Predictive Maintenance Using Digital TwinSheron SisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument56 pagesUnit 1 PDFDaily SerialsNo ratings yet
- The Methodology of Patternless Casting Manufacturing: Wei-Yuan DzanDocument8 pagesThe Methodology of Patternless Casting Manufacturing: Wei-Yuan DzanLaural MarshallNo ratings yet
- Case Study Workshop Technology 2Document23 pagesCase Study Workshop Technology 2AnnaIzzatNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping IntroductionDocument90 pagesRapid Prototyping Introductionharsh vaghelaNo ratings yet
- Requirements Engineering in Scrum Framework ExplainedDocument7 pagesRequirements Engineering in Scrum Framework ExplainedCarlos QueirosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ADMDocument43 pagesUnit 1 ADMCHINTAKINDI VENKATAIAH RAGHUVAMSHINo ratings yet
- Design For Manufacturing and Assembly (Dfma) Technique Applicable For Cost Reduction - A ReviewDocument6 pagesDesign For Manufacturing and Assembly (Dfma) Technique Applicable For Cost Reduction - A ReviewTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Shuttle Bus Timetable JNU CampusDocument2 pagesShuttle Bus Timetable JNU CampusPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Courses Offered in The Semester During I Semester 2015-16Document70 pagesCourses Offered in The Semester During I Semester 2015-16Pawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Delhi: Semester Schedule For I Semester 2015-16 (Revised Aug 5, 2015)Document2 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Delhi: Semester Schedule For I Semester 2015-16 (Revised Aug 5, 2015)Pawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- RPD 1Document1 pageRPD 1Pawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- RPD 1Document1 pageRPD 1Pawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- RPD 1Document1 pageRPD 1Pawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fe For CompDocument14 pagesFe For CompPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM and Its IntegrationDocument15 pagesCAD CAM and Its IntegrationPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anna Notes 1 PDFDocument39 pagesAnna Notes 1 PDFPawan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 2: Manual and CAD Plotting of Lot by Technical Descriptions and Plane Coordinates MethodDocument9 pagesExercise No. 2: Manual and CAD Plotting of Lot by Technical Descriptions and Plane Coordinates Methodokello denishNo ratings yet
- Multiprocessor Architecture and ProgrammingDocument20 pagesMultiprocessor Architecture and Programmingவெ. விஷ்வாNo ratings yet
- F5 APM Day Wise 4 DaysDocument7 pagesF5 APM Day Wise 4 DaysAman VermaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer and NetworkSecurityDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Computer and NetworkSecuritySahib SodhiNo ratings yet
- Punit Training Report 2Document11 pagesPunit Training Report 22K19-EC-004 Aakash SoniNo ratings yet
- DG Mobility Controllers Deployment Models 5.0 VRDDocument126 pagesDG Mobility Controllers Deployment Models 5.0 VRDsujeet_hatNo ratings yet
- MV-WEB v6 5 Database SchemaDocument12 pagesMV-WEB v6 5 Database SchemaHugo ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Linux Booting ProcessDocument18 pagesLinux Booting ProcessPrashant RawatNo ratings yet
- MSP 430 DatasheetDocument78 pagesMSP 430 DatasheetKarthik AnanthamNo ratings yet
- Conduct Test On The Installed Computer SystemDocument11 pagesConduct Test On The Installed Computer SystemJoseantonioynigo CerdaNo ratings yet
- LinuxSDK DocumentDocument19 pagesLinuxSDK DocumentJoao ThomeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For MSC Big Data Analytics Entrance ExamDocument8 pagesSyllabus For MSC Big Data Analytics Entrance Examahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PyhtonDocument7 pagesCh1 PyhtonMohamedNo ratings yet
- Amanda Lowery Resume 10 13 20Document1 pageAmanda Lowery Resume 10 13 20api-305345905No ratings yet
- MSCSE Course ScheduleDocument6 pagesMSCSE Course Schedulevl coderNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Advantage V6 I2 2012Document56 pagesANSYS Advantage V6 I2 2012j_c_garcia_dNo ratings yet
- Interface and Base TablesDocument34 pagesInterface and Base TablesMohinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Specialized Lookup Examples (Excell)Document19 pagesSpecialized Lookup Examples (Excell)FrozenNo ratings yet
- LC5 PDFDocument92 pagesLC5 PDFGanesh VhanagadeNo ratings yet
- Stata 1Document45 pagesStata 1Chu BundyNo ratings yet
- ONLINE BIDDING ZONEDocument22 pagesONLINE BIDDING ZONEKirpal RaviNo ratings yet
- Distributed Databases AND Client-Server ArchitechuresDocument73 pagesDistributed Databases AND Client-Server ArchitechurestvsnNo ratings yet
- C Celect1Document17 pagesC Celect1anupcoolrocksNo ratings yet
- Pentesting Magazine - 2022-05 - Open-Source Pentesting ToolkitDocument109 pagesPentesting Magazine - 2022-05 - Open-Source Pentesting ToolkitjesusNo ratings yet
- BeamTool User ManualDocument254 pagesBeamTool User ManualNguyen Duc DungNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Sensors in The Autoclave-Modelling and Implementation of The Iot Steam Sterilization Procedure CounterDocument17 pagesSensors: Sensors in The Autoclave-Modelling and Implementation of The Iot Steam Sterilization Procedure CounterUsman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Black Box Testing GuideDocument28 pagesBlack Box Testing GuidevidyaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Unified Method (OUM) Implement Core WorkflowDocument19 pagesOracle Unified Method (OUM) Implement Core WorkflowsuchaiNo ratings yet
- Pipeliner Sales CRM Complete User Guide PDFDocument166 pagesPipeliner Sales CRM Complete User Guide PDFpalsNo ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument69 pagesPython BasicsSecond BooksNo ratings yet