Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Marrow Puncture & Transplantation: Prof. Dr. Dr. Adi Priyana SPPK Bag. Patologi Klinik
Uploaded by
elsie levina aisha lourent0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views15 pagesTransplatasi sumsum tulang
Original Title
Transplantasi Sst
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTransplatasi sumsum tulang
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views15 pagesBone Marrow Puncture & Transplantation: Prof. Dr. Dr. Adi Priyana SPPK Bag. Patologi Klinik
Uploaded by
elsie levina aisha lourentTransplatasi sumsum tulang
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Bone marrow puncture &
transplantation
Prof. Dr. dr. Adi Priyana SpPK
Bag. Patologi klinik
Transplantasi sst
Prosedur medis untuk sst yang rusak diganti
dengan sel induk sst yang baru.
Jenis kanker darah yang umum diobati dengan
transplantasi sst adalah lekemia dan limfoma.
Efek samping yang sering: mual, muntah,
kerusakan hati, perdarahan, infeksi, rambut
rontok.
Prosesnya disebut harvesting (panen).
Diusahakan donor berasal dari saudara dekat
sehingga dapat dihindari proses graft versus host
disease (GVHD).
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
are now well-accepted procedures for
evaluation both the cellularity of the marrow and the
nature of the cells present. Although sternum (breast
bone) is the traditional site for bone marrow aspiration (but
not for biopsy), our preferred site is the posterior Iliac crest
(the hip bone) because of ease and safety and the fact
that the posterior Iliac crest is usually quite cellular.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Hemophilia and other Clotting disorder
Previous Radiation Therapy site.
INDICATIONS:
Unexplained anemia. Decreased presence of red blood cells,
the cause of which may be a variety of reasons, the most
common being deficiency of iron stores and Myelodysplasia.
Thrombocytopenia. Decreased production of platelets, I.T.P.
(or Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia) being most
common. Physicians determine if adequate number of platelet
producing cells (Megakaryocytes) are present in the bone
marrow.
Pancytopenia. Decreased production of all three cell lines,
differentiates relative involvement of red cell, white cell and
platelet lines in a disease.
Leukemia, Lymphoma, or Myeloma (helpful in diagnoses,
staging and determining results of the treatment)
Lympho and Myeloproliferative disorders.
Metastatic disease. To determine if bone marrow is involved
with cancers from other sites.
Chromosomal analyses
Unusual infection. Such as Tuberculoses, Fungi and Fevers of
Unknown Origin
What are ‘Stem Cells’?
Stem cells are uncommitted, self renewing
cells, able to differentiate into many different
kinds of tissue.
TWO different sources of stem cells
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC): Early embryonic
(day 5-8 blastocyst cells) self renewing cells
‘Adult’ or Somatic stem cells (ASC): a minor
population of self renewing cells found in
most tissues
Adult Stem Cells (ASC)
Problems with ESC mean that:
ASC are the only practical approach to regenerative
therapy
NO ETHICAL PROBLEMS
Patients’ own cells can be used after expansion in
vitro: no rejection, therefore no immunosuppressive
drugs needed.
Source of Embryonic Stem Cells
Source: Scientific American, July 2005
Adult Stem Cells to Treat CVD
Current status of treatments
Two different approaches to
therapy:
1) commercial, uncontrolled, for
profit
2) clinical trials, controlled, not
for profit
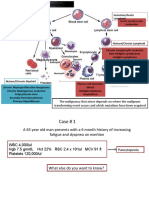
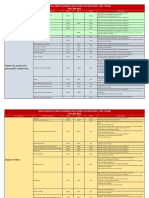
Common Indications for Stem Cell Transplantation
Autologous Transplantation Allogeneic Transplantation
Malignant Disorders Nonmalignant Malignant Disorders Nonmalignant Disorders
Disorders
Multiple myeloma Autoimmune AML Aplastic Anemia
Neuroblastoma disorders Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Fanconi anemia
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Amyloidosis Hodgkin disease SCID
Hodgkin disease ALL Thalassemia major
AML CML Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Medulloblastoma MDS Sickle cell anemia
Germ-cell tumors Multiple myeloma Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
CLL Osteopetrosis
Inborn errors of metabolism
Autoimmune disorders
You might also like
- Stem Cell BookDocument20 pagesStem Cell Bookbabasolai83No ratings yet
- Lecture 33-LeukemiaDocument21 pagesLecture 33-LeukemiaYasir KareemNo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenDocument95 pagesProf. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenAarpit PatwaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors & TreatmentDocument28 pagesLeukemia Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors & TreatmentGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarNo ratings yet
- Simulators of Malignancy in Bone MarrowDocument12 pagesSimulators of Malignancy in Bone Marrowlavisha.s.punjabiNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia: Dimas Bayu Tutik Harjianti A. FachruddinDocument41 pagesAcute Leukemia: Dimas Bayu Tutik Harjianti A. FachruddinFI 034 Mega Rahmawati MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Young Man with Bruising Diagnosed with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALLDocument4 pagesYoung Man with Bruising Diagnosed with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALLRayNo ratings yet
- Print - Acute Myeloid Leukaemia AML - NovDocument6 pagesPrint - Acute Myeloid Leukaemia AML - Novsiti fatimahNo ratings yet
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia and Acute Lmphocytic Leukemia: OccurrenceDocument12 pagesAcute Monocytic Leukemia and Acute Lmphocytic Leukemia: OccurrenceAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationDocument14 pagesHematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationFabLab EIUNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationDocument14 pagesHematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationFabLab EIUNo ratings yet
- Heme Malignancy Review 2020Document163 pagesHeme Malignancy Review 2020Anna StacyNo ratings yet
- AML Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocument6 pagesAML Pathophysiology and TreatmentChristine CollesNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia PathophysiologyChristine CollesNo ratings yet
- Hematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsDocument18 pagesHematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsAndre HawkNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationDocument47 pagesHaemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationPrashantTiwariNo ratings yet
- Kidapawan Doctors College Incorporated Bachelor of Science in Medical Technology Immunology & Serology Case StudyDocument8 pagesKidapawan Doctors College Incorporated Bachelor of Science in Medical Technology Immunology & Serology Case Studyrandiey john abelleraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument35 pagesMultiple Myeloma: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAina CempakaNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis and Clinical ApplicationDocument42 pagesHaemopoiesis and Clinical Applicationtamer273No ratings yet
- Current Diagnosis and Classification of Hematological MalignanciesDocument59 pagesCurrent Diagnosis and Classification of Hematological Malignanciesedel_herbityaNo ratings yet
- Leukemias, Lymphomas, MyelomaDocument45 pagesLeukemias, Lymphomas, MyelomaYesyNo ratings yet
- People'S College of Nursing and Research Center.: Submitted To Presented byDocument49 pagesPeople'S College of Nursing and Research Center.: Submitted To Presented byabhishek dadhichNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic System PathologyDocument78 pagesHematopoietic System PathologyNuhu SibaNo ratings yet
- DR - Agus. Current Diag and Class of Hematological Malig DR Agus FinalDocument46 pagesDR - Agus. Current Diag and Class of Hematological Malig DR Agus Finalbudi darmantaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Types, Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument26 pagesLeukemia Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentmeutia salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Myeloma Cancer: A Comprehensive Resource for Patients and FamiliesFrom EverandMultiple Myeloma Cancer: A Comprehensive Resource for Patients and FamiliesNo ratings yet
- Amlreview PDFDocument12 pagesAmlreview PDFMitaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Myeloproliferation, Myelodysplasia: Lita Septina Peyakit Dalam FK UMSUDocument47 pagesLeukemia Myeloproliferation, Myelodysplasia: Lita Septina Peyakit Dalam FK UMSUJr SparkNo ratings yet
- The Science of Cord Blood Stem Cells: An IntroductionDocument13 pagesThe Science of Cord Blood Stem Cells: An IntroductionSwati YugNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lecture 2nd CourseDocument128 pagesPathology Lecture 2nd CourseAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument41 pagesAnemiabekthyNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument91 pagesLeukemiaShadin SNo ratings yet
- Aa by AbdifatahDocument57 pagesAa by AbdifatahAbdifatah AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Research Essay Based On LeukemiaDocument5 pagesA Research Essay Based On LeukemiaPRIORITY SCHOLARNo ratings yet
- A Research Essay Based On Leukemia Student's Name University AffiliationDocument5 pagesA Research Essay Based On Leukemia Student's Name University AffiliationPRIORITY SCHOLARNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Dr. Isbandiyah SPPD Bag. Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Umm MalangDocument26 pagesLeukemia: Dr. Isbandiyah SPPD Bag. Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Umm MalangSemesta0% (1)
- Nursing Management For Patients With Hematology Problems PDFDocument44 pagesNursing Management For Patients With Hematology Problems PDFAnggie AnggriyanaNo ratings yet
- L4 LeukemiaDocument9 pagesL4 LeukemiaDrMariam DogerNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument40 pagesLeukemiaYeni Jesika SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - LecturioDocument17 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - LecturioCornel PopaNo ratings yet
- Patología de LeucocitosDocument25 pagesPatología de LeucocitosRicardo Castro MartínezNo ratings yet
- Disorders of BloodDocument3 pagesDisorders of BloodCondurache Ilie-AndreiNo ratings yet
- We are one world, one people despite our differencesDocument67 pagesWe are one world, one people despite our differencesEko PriyantoNo ratings yet
- Hematology Topics 16-20Document20 pagesHematology Topics 16-20Angelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Reviewers Topics 21 25Document13 pagesCompilation of Reviewers Topics 21 25Xed de VeyraNo ratings yet
- Anemia Lectures From Doll Very Well Covered in Pathoma Coberly Plasma Cell DyscrasiasDocument19 pagesAnemia Lectures From Doll Very Well Covered in Pathoma Coberly Plasma Cell DyscrasiasTeehee JonesNo ratings yet
- 17.hematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsDocument18 pages17.hematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsHafiz Idul FitranulNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Leukemia FinalDocument68 pagesAcute and Chronic Leukemia FinalHannah LeiNo ratings yet
- MielomaDocument4 pagesMielomaJefferson MorenoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Leukemia Lecture.Document47 pagesChronic Leukemia Lecture.sherifref3atNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, FinasimDocument96 pagesLeukemia: Dr. Suhaemi, SPPD, Finasimwie_wie_wieNo ratings yet
- Multiple myeloma symptoms and causes explainedDocument15 pagesMultiple myeloma symptoms and causes explainedjuanNo ratings yet
- MyeloProliferative DisordersDocument5 pagesMyeloProliferative DisordersMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Haematologic MalignanciesDocument18 pagesHaematologic MalignanciesMukesh SahooNo ratings yet
- "Leukemia": Dr. Meddy Setiawan, SPPDDocument23 pages"Leukemia": Dr. Meddy Setiawan, SPPDAldaka Yoga BaskaraNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument26 pagesLeukemiaochamocha100% (1)
- Myeloproliferative Disorders (Bhs Inggris)Document57 pagesMyeloproliferative Disorders (Bhs Inggris)Denny DedenNo ratings yet
- Adult Intussusception - A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis 2019Document10 pagesAdult Intussusception - A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis 2019吳醫師No ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation-2022Document138 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing Radiation-2022Waleed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Animal Testing ProsDocument6 pagesAnimal Testing ProsShalini KanganNo ratings yet
- Fam 1Document3 pagesFam 1novaNo ratings yet
- Individualized Neoantigen-Specific ImmunotherapyDocument16 pagesIndividualized Neoantigen-Specific ImmunotherapyEhed AymazNo ratings yet
- Lista de Dispositivos Medicos PrioritariosDocument20 pagesLista de Dispositivos Medicos PrioritariosEimyNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument2 pagesBreast Cancer Concept MapMaria Cristina100% (1)
- DOH Breast Cancer Guidelines FinalDocument123 pagesDOH Breast Cancer Guidelines Finalsupratimbiswas073380No ratings yet
- Radiation Therapy Case Study 2Document11 pagesRadiation Therapy Case Study 2api-278170649No ratings yet
- Problem Statement WORLD Cancer Afflicts All Communities WorldwideDocument30 pagesProblem Statement WORLD Cancer Afflicts All Communities Worldwidesalma0430100% (2)
- Manage Solitary Thyroid NodulesDocument6 pagesManage Solitary Thyroid NodulesSathiyamoorthy KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Reiki Science & ResearchDocument21 pagesReiki Science & ResearchGiritharanNaiduEsparanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology, Molecular Classification and WHO Grading of EpendymomaDocument5 pagesEpidemiology, Molecular Classification and WHO Grading of EpendymomaGeovanny OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Health in Your Hands by Devendra Vora, M.D.Document270 pagesHealth in Your Hands by Devendra Vora, M.D.Iftikhar Ahmad88% (40)
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1Hai AnhNo ratings yet
- Principii Psiho OncologieDocument16 pagesPrincipii Psiho OncologieCristina Tulba100% (1)
- Scientific African: Joachim M. Dotto, James S. ChachaDocument14 pagesScientific African: Joachim M. Dotto, James S. Chacharetno kusmaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CaseDocument53 pagesThyroid CaseKenisha HutsonNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyDocument9 pages7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyRajak Mohamed100% (6)
- Kajian Penggunaan Obat Kemoterapi Pada Pasien Leukemia Anak Di Rsud Abdul Wahab Sjahranie Kota SamarindaDocument8 pagesKajian Penggunaan Obat Kemoterapi Pada Pasien Leukemia Anak Di Rsud Abdul Wahab Sjahranie Kota SamarindaamandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 001 QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 001 Questionsjuan pablo escobarNo ratings yet
- Cancer Bathinda's Dubious DistinctionDocument2 pagesCancer Bathinda's Dubious DistinctionPardeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Sol Roberts: Shining As Bright As EverDocument5 pagesSol Roberts: Shining As Bright As EverAlicia ArteagaNo ratings yet
- Senior Project Paper FinalDocument5 pagesSenior Project Paper Finalapi-281742815No ratings yet
- DRUGS (Topotecan)Document2 pagesDRUGS (Topotecan)BARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Metabolic Reprogramming 2Document13 pagesMetabolic Reprogramming 222194No ratings yet
- A Clinically Relevant Gene Signature in Triple Negative and Basal-Like Breast CancerDocument16 pagesA Clinically Relevant Gene Signature in Triple Negative and Basal-Like Breast CancerAlexandra TeodorescuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Burzynski Antinewoplastons Cancer TreatmentDocument13 pagesDr. Burzynski Antinewoplastons Cancer TreatmentJo RoNo ratings yet
- Foreign Trade of The DPRK - 02 - 2019Document20 pagesForeign Trade of The DPRK - 02 - 2019StirlitzNo ratings yet
- Molecular Pathology of Endocrine Diseases - J. Hunt (Springer, 2010) WW PDFDocument268 pagesMolecular Pathology of Endocrine Diseases - J. Hunt (Springer, 2010) WW PDFMoldovan Tiberiu100% (1)