Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Refrigerator
Uploaded by
Vikram Porje0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
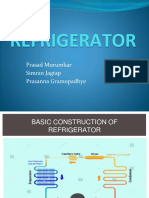
70 views12 pagesDomestic refrigerators use a refrigeration system to transfer heat from inside the fridge to the outside. The five basic components are the evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and refrigerant. The evaporator removes heat from products using the refrigerant. The compressor increases the refrigerant's pressure and temperature. The condenser extracts heat from the refrigerant to the outside air. The expansion valve reduces the refrigerant's pressure and temperature before it enters the evaporator. Common refrigerator motor issues include failure to start, running slower or with noise, and insufficient or sudden defrosting, which can be caused by problems like low voltage, overload, lack of refrigerant, or moisture in the system.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDomestic refrigerators use a refrigeration system to transfer heat from inside the fridge to the outside. The five basic components are the evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and refrigerant. The evaporator removes heat from products using the refrigerant. The compressor increases the refrigerant's pressure and temperature. The condenser extracts heat from the refrigerant to the outside air. The expansion valve reduces the refrigerant's pressure and temperature before it enters the evaporator. Common refrigerator motor issues include failure to start, running slower or with noise, and insufficient or sudden defrosting, which can be caused by problems like low voltage, overload, lack of refrigerant, or moisture in the system.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views12 pagesRefrigerator
Uploaded by
Vikram PorjeDomestic refrigerators use a refrigeration system to transfer heat from inside the fridge to the outside. The five basic components are the evaporator, compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and refrigerant. The evaporator removes heat from products using the refrigerant. The compressor increases the refrigerant's pressure and temperature. The condenser extracts heat from the refrigerant to the outside air. The expansion valve reduces the refrigerant's pressure and temperature before it enters the evaporator. Common refrigerator motor issues include failure to start, running slower or with noise, and insufficient or sudden defrosting, which can be caused by problems like low voltage, overload, lack of refrigerant, or moisture in the system.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
DOMESTIC REFRIGERATOR
INTRODUCTION
Principle
The basic principle of refrigeration is heat
transfer, that is, to remove heat from one
area (i.e. inside your fridge) and locate it to
another area (i.e. outside of your fridge).
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS
There are five basic components of a
refrigeration system, these are:
Evaporator
Compressor
Condenser
Expansion Valve
Refrigerant; to conduct the heat from the
product
In order for the refrigeration cycle to operate
successfully each component must be present
within the refrigeration system.
The Evaporator
To remove unwanted heat from the product,
via the liquid refrigerant.
To enable the transfer of heat, the
temperature of the liquid refrigerant must be
lower than the temperature of the product
being cooled.
The Compressor
To draw the low-temperature, low-pressure
vapor from the evaporator via the suction
line.
Transforms the vapor from a low-
temperature vapor to a high-temperature
vapor, in turn increasing the pressure.
The Condenser
To extract heat from the refrigerant to the
outside air.
As heat has to flow from the condenser to the
air, the condensation temperature must be
higher than that of the air, usually between
12°C and -1°C.
The Expansion Valve
Located at the end of the liquid line, before
the evaporator
The valve then reduces the pressure of the
refrigerant as it passes through the orifice,
which is located inside the valve.
On reducing the pressure, the temperature of
the refrigerant also decreases to a level below
the surrounding air.
SYMPTOMS CAUSES
Motor fails to start Blown fuses
Open thermostat
Burnt or shorted windings
Excessive overload
Motor runs slower Low voltage
Overload
Worn bearings
Motor does not start Low voltage
Overload
Defective electromagnetic relays
contacts being open
SYMPTOMS CAUSES
Motor runs with noise Shorted windings
Improperly connected poles
Too much end play
Motor runs but cooling is nil or No refrigerant gas in system
insufficient Completely choked capillary
Motor operates normally with Presence of moisture in
good cooling but defrosting starts refrigeration cycle
all of a sudden
SYMPTOMS CAUSES
Too much frosting around the High atmospheric humidity or
freezer steaming hot liquid stored
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Automatic Washer: Study Course (Belt Drive Models)Document24 pagesAutomatic Washer: Study Course (Belt Drive Models)plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Commercial Refrigeration Systems ExplainedDocument11 pagesCommercial Refrigeration Systems ExplainedBenjie flor CalayegNo ratings yet
- 4689 - Clivet WRAT 322Document1 page4689 - Clivet WRAT 322Roko0% (1)
- Design Calculation-ASME B31.4Document3 pagesDesign Calculation-ASME B31.4yudi50% (2)
- Automatic protection ensures safe operation of refrigeration compressorsDocument50 pagesAutomatic protection ensures safe operation of refrigeration compressorsAhmed SalemNo ratings yet
- The Four Types of Refrigeration Systems You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesThe Four Types of Refrigeration Systems You Need To KnowtakayNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power Department 4 YearDocument9 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Lab: Mansoura University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Power Department 4 YearKhaled HakimNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Introduction To Refrigeration SystemDocument9 pagesMODULE 1 Introduction To Refrigeration SystemBembem DelfinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Refrig PDFDocument17 pagesBasics of Refrig PDFHoàngViệtAnhNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshDocument34 pagesRefrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Essential Properties Required in A Refrigerant Are As FollowsDocument11 pagesEssential Properties Required in A Refrigerant Are As FollowssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System Problem and SolutionDocument29 pagesRefrigeration System Problem and SolutionAngel Rose AnongNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To Room and Central Air Conditioners: Last Updated: July 2015Document26 pagesComplete Guide To Room and Central Air Conditioners: Last Updated: July 2015QOBITNo ratings yet
- Rac PPT1.Document22 pagesRac PPT1.andu gashuNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration 1Document13 pagesRefrigeration 1Vishwanathan RishanthNo ratings yet
- 409 - 5 Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument104 pages409 - 5 Refrigeration & Air Conditioningisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator: Prasad Murumkar Simran Jagtap Prasanna GramopadhyeDocument13 pagesRefrigerator: Prasad Murumkar Simran Jagtap Prasanna GramopadhyeSHREYAS JOSHINo ratings yet
- Compressor Trouble Shooting Guide: Problem Cause SolutionDocument6 pagesCompressor Trouble Shooting Guide: Problem Cause SolutionVina SulistyaNo ratings yet
- Air Condition Refilling Automobile Ac SystamDocument11 pagesAir Condition Refilling Automobile Ac SystamMechanical DepartmentNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 RAC Servicing and MaintenanceDocument23 pagesMODULE 3 RAC Servicing and MaintenanceBembem DelfinNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of Cold Air Flow: EvaporatorDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram of Cold Air Flow: EvaporatorMario FabrisNo ratings yet
- My Freezer Isn't Freezing - HomeServe USADocument9 pagesMy Freezer Isn't Freezing - HomeServe USAAla SamuelNo ratings yet
- Guide to Welding ElectrodesDocument25 pagesGuide to Welding ElectrodesrajuNo ratings yet
- refrigerator common problemsDocument3 pagesrefrigerator common problemsMateo, Dale Vincent A.No ratings yet
- Household Refrigerators and FreezersDocument12 pagesHousehold Refrigerators and FreezersLuis Carlos PardoNo ratings yet
- Bohler Welding in Tool MakingDocument24 pagesBohler Welding in Tool MakingcfcshakerNo ratings yet
- Welding Soldering BrazingDocument100 pagesWelding Soldering BrazingMore YashNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document53 pagesCH 1huien ababuNo ratings yet
- CompressorDocument20 pagesCompressorS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Welding Electrodes GuideDocument1 pageStainless Steel Welding Electrodes GuideRajeev KhantwalNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Compressor Failure: Cause & Cure - Part 1Document5 pagesRefrigeration Compressor Failure: Cause & Cure - Part 1ADARSH GADDAMNo ratings yet
- Piping SolderingDocument33 pagesPiping SolderingKristian UretaNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant System Components and ControlsDocument16 pagesRefrigerant System Components and ControlssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arc WeldingDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Arc WeldingcfcshakerNo ratings yet
- Vibration Monitoring Techniques (CMDocument28 pagesVibration Monitoring Techniques (CMAhmed SalemNo ratings yet
- Kertas Penerangan 3Document23 pagesKertas Penerangan 3neddylalolaNo ratings yet
- ME362 Nozzle Flow AnalysisDocument6 pagesME362 Nozzle Flow Analysisদুর্জয় দুর্বারNo ratings yet
- Assignment Style GuideDocument7 pagesAssignment Style GuideAhmed Farazv SoomroNo ratings yet
- Weldability TestDocument11 pagesWeldability TestRajan BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - Advanced Welding TechnologyDocument60 pagesDocuments - Pub - Advanced Welding TechnologybalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling Fan: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroDocument9 pagesEngine Cooling Fan: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroAnimemanuel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic FlowmeterDocument6 pagesUltrasonic Flowmeterদুর্জয় দুর্বারNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air UsesDocument5 pagesCompressed Air Usesandy habibiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 & 7: Results and DiscussionDocument29 pagesLesson 6 & 7: Results and DiscussionJ i n100% (1)
- Pipe Elements 1Document310 pagesPipe Elements 1Ryan Llona FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ref BasicsDocument15 pagesRef BasicsManasvini KarthihaNo ratings yet
- How to Fix a Refrigerator Not Cooling in Less Than 40 StepsDocument3 pagesHow to Fix a Refrigerator Not Cooling in Less Than 40 StepsArnel PorlasNo ratings yet
- EPOS4 EtherCAT Card Hardware ReferenceDocument28 pagesEPOS4 EtherCAT Card Hardware ReferenceHoang ManhNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Management to Prevent Compressor DamageDocument7 pagesRefrigerant Management to Prevent Compressor DamageSlavikNZNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Troubleshooting GuideDocument6 pagesRefrigerator Troubleshooting GuideWubliker WubamlakNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Selection ConsiderationsDocument27 pagesRefrigerant Selection Considerationsme12m113No ratings yet
- #2 PDFDocument20 pages#2 PDFplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Fridge ManualDocument24 pagesFridge ManualDylan NelsonNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Refrig Service TechsDocument127 pagesTraining Manual For Refrig Service Techsjohnnybe51No ratings yet
- Compressor, Main Parts, Types and Working Principle: PV NRT P TDocument6 pagesCompressor, Main Parts, Types and Working Principle: PV NRT P TMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationDocument14 pagesUnit 6 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning System Need For RefrigerationamitNo ratings yet
- (2PRD-002A) Refrigeration CycleDocument57 pages(2PRD-002A) Refrigeration CycleKyaw San Oo100% (1)
- Refrigeration FundamentalsDocument92 pagesRefrigeration FundamentalsThomas Westgate100% (1)
- Cooling&heatpumpDocument26 pagesCooling&heatpumpAnonymous 5HYsyrddpNo ratings yet
- Expansion valve malfunction diagnosisDocument1 pageExpansion valve malfunction diagnosisJulietina PerezNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump Lab ReportDocument11 pagesHeat Pump Lab ReportPrecisionetica63% (8)
- Refeer Air CompressorDocument12 pagesRefeer Air CompressorSantharam MarinerNo ratings yet
- India Disaster Report 2011 Highlights Major Floods, Earthquakes and CyclonesDocument85 pagesIndia Disaster Report 2011 Highlights Major Floods, Earthquakes and CyclonesVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- The Actual Difference Between The Terms Is As Follows:: ChhattisgarhDocument2 pagesThe Actual Difference Between The Terms Is As Follows:: ChhattisgarhVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- World Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionDocument3 pagesWorld Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Rural Urban 2011Document40 pagesRural Urban 2011kanikabasuNo ratings yet
- Definition of CapitalDocument1 pageDefinition of CapitalVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- The Pre-Event Phase: Earlier LeaksDocument19 pagesThe Pre-Event Phase: Earlier LeaksVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Santhara Jain RitualDocument2 pagesSanthara Jain RitualVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- World Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionDocument3 pagesWorld Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 0g 7o Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument10 pagesHttps Doc 0g 7o Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDivya NadarNo ratings yet
- The Bhopal DisasterDocument27 pagesThe Bhopal DisasterkrishshellyNo ratings yet
- 7 WastesDocument21 pages7 WastesNithya SivasoorianNo ratings yet
- World Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionDocument3 pagesWorld Ozone Day highlights need to protect layer from depletionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- ShivajiDocument17 pagesShivajiVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Report On Combatting Terrorism' Genesis and Different Types of TerrorismDocument14 pagesReport On Combatting Terrorism' Genesis and Different Types of TerrorismsubhashsinghkislayNo ratings yet
- Distribution Transformer Monitoring Controlling and ProtectionDocument18 pagesDistribution Transformer Monitoring Controlling and ProtectionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Power Contactors: Basics Constructions Operation Parameters SelectionDocument22 pagesPower Contactors: Basics Constructions Operation Parameters SelectionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Substation Automation For The Smart Grid: Figure 1. Substation Migration in ProcessDocument4 pagesSubstation Automation For The Smart Grid: Figure 1. Substation Migration in ProcessPrasun MathurNo ratings yet
- AC Motor Testing and Predictive MaintenanceDocument4 pagesAC Motor Testing and Predictive Maintenanceslimmons2009No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Smart Grid: Luther Dow Quanta Technology, LLC, August 5, 2008Document7 pagesSmart Grid Smart Grid: Luther Dow Quanta Technology, LLC, August 5, 2008Vikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Energy Audit in Sugar IndustryDocument6 pagesEnergy Audit in Sugar IndustryVikram Porje100% (1)
- FINAAAAAAAAAAAAL SupercapacitorsDocument28 pagesFINAAAAAAAAAAAAL SupercapacitorsVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- 15 Busbar ProtectionDocument21 pages15 Busbar ProtectionSristick100% (8)
- AnticollisionDocument10 pagesAnticollisionVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Induction LaunchersDocument3 pagesInduction LaunchersVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergyDocument7 pagesBio EnergyVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Methods of Starting Synchronus MotorsDocument15 pagesMethods of Starting Synchronus MotorsRahul KusumaNo ratings yet
- Valvula de Seguridad PRV Rego 2Document1 pageValvula de Seguridad PRV Rego 2Erick MontejoNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Quotation No. TO: Branch AddressDocument2 pagesQuotation: Quotation No. TO: Branch AddressSohail SurveNo ratings yet
- Lower Heat Exchanger For Extra 1,2 3 VT CalorifiersDocument9 pagesLower Heat Exchanger For Extra 1,2 3 VT CalorifiersSpinu DanielNo ratings yet
- Hot Water System Design ManualDocument56 pagesHot Water System Design Manualparrilla506No ratings yet
- Bag Filter Fan To Stack EndDocument6 pagesBag Filter Fan To Stack EndganeshNo ratings yet
- Bolt and Stud Bolt Dimensions For ANSI / ASME B16.5 Class 150 FlangesDocument1 pageBolt and Stud Bolt Dimensions For ANSI / ASME B16.5 Class 150 Flangesגרבר פליקסNo ratings yet
- Technical RoofTopsDocument64 pagesTechnical RoofTopsnairam2003100% (1)
- High-Performance HVAC - WBDG - Whole Building Design GuideDocument16 pagesHigh-Performance HVAC - WBDG - Whole Building Design GuideBalakathiresanNo ratings yet
- Quickly join preinsulated Ecoflex pipes with Uponor's Q&E technologyDocument8 pagesQuickly join preinsulated Ecoflex pipes with Uponor's Q&E technologyciocarda andreeaNo ratings yet
- Midea Tfa, Cassett & Wall Tyep Indoor Unit PDFDocument53 pagesMidea Tfa, Cassett & Wall Tyep Indoor Unit PDFZahangir KabirNo ratings yet
- Kemper Hammerseal SpecsDocument2 pagesKemper Hammerseal SpecsReyna NavaNo ratings yet
- Install Piping Systems of PACU and CREDocument65 pagesInstall Piping Systems of PACU and CREBeth AusteNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Boilers and Heaters With KeyDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire On Boilers and Heaters With Keyngochung99n2No ratings yet
- BOQ For Yard Tap Distribution Pipe Line and FittingDocument6 pagesBOQ For Yard Tap Distribution Pipe Line and FittingsultanNo ratings yet
- PLH130 enDocument28 pagesPLH130 enkachanansNo ratings yet
- (20200922) Theo Doi AW RFQ 1-5Document29 pages(20200922) Theo Doi AW RFQ 1-5Tuấn PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop & Water HeatersDocument22 pagesPressure Drop & Water HeatersparthivNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Boiler - Dimas Arya Thayeb - 1606871165Document10 pagesPresentasi Boiler - Dimas Arya Thayeb - 1606871165Dimas ThayebNo ratings yet
- Den Islam Intern ReportDocument95 pagesDen Islam Intern ReportDen Islam100% (1)
- Heatcraft Installation ManualDocument48 pagesHeatcraft Installation ManualJacob PettitNo ratings yet
- 021-29501-000-REP-001 - Report Pryme Cooling Water System RedesignDocument8 pages021-29501-000-REP-001 - Report Pryme Cooling Water System Redesignbarun1977No ratings yet
- MYPRO TOUCH AREA MODBUS Protocol GuideDocument9 pagesMYPRO TOUCH AREA MODBUS Protocol GuideFelipe Vesenick RadelNo ratings yet
- Asme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Document1 pageAsme B36-10M-2004 (Schedule STD)Jesús Alberto Díaz CostaNo ratings yet
- Marco GBL Spec 3bmix 2021-1Document2 pagesMarco GBL Spec 3bmix 2021-1Umut GökdenizNo ratings yet
- Ac DodgeDocument192 pagesAc Dodgejosecuellar69No ratings yet
- I - MarketingBarkellWebsiteWebsite Contentair Handling Units4. AHU DesignAHU Unit Design SheetUnit Design Enquiry Form - Email Version Vfinal PDFDocument2 pagesI - MarketingBarkellWebsiteWebsite Contentair Handling Units4. AHU DesignAHU Unit Design SheetUnit Design Enquiry Form - Email Version Vfinal PDFMd Musa MahmudNo ratings yet
- YCIVDocument64 pagesYCIVAvce Cw100% (2)
- Master Plumber Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesMaster Plumber Exam ReviewRuis Raphael HidalgoNo ratings yet