Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Andrews - Chapter 1 - Skin Basic Structure and Function
Uploaded by
Angeli Ramos-Estrella0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views38 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views38 pagesAndrews - Chapter 1 - Skin Basic Structure and Function
Uploaded by
Angeli Ramos-EstrellaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 38
SKIN:
BASIC STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Chapter 1
Andrews Diseases of the Skin 12th Edition
Basic Structure and Function
• 3 layers
• Epidermis – viable keratinocytes covered by keratin (stratum corneum)
• Thickest on the palms and soles (1.5mm)
• Eyelids – 0.1mm
• Dermis – collagen
• Thickest at the back – 30-40x as thick as the epidermis
• Subcutaneous fat (panniculus) – lipocytes separated by a septa containing
neurovascular bundles
• Generous on the abdomen and buttocks
• Meager on nose and sternum
Epidermis and Adnexa
• Fetal skin
• First weeks - Periderm (nonkeratinizing cuboidal cells)
• Replaced by multilayered epidermis later on
• 3rd fetal month – adnexal structures : follicles and eccrine sweat glands
• Later – apocrine sweat units, sebaceous glands (cephalocaudal appearance)
• Adult skin: 3 basic cell types
• Keratinocytes
• Melanocytes
• Langerhans cells
• Merkel cell
Epidermis: Keratinocytes
• Squamous cells
• Principal cells of epidermis
• Origin: ectoderm
• Function: produce keratin (complex filamentous protein)
• Keratin genes subfamilies: acidic, basic
• Critical for normal functioning of epidermis
• Mutations cause disease
• Keratin 5 and 14 mutation: Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
• Keratin 1 and 10 mutation: Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis
• Mild forms: localized or widespread expressions of mosaicism
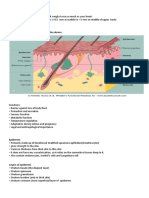
Epidermis: layers
• Stratum germinativum – innermost basal layer
• Stratum spinosum – malpighian or prickle layer
• Stratum granulosum – granular layer
• Stratum corneum – horny layer
• Stratum lucidum – palms, soles
• Other sites: S. spinosum and granulosum thicken forming S. lucidum = thicker
s. corneum
Epidermis: Keratinization
• Histones – regulate epidermal differentiation
• Deacetylation – suppresses expression of profilaggrin
• Slow-cycling stem cells – reservoir for regeneration
• Sites rich in stem cells: deepest areas of rete, palmoplantar skin, hair bulge
• High expression of β1 integrins
• Lack of terminal differentiation markers
• Low levels of desmosomal proteins (desmoglein 3)
• Basal cells divide -> move upward -> flatten -> nucleus disappears
• Abnormal keratinization:
• Parakeratosis: retained nuclei
• Corps ronds: round, clear to pink, abnormally keratinized cells
• Grains: elongated, basophilic, abnormally keratinized cells
Epidermis: Keratinization
• Keratinocyte
• Synthetic phase:
• cytoplasm accumulates intermediate filaments (fibrous protein, keratin) arranged in α-
helical coiled pattern fashioned into bundles -> converge and terminate at the plasma
membrane -> end in specialized attachment plates called desmosomes
• Degradative phase
• Disappearance of cell organelles
• Consolidation of contents = mixture of filaments and amorphous cell envelopes
• Terminal differentiation – programmed process of maturation
• Apoptosis – H&E stain (bright-red cells with small, black, pyknotic nuclei) present at
various levels of epidermis because it is not part of the normal process of maturation
Epidermis
• Intercellular space – separates plasma membranes of adjacent cells
• Contains glycoproteins (water-barrier) and lipids
• Lamellar granules (Odland bodies, membrane-coating granules) for skin
cohesion and impermeability
• Abnormality: lamellar ichthyosis, Flegel’s hyperkeratosis
• Cadherins (desmogleins, desmocollins)
• Desmosomal adhesion (antibodies against cadherins result to immunobullous diseases)
• Differentiation – binding to Erbin (scaffolding protein) downregulates the Ras-Raf
pathway to promote stratification and differentiation of keratinocytes
Epidermis: Granular zone
• Keratohyaline granules
• Amorphous particulate material of high sulfur-protein content (profilaggrin)
• Profilaggrin – precursor to filaggrin (responsible for keratin filament aggregation)
• Conversion to filaggrin takes place in the granular layer, forming the interfilamentous
prtein matrixof mature epidermal keratin
• Kallikrein-related peptidase 5 – serine protease for profillagrin cleavage
• Desquamation
• Result of repeated hydration and dehydration of the stratum corneum
• Ichthyosis vulgaris – diminished/absent granular layer = retention
hyperkeratosis
• Keratohyalin – forms soft, flexible keratin
• Absence causes hard and rigin keratin (nails, hair fibers)
Epidermis
• Keratinocytes
• Active role in skin immunity
• Allergic contact dermatitis – induction of immune response
• Secrete cytokines and inflammatory mediators (TNFα)
• Express ICAM1 (intercellular adhesion molecule) and MHC II
Epidermis: Melanocytes
• Origin: Neural crest
• 8th week: found in fetal epidermis
• Reside in basal layer (1 in every 10 basal keratinocytes)
• Greater density at face, skins, genitalia
• Heavily damaged facial skin: 1:1
• Melanocyte:keratinocyte ratio – critical in interpretation of biopsies of suspected lentigo maligna
• Racial differences in skin color – not by number of melanocytes, but by number, size, and distribution of
melanosomes within keratinocytes
• Chronic sun exposure – stimulates melanocytes to produce larger melanosomes
• Dendritic cell – extends long, in contact with a lot of keratinocytes
• Forms epidermal melanin unit
• Keratinocytes ingests the tops of dendrites, imbibing the melanosomes
• Melanocytes and keratinoncytes express neurotrophins (ectodermal nerve growth factors)
• Neurotrophin 4 – released by melanocytes – downregulated by UVB, thus can be possible targets for therapy of disorders of
pigmentation
• Melanocytes express toll-like receptors (TLR)
• Stimulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides increases pigmentation
Epidermis: Melanosomes
• Syntheized in the Golgi zone
• Red pigment (red hair): pheomelanin
• Melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) – regulation of melanin production
• Loss of function mutation – change from eumelanin to pheomelanin production
• Activating gene: enhance eumelanin synthesis
• Antimicrobial pepties – cathelicidin, β-defensins
• Innate immune system
• Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis
• Controls pigmentation
• Eumelanin production: optimal at pH 6.8
• Melanin forms a cap over the nucleus – photoprotection agains UVA-induced membrane damage
Epidermis: Pigmentation
• Leukoderma – whitening of skin
• Vitiligo – destruction of melanocytes
• Albinism – number of melanocytes is normal, but unable to synthesize fully-
pigmented melanosomes due to defects in enzymatic formation of melanin
• Local areas of increased pigmentation
• Freckle – localized increase in production of pigment by a near-normal
number of melanocytes
• Sunburn or ink spot – basilar hyperpigmentation and prominent melanin
within the stratum corneum
• Nevi – benign proliferations of melanocytes
• Melanoma – malignant nevi
Epidermis: Langerhans cells
• Scattered among keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum (3.5%)
• Not connected to adjacent keratinocytes by the desmosomes (like melanocytes)
• Highest density in the vestibular region
• Lowest density in the sublingual region
• With folded nucleus and distinct intracystoplasmic organelles (Birbeck granules)
• Monocyte-macrophage lineage
• Originate in bone marrow
• Function: recognition, uptake, processing, and presentation of antigens to
sensitized T lymphocytes, induction of delayed-type sensitivity
• Antigen -> migrate to lymph nodes
Epidermis: Langerhans cells
• Hyaluronan – important for maturation and migration
• Express: langerin, ATPase, CD39, CCR6, CD1α+, CD36, factor XIIIA,
chemokine receptor 5, IL-12
• UV radiation depletes Langerhans cells, skin loses ability to be
sensitized until cells are replenished = macrophages that present
antigen in Langerhan cells can induce immune tolerance
• Macrophage – produce IL-10 after UVB irradiation = downregulates
immune response
Dermoepidermal junction
• Basement membrane zone (BMZ) – junction of epidermis and dermis
• 4 ultrastructure components:
• Plasma membranes of basal cells with attachment plates (hemidesmosomes)
• Lamina lucida – electron-lucent
• Lamina densa - basal lamina (major: Type IV collagen)
• Fibrous components – anchoring fibrils, dermal microfibrils, collagen fibers (stain: PAS)
(major: Type VII collagen)
• 2 major hemodesmosomal proteins
• BP230 (Bullous pemphigoid antigen 1)
• BP180 (Blullous pemphigoid antigen 2, type XVII collagen)
• Function:
• Porous semipermeable filter – permits exchange of cells and fluid between epidermis and
dermis
• Structural support for the epidermis, holds epidermis and dermis together
• Regulate growth, adhesion, and movement of keratinocytes and fibroblasts
• Regulate apoptosis (regulation through activation of integrins and syndecans)
Epidermal Appendages: Adnexa
• Skin adnexa: eccrine and apocrine glands, ducts, pilosebaceous units
• Origin: ectoderm (downgrowths from epidermis)
• Hedgehog signaling transducer: smoothened = critical for hair development
• Abnormalities: pilar tumors, BCC
• Absence: hair germs develop into modified sweat gland or mammary epithelium
• Function: reserve epidermis (reepithelialization after injury)
• Face, scalp (contain abundant pilosebaceous units) – reepithelialize more rapidly than the
back (scarce adnexa)
• Reepithelialized wound does not produce granulation tissue
• Deep wounds in areas of few adnexa fill with granulation tissue until they are flush with the
surrounding skin
• Wounds in areas rich in adnexa will quickly be covered with epithelium – no granulation
tissue forms = contour effect created by wound will persist
• Pseudoeputheliomatous hyperplasia (infections, inflammatory conditions) consist mostly of
adnexal epithelium
Adnexa: Eccrine sweat units
• Acrosyringium – intraepidermal spiral duct which opens directly onto
skin surface
• Derived from dermal duct cells
• Small polygonal cells with central round nucleus surrounded by ample pink
cytoplasm
• Dermal portion: double layer of cuboidal epithelial cells lined by an
eosinophilic cuticle on luminal side
• Superficial panniculus: coiled secretory acinar portion
• Back: deep dermis
• 2 types:
• Large, pale, glycogen-rich – initiate formation of sweat
• Smaller, darker – reabsorb sodium, modify sweat (isotonic to hypotonic)
Adexa: Eccrine sweat glands
• Sweat – similar in composition to plasma
• Same electrolytes, but more dilute
• Hot environment: production of larger amounts of hypotonic sweat (allows greater cooling
with conservation of sodium)
• Found at virtually all skin sites (humans)
• Other mammals: apocrine gland (major sweat gland)
• Physiologic secretion
• Cholinergic innervation
• Biphasic: initial hyperpolarization, secondary depolarization (mediated by calclum and chloride ion
conductance)
• Adrenergic secretion
• Monophasic depolarization, dependent on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator GCI
• Cystic fibrosis – no adrenergic secretion = sweat high in salt
• Stimuli: heat (prime), emotional stress, VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide)
Adnexa: Apocrine units
• Outgrowths of the infundibular or upper portion of hair follicle
• Straight excretory portion: double layer of cuboidal epithelial cells
• Coiled secretory gland
• Located at junction of dermis and subcutaneous fat
• Lined by single layer of columnar to cuboidal cells
• Surrounded by a layer of myoepithelial cells
• Appear more dilated than eccrine coils
• Apocrine seat stains more deeply red in H&E (eccrine: pale pink)
• Composition: protein, cabohydrate, ammonia, lipid, iron
• Apocrine sweat
• Appears milky white (lipofuscin: dark brown, gray-blue (apocrine chromhidrosis)
• Odorless until it reaches skin surface, where it is altered by bacteria = odoriferous
• Secretion
• Innervation: Adrenergic innervation, circulating catecholamines (adrenomedullary origin), VIP
• Episodic excretion, continuous secretion
• Function in humans: not known
• Other species: protective, sexual, thermoregulation
• Generally confined to the ff sites:
• Axillae, areolae, anogenital, external auditory canal (cerumenious glands), eyelids (glands of Moll), stroma of sebaceous nevus of Jadassohn
• Do not begin to function until puberty
Adnexa: Hair follicles
• Origin: mesenchyme
• Embryogenesis: mesenchymal cells collect below the basal layer of epidermis
• epidermal buds grow down into the dermis at and angle to the skin surface
• Base: forms bulb containing mesenchymal bodies with mesenchymal stem cells (mice: extramedullary hematopoietic stem
cell activity = potential therapeutic source)
• Fetal follicle: 2 buds
• Upper bud: sebaceous gland
• Lower bud: attachment for the arrector pili muscle
• 3rd bud: apocrine gland (above sebaceous gland)
• Infundibular segment: uppermost portion of follicle
• From surface opening to entrance of sebaceous duct
• permanent
• Isthmus: portion of follicle between sebaceous duct and insertion of the arrector pili musle
• where inner root sheath fully keratinizes and sheds
• permanent
• Hair bulb – lowermost part of follicle
• Undergoes cycles of involution and regeneration throughout life
• Completely replaced with each new cycle of hair growth
Adnexa: Hair follicles
• Develop sequentially in rows of three
• Primary follicle is surrounded by 2 secondary follicles
• Density of pilosebaceous units decreases throughout life
• Dropout of secondary follicles
• Mice: signaling by ectodysplasin A and noggin = essential for development of
pimary hair follicles and induction secondary hair follicles
• Arrector pili muscles interconnect at the level of the isthmus
• Hair shaft + inner and outer root sheath
• Produced by the matrix portion of the hair bulb
• Move together as the hair grows upward until fully keratinized inner root
sheath sheds at the level of the isthmus
Adnexa: Hair growth
• Anagen: active growth phase
• Scalp: 3-5 years
• 85-90% of all scalp hairs (decreases with age and in male-pattern baldness [length of anagen decreases])
• Growth rate: 0.37 mm/day
• Catagen: involution
• 2 weeks
• Telogen: resting phase
• 3-5 months
• Most sites of body: shorter anagen, longer telogen = short hairs for longer periods
• Prolongation of anagen phase = long eyelashes (seen in patients with AIDS)
• Cyclic hair growth, but each follicle is an independent unit
• Humans do not shed hair synchronously, as most animals
• Each hair follicle – intermittent stages of activity and quiescence
• Synchronous termination of anagen or telogen = telogen effluvium (result of early release from
anagen, induced by fever, surgery, weight loss)
Adnexa: Hair growth
• Pregnancy: retention of anagen hairs, prolongation of telogen
• After delivery: abnormally prolonged telogen hairs released, abnormally
prolonged anagen hairs are converted to telogen
• Chemotherapy: drugs interfere with mitotic activity of hair matrix =
hair loss due to tapered fracture
• Only anagen hairs are affected = leaves a sparse coat of telogen hairs on scalp
• As matrix recovers, anagen hairs resume growth without having to cycle
through catagen and telogen
• Growing anagen hair: pigmented bulb and inner root sheath
• Catagen hairs: many apoptotic cells in outer root sheath
• Telogen hairs: nonpigmented bulb with shaggy lower border
Adnexa: Hair follicle
• Hair shape – controlled by trichohyalin gene
• White people scalp: round
• White people pubic hair, beard, eyelashes: oval
• Black people scalp: oval (curly)
• Uncombable hair: triangular with a central canal
• Hair color
• Depends on degree of melanization and distribution of melanosomes within hair shaft
• Graying of hair – decreased number of melanocytes that produce fewer melanosomes
• Repetitive oxidative stress - apoptosis of melanocytes – normal hair graying
• Premature graying – exhaustion of the melanocyte stem cell pool
• Balding
• Polymorphisms in the androgen receptor gene (X chromosome) – for males
• Female-pattern hair loss – less clear, not associated with androgen receptor gene, but
adrenal androgens may play a role
Adnexa: Sebaceous glands
• Origin: outgrowth from the upper portion of hair follicle
• Lobules of pale-staining cells with abundant lipid droplets in cytoplasm
• Periphery of lobules: basaloid germinative cells
• Give rise to lipid-filled pale cells, continuously being extrutded through the short
sebaceous duct into the infundibular portion of hair follicle
• Sebaceous duct: lined by red cuticle
• Distribution
• Abundant: face, scalp
• Distributed thoughout all skin sites EXCEPT palms, soles
• Always associated with hair follicles EXCEPT at tarsal plate of eyelids (Meibomian
glands), buccal mucosa, vermillion border of lip (Fordyce spots), prepuce and mucosa
lateral to the penile frenulum (Tyson glands), labia minora, female areola
(Montgomery tubercles)
Adnexa: Sebaceous glands
• Anatomically and functionally related to hair follicle
• Acne vulgaris
• Disorder of entire pilosebaceous unit
• Clinical manifestations will not form as long as the sebaceous duct and hair
infundibulum remain patent, and lipid and cell debris are able to reach surface
• Most lipids produced are also produced elsewhere in body
• Unique products: wax esters, squalene
• Sebocytes – express histamine receptors
• Antihistamine reduces squalene levels
• Skin lipids function
• Barrier
• Antimicrobial (spienic acid from triglycerides, sphingoid bases from ceramides)
Nails
• Function
• Assist in grasping small objects
• Protect the fingertip fro trauma
• Keratinization leads to formation of nail plate
• Growth: 0.1mm/day (4-6 mos to replace complete nail plate)
• Slower in toenails: 12-18 mos to replace the great toenail)
• Nail abnormalities: clues to cutaneous and systemic diseases
• Keratin type: mixture of hair (dominant) and epidermal hair type
• Keratin: only 10% of nail isthmus
• Brittle nails: widening of intercellular space between nail keratinocytes
• Parallel rete ridges
• Formation of splinter hemorrhages (extravasated blood)
• Nail cuticle – keratinocytes of proximal nailfold
• Nail plate – matrix keratinocytes
• Endogenous pigments – follow the contour of the lunula (distal portion of matrix)
• Exogenous pigments – follow contour of cuticle
• Dorsal nail plate: formed by proximal matrix
• Ventral nail plate: formed by distal matrix + nail bed
Dermis
• Origin: mesoderm (except nerves ie melanocytes derived from neural crest)
• Fetal development:
• 6th wk fetal life: pool of scattered dendritic-shaped cells containing acid mucopolysacharide (precursors of
fibroblasts)
• 12th wk: fibroblast actively synthesize reticulum fibers, elastic fibers, collagen
• 25th wk: vascular network, fat cells beneath dermis
• Wnt/ β catenin signaling – critical for differentiation of ventral and dorsal dermis
• Function:
• Scaffold for adnexal structures
• Infant dermis: small collagen bundles (Stain deep red due to abdundant fibroblasts)
• Adult dermis: few fibroblasts, with thick collagen bundles (stain pale red)
• 2 dermal dendritic cells
• Factor XIIIa+ dermal dendrocytes: give rise to dermatofibromas, angiofibromas, fibrokeratomas, fibromas,
fibrous papules
• CD34+ dermal dendrocytes
Dermis: Collagen
• Collagen: principal component
• Major structural protein for entire body
• 70% dry weight of skin
• Formation: fibroblast synthesizes procollagen -> assembled into collagen fibrils
• Rich in amino acids: hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine, glycine
• Function– stress resistant
• Resists deformation and tearing of skin
• Types
• Type I – major component of dermis
• Type IV – BMZ
• Type VII – anchoring fibrils, produced by keratinocytes
• Abnormalities: epidermolysis bullosa
• Spare collagenases: proteolytic enzymes that continuously degrades collagen
fibers
Dermis: Elastic fibers
• Fibroblast also synthesized elastic fibers and ground substance of
dermis (GAGs, acid mucopolysaccharides
• Aggregates of protein filaments and elastin
• Unique to elastic fibers: desmosine, isodesmosine
• Characteristics
• Papillary dermis: fine
• Reticular dermis: coarse
• Function: maintains elasticity
• Little role in stress-resistance
Dermis
• ECM or ground substance
• Sulfate acid mucopolysaccharide - chondoritin sulfate, dermatan sulfate
• Neutral mucopolysaccharides
• Electrolytes
• Hyaluronan - minor component of normal dermis
• Major MPS that accumulates in pathologic states
• Connective tissue diease
• Scleroderma – most visible collagen abnormality (space between collagen bundles diminishes as collagen
bundles become hyalinized)
• Lupus, dermatomyositis – increased dermal mucin (hyaluronic acid)
• Bullous lupus – autoantibodies against type VII collagen
• Defects in collagen synthesis
• Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
• X-linked cutis laxa
• Osteogeneis imperfecta
• Defects in elastic tissue:
• Marfan syndome
• Pseydoxanthoma elasticum
Dermis: vasculature
• 2 intercommunicating plexuses
• Subpapillary plexus – upper horizontal network
• Postcapillary venules
• Courses the junction of the papillary and reticular dermis’furnishes a rich supple of
capillaries, end arterioles, venules, to the dermal papillae
• Lower horizontal plexus
• Dermal subcutaneous interface
• Larger vessels
• Well-developed at sites of adnexal structures
• Associated with dermal lymphatics and nerves
Dermis: Muscles
• Smooth muscles: desmin intermediate filaments
• Arrectores pilorum – erectors of hairs
• Attached to hair follicles below sebaceous gland -> contracts -> pull hair follicle upward
• Tunica dartos – scrotum
• Areolas – around nipples
• Muscularis of dermal and subcutaneous blood vessels: vimentin
intermediate filaments
• Veins – small bundles of smooth muscle that cris cross at right angles
• Arteries – smooth muscles form a concentric ring
• Glomus bodies (aggregates of smooth muscles) – digits, lateral margins of palms and
soles
• Serve to shunt blood and regulate temperature
• Striated voluntary muscle
• Skin of neck (platysma), skin of face (muscles of expresssion)
• Superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS) – complex network of striated
muscle, fasica, aponeuroses
Dermis: Nerves
• Nerve bundles are found together with arterioles and venules as part of neurovascular bundle
• Deep dermis: nerves travel parallel of surface
• Sausage-like granulomas following this path: Hansen’s disease
• Touch and pressure
• Mesissner corpuscles: Dermal papillae (digits, palms, soles)
• Vater-Pacini corpulses: deeper dermis of weight bearing surfaces, genitalia
• Mucocutaneous end organs
• Papillary dermis of modified hairless skin (glans, prepuce, clitoris, labia minora, perianal region, vermillion border of lips
• Temperature, pain, itch
• Unmyelinated nerve fibers that terminate in the papillary dermis and around hair follicles
• Impulses pass to CNS by dorsal root ganglia
• Histamine-invoked itch – transmitted by slow-conducting unmyelinated C fibers
• Postganglionic adrenergic fibers of ANS
• Regulate vasoconstriction, apocrine gland secretions, contraction of arrector pili muscles
• Cholinergic fibers
• Eccrine sweat secretion
Dermis: Mast Cells
• Function
• Normal immune response
• Immediate-type sensitivity, contact allergy, fibrosis
• Fried egg appearance
• 6-12microns diameter, ample amphpphilic cytpplasm, small round central nucleus
• Contains up to 1000 granules, glycoprotein receptor sites for IgE
• Type I –connective tissue mast cells in dermis and submucosa
• Type II – mucosal mast cells in bowel and respiratory tract
• Cutaneous mast cells respond to environmental changes
• Dry – increase in number and histamine content
• Mastocytosis – mast cells accumulate in skin because of abnormal
proliferation, migration, and failure of apoptosis
Subcutaneous tissue (panniculus)
• Beneath the dermis
• Lobules of fat cells/ lipocytes separated by fibrous composed of collagen septa
(continuous with collagen of dermis) and large blood vessels
• Function
• Provides buoyancy
• Repository of energy
• Endocrine organ
• Site of hormone conversion (androstenedione to estrone by aromatase)
• Regulates body weight (leptin, produced by lipocytes)
• Obestatin – polypeptide, reduces feed intake and weight gain (rodents)
• Ternatin – inhibits fat accumulation (mushroom: Coriolus versicolor)
• Abnormal fat distribution – Cushing syndrome, antiretroviral therapy, diabetes
• Panniculitides – inflammatory dematoses
• Produces subcutaneous nodules
You might also like
- Dr. Dewi - Dermatologi DasarDocument63 pagesDr. Dewi - Dermatologi DasarSuryooNo ratings yet
- Null (1) (Autosaved)Document82 pagesNull (1) (Autosaved)SamNo ratings yet
- Skin AnatomyDocument71 pagesSkin AnatomyHardik DaveNo ratings yet
- Dr. Chandra Wijaya, M. Biomed, SPJP - Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem IntergumentDocument116 pagesDr. Chandra Wijaya, M. Biomed, SPJP - Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem IntergumentAgva Dwi FatikaNo ratings yet
- Histophysiology+of+the+Skin+for+Vula+ Dr+MowlaDocument28 pagesHistophysiology+of+the+Skin+for+Vula+ Dr+MowlaYaaseen GallantNo ratings yet
- Histology of SkinDocument33 pagesHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- K1 - Histo Skin 2013Document36 pagesK1 - Histo Skin 2013Desi Indah LaisNo ratings yet
- Aanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2Document77 pagesAanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2AdiNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument15 pagesReviewerYza Grace S. PayangdoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Skin, Hair, and NailsDocument31 pagesThe Integumentary System: Skin, Hair, and NailsAzwirNo ratings yet
- Int - Sys ComDocument19 pagesInt - Sys ComBernard FernandezNo ratings yet
- Integument SystemDocument76 pagesIntegument Systemyuli mrNo ratings yet
- Integumentary PDFDocument35 pagesIntegumentary PDFloey skiiesNo ratings yet
- Histology of Integument: Structure and Function of Skin and Its AppendagesDocument50 pagesHistology of Integument: Structure and Function of Skin and Its AppendagesMsatriaNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 4 - IntegumentaryDocument45 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 4 - Integumentaryprincesinclair77No ratings yet
- DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGDocument65 pagesDR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGأمال داودNo ratings yet
- DMS1-K1-Histologi KulitDocument33 pagesDMS1-K1-Histologi KulitMarieta RitongaNo ratings yet
- IntegumentDocument35 pagesIntegumentSeftiana WahyuniNo ratings yet
- 1.a & P SkinDocument14 pages1.a & P Skinsivabalan rajagopalNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2022Document57 pagesIntegumentary System 2022francisalipio.medNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the SkinDocument33 pagesAnatomy of the SkinHarishchandra Yanamandala VenkataNo ratings yet
- Histology of Skin: A Concise Overview of the Structure and FunctionsDocument37 pagesHistology of Skin: A Concise Overview of the Structure and Functionsbenny pradanaNo ratings yet
- StrufunDocument135 pagesStrufunAmalia RizqiNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - The Integumentary SystemDocument42 pages4.2 - The Integumentary SystemEmman ImbuidoNo ratings yet
- Skin Structure and Functions OverviewDocument51 pagesSkin Structure and Functions OverviewWahyu Agung Dwi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument132 pagesIntegumentary SystemAlyssa VillaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Dr. Abdul Ahad ShaikhDocument55 pagesIntegumentary System: Dr. Abdul Ahad ShaikhPharmacist DinaNo ratings yet
- Policy For B.ed HonsDocument67 pagesPolicy For B.ed HonsJameelaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument97 pagesIntegumentary SystemetNo ratings yet
- Histo IntDocument3 pagesHisto IntNooredin JomaaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System, EdDocument42 pagesIntegumentary System, EdGirmay GebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- K - 1 Histologi of Skin (Histologi)Document37 pagesK - 1 Histologi of Skin (Histologi)Monika AyuningrumNo ratings yet
- 302573.radioloka Dijagnostika U Oralnoj Kirurgiji Diplomski RadDocument127 pages302573.radioloka Dijagnostika U Oralnoj Kirurgiji Diplomski RadEdina BrkicNo ratings yet
- 0401 Histo LectureDocument57 pages0401 Histo LectureJoe JNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemDocument64 pagesLecture 9 Integumentary Systemhafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Larry PlonDocument63 pagesDr. Larry Plonparedes916No ratings yet
- SKINDocument45 pagesSKINLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Histology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1Document40 pagesHistology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1HusseinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Histo Physio DR - AdilDocument73 pagesAnatomy Histo Physio DR - AdilHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Document25 pagesIntegumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Islam SamirNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- Biol163 Integumentary SystemDocument46 pagesBiol163 Integumentary SystemGladdyll Raico DizonNo ratings yet
- Skin Organ Structure and FunctionsDocument20 pagesSkin Organ Structure and FunctionsDr. Mary MjeedNo ratings yet
- جلدية Coppy AllowedDocument118 pagesجلدية Coppy AllowedAssssssNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Functions of the Integumentary SystemDocument38 pagesThe Anatomy and Functions of the Integumentary Systemvanderphys100% (1)
- "Vision Without Action Is A Daydream. Action Without Vision Is A Nightmare." Japanese ProverbDocument22 pages"Vision Without Action Is A Daydream. Action Without Vision Is A Nightmare." Japanese Proverb123456100% (1)
- Physiology of SkinDocument29 pagesPhysiology of SkinIlham KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: Layers of The SkinDocument4 pagesLearning Outcomes:: Layers of The SkinRumaisa ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Integumentary SystemDocument25 pagesChapter 5: Integumentary SystemTom NguyenNo ratings yet
- Skin Structure and FunctionsDocument31 pagesSkin Structure and FunctionsAfifa Prima Gitta100% (2)
- Structure of Skin SeminarDocument65 pagesStructure of Skin SeminarVikas PurushottamNo ratings yet
- K1 Kulit Dan AdnexaDocument23 pagesK1 Kulit Dan AdnexaJimmy Fran IINo ratings yet
- Structure of Skin - MBBS PresentationDocument10 pagesStructure of Skin - MBBS PresentationPratikNo ratings yet
- 9 Integumentary System PDFDocument32 pages9 Integumentary System PDFMaria Angelica AlmendrasNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument29 pagesThe Integumentary SystemSawera RaheemNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System1Document9 pagesIntegumentary System1Nurani AtikasariNo ratings yet
- Martin If AP 7 CH 52 RevisedDocument132 pagesMartin If AP 7 CH 52 RevisedAnas HamdanNo ratings yet
- E!y Q@N) ) Y@mj) VH ( PDFDocument39 pagesE!y Q@N) ) Y@mj) VH ( PDFRejane GorospeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument46 pagesEvaluation and Management of Pediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaJan Marvin Lichauco MendozaNo ratings yet
- IDSA NeumoníaDocument52 pagesIDSA NeumoníaAstrid QuinteroNo ratings yet
- (IMCI) Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument34 pages(IMCI) Integrated Management of Childhood Illnessɹǝʍdןnos97% (34)
- Andrews - Chapter 4 - Pruritus and Neurocutaneous DermatosesDocument40 pagesAndrews - Chapter 4 - Pruritus and Neurocutaneous DermatosesAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Andrews - Chapter 5 - Atopic DermatitisDocument64 pagesAndrews - Chapter 5 - Atopic DermatitisAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Andrews - Chapter 2 - Cutaneous Signs and DiagnosisDocument18 pagesAndrews - Chapter 2 - Cutaneous Signs and DiagnosisAngeli Ramos-Estrella100% (1)
- Andrews - Chapter 3 - Dermatosis Resulting From Physical FactorsDocument71 pagesAndrews - Chapter 3 - Dermatosis Resulting From Physical FactorsAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Nelson - KawasakiDocument14 pagesNelson - KawasakiAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Contoh Leaflet BronkitisDocument2 pagesContoh Leaflet BronkitisVira Noor AzharNo ratings yet
- Biosafety and BiosecurityDocument39 pagesBiosafety and BiosecurityAlliah Angelica NavalNo ratings yet
- B.L.I.S.T.T Health Declaration Form: Baguio - La Trinidad - Itogon - Sablan - Tuba - TublayDocument1 pageB.L.I.S.T.T Health Declaration Form: Baguio - La Trinidad - Itogon - Sablan - Tuba - TublayIsaias IsaiasNo ratings yet
- Form 5: Chapter 12 Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesForm 5: Chapter 12 Coordination and Responseapi-3841154No ratings yet
- Managing TMDs: Classification and Local Muscle SorenessDocument6 pagesManaging TMDs: Classification and Local Muscle SorenessheidyNo ratings yet
- Fccu Catalyst Material Safety Data Sheet (2001)Document2 pagesFccu Catalyst Material Safety Data Sheet (2001)Knipselkrant CuracaoNo ratings yet
- Case Report on Right Knee FuruncleDocument47 pagesCase Report on Right Knee Furuncle馮宥忻No ratings yet
- Infant Oral Health CareDocument27 pagesInfant Oral Health Caredr parveen bathla0% (1)
- Female Life CycleDocument24 pagesFemale Life CycleHenniwidiaa100% (1)
- Embryonic structures and their adult fatesDocument5 pagesEmbryonic structures and their adult fatesDana Lightha DelaTorre BabelaNo ratings yet
- The Doctrine of SignaturesDocument5 pagesThe Doctrine of SignaturesJoko RinantoNo ratings yet
- Artificial InseminationDocument19 pagesArtificial InseminationDonna Lei G. RosarioNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PART2 QUESTIONS CH15-18Document6 pagesBIOLOGY PART2 QUESTIONS CH15-18Ahmed Ali Khan100% (1)
- Bioelectricity and Microcurrent TherapyDocument11 pagesBioelectricity and Microcurrent TherapyGustavo Cabanas100% (2)
- Nutri Most H CL Whole Body DetoxDocument4 pagesNutri Most H CL Whole Body DetoxdeylafeisNo ratings yet
- VIH-SIDA Prevension y TratamientoDocument8 pagesVIH-SIDA Prevension y TratamientoDaniel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lingualied OcclDocument7 pagesLingualied Occlsiddu76No ratings yet
- Protists: By: Harrison DempseyDocument8 pagesProtists: By: Harrison DempseyharrisonNo ratings yet
- SK Tim Teknis PPK 2019-1Document24 pagesSK Tim Teknis PPK 2019-1MargaNo ratings yet
- A Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With AcitretinDocument3 pagesA Case of Subcorneal Pustular Dermatosis Successfully Treated With Acitretindr_RMNo ratings yet
- Standard Edgewise Technique: First Order BendsDocument45 pagesStandard Edgewise Technique: First Order BendsAgia Tessa AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Porges-2003-The Polyvagal Theory-Phylogenetic Contributions To Social BehaviorDocument11 pagesPorges-2003-The Polyvagal Theory-Phylogenetic Contributions To Social BehaviorJohn Bakalis100% (1)
- 2013 May Chinese BooksDocument17 pages2013 May Chinese BooksJonathan LiNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy An Illustrated Colour Text Crossman 6 Ed 2020 PDFDocument185 pagesNeuroanatomy An Illustrated Colour Text Crossman 6 Ed 2020 PDFKatrin CoolChe100% (3)
- Modified and Radical Neck Dissection TechniqueDocument19 pagesModified and Radical Neck Dissection TechniquethtklNo ratings yet
- Sujok Therapy and Treatment of Diseases Part IiDocument7 pagesSujok Therapy and Treatment of Diseases Part IiDoctor A SethiNo ratings yet
- God's Cancer ParmacyDocument5 pagesGod's Cancer ParmacyNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- Topical CorticosteriodsDocument11 pagesTopical CorticosteriodsIfra ShaikhNo ratings yet
- RADHAMADHAVAN A Saga of Love and PainDocument3 pagesRADHAMADHAVAN A Saga of Love and PainAnupama JanardhananNo ratings yet
- History and Functions of the Cholinergic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesHistory and Functions of the Cholinergic Nervous SystemmiznahNo ratings yet