0% found this document useful (0 votes)
836 views24 pagesUnderstanding Folded Plate Structures
The document discusses folded plate structures, which are assemblies of flat plates rigidly connected along their edges to form a structural system without additional beams. It outlines the basic concept of folding found in nature, the principles of folding, types of folded structures, and their applications. Examples are given of folded plate uses as roofs, walls, floors, and steel sheet piles. Advantages include light construction and longer spans, while disadvantages include complex formwork and construction precision needed. The Air Force Academy Chapel is highlighted as a notable example using this structural system.
Uploaded by
Shrea ZopeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
836 views24 pagesUnderstanding Folded Plate Structures
The document discusses folded plate structures, which are assemblies of flat plates rigidly connected along their edges to form a structural system without additional beams. It outlines the basic concept of folding found in nature, the principles of folding, types of folded structures, and their applications. Examples are given of folded plate uses as roofs, walls, floors, and steel sheet piles. Advantages include light construction and longer spans, while disadvantages include complex formwork and construction precision needed. The Air Force Academy Chapel is highlighted as a notable example using this structural system.
Uploaded by
Shrea ZopeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction
- Definition and Folding Systems
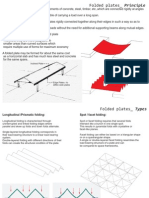
- The Basic Concept of Folding
- The Principle of Folding
- Structural Behavior of Folding
- Types of Folded Structures
- Basic Elements and Tapered Folded Plates
- Folded Plate Truss and Rigid Frame
- Edge Supported Folded Plates
- Three Segment Folded Plate
- Applications of Folded Structures
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Case Study: Air Force Academy Chapel
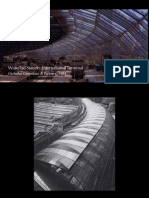
- Case Study: Yokohama Port Terminal
- Real Life Examples of Folded Plate Structure