Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Condenser: By: Ragragio, Millaine Joy E
Uploaded by
Laine Ragragio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views11 pagesOriginal Title
SURFACE CONDENSER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views11 pagesCondenser: By: Ragragio, Millaine Joy E
Uploaded by
Laine RagragioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
CONDENSER
By: Ragragio, Millaine Joy E.
What is Condenser
• Is a device or unit used to condense a substance from its gaseous to
its liquid state, by cooling it.
• Used in air conditioning, industrial chemical processes such as
distillation, steam power plants and other heat-exchange systems.
• Use of cooling water or surrounding air as the coolant is common in
many condensers.
• can be made according to numerous designs, and come in many sizes
ranging from rather small (hand-held) to very large (industrial-scale
units used in plant processes).
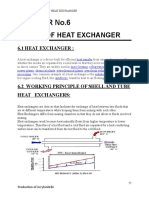
Surface Condenser
• is a commonly used term for a water-cooled shell and tube heat
exchanger installed on the exhaust steam from a steam turbine in
thermal power stations. These condensers are heat exchangers which
convert steam from its gaseous to its liquid state at a pressure below
atmospheric pressure.
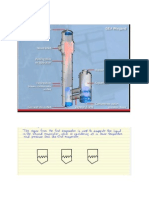
Parts
• Shell
The shell is the condenser's outermost body and contains the heat
exchanger tubes. The shell is fabricated from carbon steel plates and is
stiffened as needed to provide rigidity for the shell. When required by
the selected design, intermediate plates are installed to serve as baffle
plates that provide the desired flow path of the condensing steam. The
plates also provide support that help prevent sagging of long tube
lengths.
Vacuum system
• For water-cooled surface condensers, the shell's internal vacuum is most
commonly supplied by and maintained by an external steam jet ejector
system.
Tube sheets
• At each end of the shell, a sheet of sufficient thickness usually made of
stainless steel is provided, with holes for the tubes to be inserted and rolled.
Tubes
• Generally the tubes are made of stainless steel, copper alloys such as brass
or bronze, cupro nickel, or titanium depending on several selection criteria.
Waterboxes
• The tube sheet at each end with tube ends rolled, for each end of the
condenser is closed by a fabricated box cover known as a waterbox,
with flanged connection to the tube sheet or condenser shell. The
waterbox is usually provided with man holes on hinged covers to
allow inspection and cleaning.
• The steam can be condensed in surface steam condenser in two ways. Firstly,
cooling water is passed through a series of tubes and steam passes over the tubes.
• Secondly, the steam is passed through a series of tubes and water is allowed to
flow in the form of thin film outside the tubes.
• A surface condenser mainly consists of a cast iron shell. The shell is cylindrical in
shape and closed at both end to form a water box. A tube plate is located between
each cover head and the shell. A number of water tubes are fixed to the tube
plates. The shell is provided with exhaust steam inlet at the top and condensed
steam outlet at the bottom. The hot exhaust steam enters through the top inlet of
the surface condenser shell cooling water enters into the inlet water box and then
flows through the water tubes runs from one end to other end of the condenser
shell as shown.
You might also like
- Steam Turbine Condenser: How it Works and TypesDocument33 pagesSteam Turbine Condenser: How it Works and TypesSatyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemSam100% (1)
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemDalveer SinghNo ratings yet
- CondensersDocument35 pagesCondensersbibobib100% (1)
- EvaporatorsDocument37 pagesEvaporatorsGerald JobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Steam CondenserDocument53 pagesChapter 8 Steam CondenserPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Surface Condenser: Applications of Surface Condensers and Requirement of Surface CondenserDocument17 pagesSurface Condenser: Applications of Surface Condensers and Requirement of Surface Condenserdroffilcz27100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Equipment Design and SelectionDocument24 pagesHeat Transfer Equipment Design and SelectionCynosure SkyNo ratings yet
- EvaporatorDocument24 pagesEvaporatorS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument53 pagesSteam CondenserGeorge Markas100% (1)
- Heat ExchangersDocument32 pagesHeat ExchangersAnto KattikkaranNo ratings yet
- Forced Air Cooled Transformer GuideDocument12 pagesForced Air Cooled Transformer GuideRizal BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Surface CondenserDocument33 pagesSurface CondensershivvaramNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument49 pagesVacuum Systemssmith2007100% (3)
- CondenserDocument6 pagesCondenserSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Project PdeDocument16 pagesProject Pdesparsh dateyNo ratings yet
- CondensersDocument25 pagesCondensersARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers - Part 2: Che213 Heat Transfer in Chemical EngineeringDocument17 pagesHeat Exchangers - Part 2: Che213 Heat Transfer in Chemical EngineeringGeeva Prasanth ANo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger ClasificationDocument55 pagesHeat Exchanger ClasificationNikhil Sawant100% (1)
- Surface CondenserDocument7 pagesSurface Condensermhd_bashiriNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pressure EquipmentsDocument23 pagesBasics of Pressure EquipmentsSabariMechyNo ratings yet
- RAC - Unit 5 - Types of EvaporatorsDocument12 pagesRAC - Unit 5 - Types of EvaporatorsSAATVIK JAINNo ratings yet
- Internship report on finned tube heat exchangersDocument22 pagesInternship report on finned tube heat exchangersWorld Statistics AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger TrainingDocument53 pagesHeat Exchanger TrainingJose Luis Salinas Minaya100% (1)
- Evaporator and Condensers TypesDocument4 pagesEvaporator and Condensers TypesOwais SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers Fin-Fan: by M.M.SorourDocument64 pagesAir-Cooled Heat Exchangers Fin-Fan: by M.M.SorourNader GaafarNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.6: Design of Heat ExchangerDocument35 pagesChapter No.6: Design of Heat ExchangerGlacier RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger For PMS S-3 and CoCDocument36 pagesHeat Exchanger For PMS S-3 and CoCAhmed BilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Condensate SystemDocument11 pagesChapter 15 Condensate SystemsambhuNo ratings yet
- Condenser Functions of Condensers: Plant Maintenance Work and Service - PracticeDocument18 pagesCondenser Functions of Condensers: Plant Maintenance Work and Service - PracticeTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology: AssignmentDocument11 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology: AssignmentMuhammad NaumanNo ratings yet
- Nashik Generation Training Centre: Boiler Drum & Its InternalsDocument17 pagesNashik Generation Training Centre: Boiler Drum & Its InternalsAhemadNo ratings yet
- Types of CondenserDocument1 pageTypes of CondenserCally LimNo ratings yet
- Types of Heat Exchangers ClassificationDocument13 pagesTypes of Heat Exchangers ClassificationAbhijit NathNo ratings yet
- Power plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesDocument7 pagesPower plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesMustafam98No ratings yet
- Condenser CondenserDocument36 pagesCondenser Condenserobisonandlaw100% (1)
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design ConsiderationsDocument55 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design ConsiderationsCc12 22tNo ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument26 pagesSteam CondenserPushkar Pandit100% (1)
- Document 1Document4 pagesDocument 1SAMARTHNo ratings yet
- Types of Evaporators Castro EdgarDocument18 pagesTypes of Evaporators Castro EdgarJeshua Llorera100% (1)
- TOCE - Module IIIDocument75 pagesTOCE - Module IIIAnnwin Moolamkuzhi shibuNo ratings yet
- HPLC Heat Exchanger Design PhilosophyDocument28 pagesHPLC Heat Exchanger Design Philosophyagarwalashwin320% (1)
- Power Engineering MicroprojectDocument14 pagesPower Engineering MicroprojectROHANNo ratings yet
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger - PresentationDocument17 pagesShell & Tube Heat Exchanger - Presentationtantri.hellyantiNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower: Presented by Anis Abbas ME-1Document36 pagesCooling Tower: Presented by Anis Abbas ME-1muddasirmasoodNo ratings yet
- CondensorDocument20 pagesCondensorLaka 98No ratings yet
- Chapter One: CondenserDocument10 pagesChapter One: Condenserشاكر العاقل100% (1)
- PHT Unit-5 (THEORY)Document81 pagesPHT Unit-5 (THEORY)521 Balaji ONo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger.Document10 pagesHeat Exchanger.RajarajeswariNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.1 Cooling TowersDocument12 pagesTopic 4.1 Cooling Towersjonnel batuigasNo ratings yet
- Condenser & BoilerDocument33 pagesCondenser & BoilerShaun Patrick Albao100% (1)
- Seminar ON "Heat Pipes"Document15 pagesSeminar ON "Heat Pipes"mantusubudhi100% (4)
- Condensers: Sankar BandyopadhyayDocument37 pagesCondensers: Sankar BandyopadhyayAlidin Gayo100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Cooling Towers Etabs StadDocument33 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cooling Towers Etabs StadMohammed MurtuzaNo ratings yet
- Study of Condenser Performance Evaluation and Measures To Improve ItDocument26 pagesStudy of Condenser Performance Evaluation and Measures To Improve ItPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 100 Things Every Homeowner Must KnowFrom Everand100 Things Every Homeowner Must KnowFamily HandymanNo ratings yet
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Group I Cations: BY: Edang, Andrea Anca Diana, Emmanuel Mapa, Joyce Ragragio, Millaine JoyDocument12 pagesGroup I Cations: BY: Edang, Andrea Anca Diana, Emmanuel Mapa, Joyce Ragragio, Millaine JoyLaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- What is a CondenserDocument13 pagesWhat is a CondenserLaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- SCULPTUREDocument5 pagesSCULPTURELaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- III. Company DescriptionDocument1 pageIII. Company DescriptionLaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- Group Iv Anions: - Distinguish by The Insolubility of Their Silver Salts in Acid SolutionDocument24 pagesGroup Iv Anions: - Distinguish by The Insolubility of Their Silver Salts in Acid SolutionLaine RagragioNo ratings yet
- Onshore Pipeline Engineering: Challenges: Oliver Sokoll - Pipeline Lead EngineerDocument25 pagesOnshore Pipeline Engineering: Challenges: Oliver Sokoll - Pipeline Lead EngineerdanielNo ratings yet
- Pollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Document2 pagesPollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Rakesh Agarwal57% (7)
- Shell Turbo Oil T 46 (MSDS) 1Document7 pagesShell Turbo Oil T 46 (MSDS) 1Anonymous F2TxS3YoaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2Document12 pagesFluid Mechanics 2Acads by NagiNo ratings yet
- PV Commissioning FormDocument31 pagesPV Commissioning FormSimon ChangNo ratings yet
- International Atomic Energy AgencyDocument4 pagesInternational Atomic Energy AgencylibertyngNo ratings yet
- GENED Science1Document78 pagesGENED Science1Mary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument49 pagesChapter 6 PDFJasmineVeenaNo ratings yet
- Instructions To The Candidate Attempt All Questions From Part I (Compulsory)Document5 pagesInstructions To The Candidate Attempt All Questions From Part I (Compulsory)Mehul TholiyaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Knowledge For Sustainable Living PPT 1'Document8 pagesTraditional Knowledge For Sustainable Living PPT 1'Maitri VyasNo ratings yet
- Issuance of Energy Label For Refrigerating Appliances 2023Document23 pagesIssuance of Energy Label For Refrigerating Appliances 2023ASYA ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Innovative approaches to moving lunar regolithDocument63 pagesInnovative approaches to moving lunar regolithWaseem TahirNo ratings yet
- Opportunities and Challenges in CO2 UtilizationDocument23 pagesOpportunities and Challenges in CO2 UtilizationDaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Dta & Dsc01Document22 pagesLecture 6 Dta & Dsc01ZUL KAMARUDDINNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Space EnvironmentDocument9 pagesModule 1 Space EnvironmentPrajwal B NaikNo ratings yet
- Intro Lab Report Biology 091Document2 pagesIntro Lab Report Biology 091Danish Fitri RoslanNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 on the Rise of Industrial PollutionDocument21 pagesQuiz #1 on the Rise of Industrial PollutionGautam SauravNo ratings yet
- Three Futuristic Materials: Super-Hydrophobic Cement, CLT and Hollow Clay BricksDocument3 pagesThree Futuristic Materials: Super-Hydrophobic Cement, CLT and Hollow Clay BricksVrushank WarangNo ratings yet
- Cellular Light Weight ConcreteDocument35 pagesCellular Light Weight ConcreteUTP gamingNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Heat PumpDocument36 pagesRefrigeration & Heat PumpMd. Ahsanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International School Syllabus Plan Term 1 EVMDocument3 pagesCambridge International School Syllabus Plan Term 1 EVMHabiba ElwaselyNo ratings yet
- Tunisian Electric System ProjectDocument10 pagesTunisian Electric System ProjectAchref Ben MabroukNo ratings yet
- Global Culture and Tourism Geography Exam GuideDocument7 pagesGlobal Culture and Tourism Geography Exam GuideHeart Thea PlacidoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument52 pagesUntitledNaima RehanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Degassing Fundamentals R4i1 enDocument6 pagesThermal Degassing Fundamentals R4i1 enAnonymous v5uipHNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Population Changes Over Time in Living SystemsDocument23 pagesMODULE 6 Population Changes Over Time in Living SystemsEdward VicenteNo ratings yet
- Coastal TerminologyDocument54 pagesCoastal TerminologyRam AravindNo ratings yet
- Steam-Utilization Spirax SarcoDocument66 pagesSteam-Utilization Spirax SarcoMauricio Rojas100% (1)
- Hydrologic Cycle and Water Budget EquationDocument14 pagesHydrologic Cycle and Water Budget EquationShafizatulNo ratings yet