Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost of Quality - Session3
Uploaded by
Ritu RajOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost of Quality - Session3
Uploaded by
Ritu RajCopyright:
Available Formats
COST OF QUALITY
Try to understand:
1.Cost of quality
2. Defects classification and
3. Quality cost grid
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 1
Understanding Quality cost:
• Understand quality costs enables you to
– Understand hidden costs
– Reduce and eliminate unnecessary cost
• Prevent problems from happening
• Management responsibility to enable this
• Quality costs are real and estimated at:
– 25% of costs in manufacturing
– 35% of costs in service industry
• Quality costs can be categorised to enable better understanding
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 2
Why to calculate quality cost ?
Management will give special attention when quality is measured in
monetary terms
Quality costing is one of the tools
• to provide initial assessments and hard evidence that improvement is
needed or had been made
• To monitor the effectiveness of quality improvement initiatives
• To be used in a generic term by senior management, shareholders and
financial institutions, so that they can readily understand implication of
quality in the term of money
• Cost of quality failure is calculated as a percentage of profit or annual
turnover
• It is easy to understand
By front-line operator
By middle management
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 3
Benefits of using Quality costing:
1. Greater accuracy in the evaluation and forecasting of resource use
2. Justification for investment in the prevention and appraisal of
failures
3. Ability to cost and compare performance across all departments
functions and activities
4. Identification and prioritization of activities, processes and
departments in terms of corrective action, investment, or quality
improvement initiatives
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 4
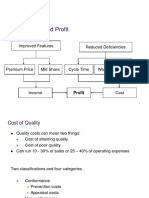
Cost of Quality :
Quality costs are defined as costs associated with non-achievement of
product/service quality. In simple terms, quality cost is the cost of poor
products/services.
The cost of poor quality can add to other costs such as design, production,
maintenance, inspection, sales, etc. Quality costs cross department
boundaries by involving all activities of the organization – marketing,
purchasing, design, manufacturing, service, etc.
The price of nonconformance (Philip Crosby) or the cost of poor quality
(Joseph Juran), the term 'Cost of Quality', refers to the costs associated
with providing poor quality product or service.
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 5
• Phillip B. Crosby (Quality is free . . . ):
• The system for causing quality is prevention, not appraisal –
Quality is Free
• The performance standard must be Zero Defects, not "that's
close enough"
• The measurement of quality is the Price of Non-
conformance.
• Cost of quality is only the measure of operational
performance
• “Quality is free. It’s not a gift, but it is free. What costs
money are the inferior things -- all the actions that involve
not doing jobs right the first time.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 6
TYPES OF QUALITY COST:
Given by Feigenbaum (Originator of ‘Total Quality’
concept)
There are basically three types of quality cost:
1. Prevention Cost
2. Appraisal Cost and
3. Failures cost ( internal & external )
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 7
Prevention Costs
Quality planning costs Training costs
costs of developing and costs of developing and
implementing quality putting on quality training
management program programs for employees and
management
Product-design costs
costs of designing products
with quality characteristics Information costs
costs of acquiring and
Process costs maintaining data related to
costs expended to make sure quality, and development of
productive process reports on quality
conforms to quality performance
specifications
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 8
Examples of prevention Cost
o Application screening o Job descriptions
o Capability studies o Market analysis
o Controlled storage
o Pilot projects
o Design review
o Procedure writing
o Prototype testing
o Equipment maintenance &
o Procedure reviews
repair
o Quality incentives
o Field testing o Safety reviews
o Fixture design and fabrication o Time and motion studies
o Forecasting o Survey
o Housekeeping o Quality training
o salesperson evaluation and selection
o Personnel reviews
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 9
Appraisal Costs
Inspection and testing
costs of testing and inspecting materials, parts, and product at
various stages and at the end of a process
Test equipment costs
costs of maintaining equipment used in testing quality
characteristics of products
Operator costs
costs of time spent by operators to gather data for testing product
quality, to make equipment adjustments to maintain quality, and to
stop work to assess quality
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 10
Examples of appraisal cost
Audit Laboratory test
Document checking Personnel testing
Diagram checking Procedure testing
Equipment calibration Prototype inspection
Final inspection Receiving inspection
In-process inspection Shipping inspection
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 11
Internal Failure Costs
Scrap costs Process downtime costs
costs of poor-quality
products that must be
costs of shutting down
discarded, including labor, productive process to fix
material, and indirect costs problem
Rework costs Price-downgrading costs
costs of fixing defective
products to conform to
costs of discounting poor-
quality specifications quality products—that is,
Process failure costs selling products as
costs of determining why “seconds”
production process is
producing poor-quality
products
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 12
External Failure Costs
Customer complaint costs Product liability costs
costs of investigating and
litigation costs resulting
satisfactorily responding to a from product liability
customer complaint resulting
from a poor-quality product and customer injury
Product return costs Lost sales costs
costs of handling and replacing costs incurred because
poor-quality products returned customers are
by customer dissatisfied with poor
Warranty claims costs quality products and do
costs of complying with product not make additional
warranties purchases
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 13
Summarised as:
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 14
1-10-100 Rule
1
Prevention
10
Correction
100
Failure
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 15
The 1:10:100 rule:
Re.1 spent on prevention will save Rs.10 spent on appraisal and Rs.100 on
failure costs.
One dollar spent on prevention will save $10 on appraisal and $100 on
failure costs.
This rule helps one to prioritize expenditure on prevention, which is sure to
bring in greater returns.
“The earlier you detect and prevent a defect the more you can save. If you
catch a Rs. 2 resistor before you use it and throw it away, you lose Rs. 2. If
you don’t find it until it has been soldered into a computer component, it
may cost Rs.10 to repair the part. If you don’t catch the component until it is
in the computer user’s hands, the repair will cost hundreds of rupees. Indeed,
if a Rs.50000 computer has to be repaired in the field, the expense may
exceed the manufacturing cost.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 16
Difficulties in using Quality costing
Management have not believed in the possibilities of improvement
Quality costing is demanding
◦ It requires a lot of data of each activity related to quality
Other limitations
◦ Does not resolve quality problems
◦ Does not provide specific actions
◦ vulnerable to short-term mismanagement
◦ difficult to match effort and accomplishment
◦ subject to measurement errors
◦ may neglect important or include inappropriate costs
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 17
Steps in implementing quality cost
1. Involve accountants right from the start
2. Decide purpose and objectives
3. Decide how to deal with overheads
4. Distinguish between basic work and quality related activities
5. Collection data which offers the prospect of real gains
6. Start by examining failure costs
7. Evaluate the costs of inspection
8. Analyze and use the data
9. Collecting and reporting quality cost data
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 18
Determine Quality Cost Categories
1. Understand your product
2. Understand your process
3. Understand where problems occur
4. Determine precisely what goes wrong
5. Determine what costs represents each problem
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 19
Quality Management Maturity Grid
Five stages of an organization’s maturity
Six measurement categories
Management understanding and attitude
Quality organization status
Problem handling
Cost of quality as a percent of sales
Quality improvement actions
Characteristic statement
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 20
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 21
Maturity Grid Stage I: Uncertainty
Quality is the responsibility of the quality department
Quality is hidden within manufacturing or engineering; no inspection
Problems are fought as they occur.
The cost of quality is unknown. In reality it is about 20%.
There are no organized quality improvement activities.
“We don’t know why we have problems with quality.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 22
Maturity Grid Stage II: Awakening
While quality management may be valuable, the organization is not
willing to commit resources.
A quality leader is appointed, but the emphasis is on appraisal and
moving the product.
Teams address major problems, but long-range solutions are not
solicited.
The cost of quality is reported at 3%, but is actually 18%.
Activities are limited to short-range, motivational efforts.
“Why do we always have problems with quality?”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 23
Maturity Grid Stage III: Enlightenment
Management adopts a supportive and helpful stance.
Quality is elevated to a functional level equivalent to engineering,
marketing, etc.
Problems are resolved openly and in an orderly way.
The cost of quality is reported as 8%, though it is really about 12% of
sales.
The fourteen-step quality improvement program is implemented.
“We are identifying and resolving our problems.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 24
Maturity Grid Stage IV: Wisdom
Top management participates in and understands quality.
The quality manager is an officer of the company.
Problems are identified in early development.
The cost of quality is reported as 6.5%. It may be 8%.
The quality improvement program is continual and accompanied by
follow-up training.
“Defect prevention is a routine part of our operation.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 25
Maturity Grid Stage V: Certainty
Quality is an essential part of the organization.
A quality manager serves on the board of directors.
Problems are prevented.
The cost of quality is reported as 2.5%, which is what it really is.
Quality improvement is normal and continual.
“We know why we do not have problems with quality.”
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 26
QUESTIONS ?
Cost of quality by Jayant Choudhary 27
You might also like
- The Cost of QualityDocument20 pagesThe Cost of QualityMariesz PleytoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Project Quality ManagementDocument29 pagesLecture 6 - Project Quality ManagementZain GhummanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TQMDocument41 pagesChapter 2 TQMana panesNo ratings yet
- The-Cost-of-QualityDocument20 pagesThe-Cost-of-Qualitymdogayo5No ratings yet
- 3-COSTS OF QUALITYDocument19 pages3-COSTS OF QUALITYKAMPARA MANOHAR 122010318056No ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument43 pagesCost of QualityDhinakaranNo ratings yet
- IPE 4205: Quality Management: Rezaul Karim Nayeem Assistant Professor (IPE Discipline) Department of MPE, AUSTDocument16 pagesIPE 4205: Quality Management: Rezaul Karim Nayeem Assistant Professor (IPE Discipline) Department of MPE, AUSTnorbik idrisNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Prepared By: Khalid Dahleez Faculty of Commerce - The Islamic University of GazaDocument41 pagesTotal Quality Management: Prepared By: Khalid Dahleez Faculty of Commerce - The Islamic University of Gazavimal Negi100% (1)
- QUALITY CONTROL ASSURANCEDocument117 pagesQUALITY CONTROL ASSURANCENarendra100% (1)
- Managing Quality: Operations Management R. Dan Reid & Nada R. SandersDocument24 pagesManaging Quality: Operations Management R. Dan Reid & Nada R. SandersFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- Construction Methods and Managenent: Assignment-IDocument8 pagesConstruction Methods and Managenent: Assignment-INiroj MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Quality Quality Tools - ShowDocument71 pagesQuality Quality Tools - ShowAbhijeet RandhirNo ratings yet
- Peration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleDocument24 pagesPeration Anagement: Concept of Quality Juran's PrincipleAyushi BisenNo ratings yet
- Are The Costs of Performing Control ActivitiesDocument2 pagesAre The Costs of Performing Control ActivitiesLee Jeon KimNo ratings yet
- 011 Icemm2013 P00017Document5 pages011 Icemm2013 P00017nandiniNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management and Just-In-Time Production SystemDocument30 pagesTotal Quality Management and Just-In-Time Production SystemJannibee EstreraNo ratings yet
- Quality Cost: by Dr. Lawrence WongDocument23 pagesQuality Cost: by Dr. Lawrence WongAtif Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Modern Business Environment and Total Quality ManagementDocument13 pagesModern Business Environment and Total Quality ManagementCA Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument18 pagesCost of QualityTumma RamaraoNo ratings yet
- Mgt6 Module 3 TQMDocument73 pagesMgt6 Module 3 TQMEzra HuelgasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - QualityDocument81 pagesChapter 5 - QualityThư Trần Nguyễn AnhNo ratings yet
- INFINITY - PMP 05 - QualityDocument22 pagesINFINITY - PMP 05 - QualityOmar KhaledNo ratings yet
- Slide DeckDocument45 pagesSlide Deckpranjal.mathurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quality ManagementDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Quality Managementsadat.samit1No ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument88 pagesQuality ManagementAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Quality Management and Control: Ataklty Adugna (Ass. Professor)Document49 pagesChapter - 6 Quality Management and Control: Ataklty Adugna (Ass. Professor)yared haftuNo ratings yet
- PQM Lecture 1Document29 pagesPQM Lecture 1Muhammad Fahad RazaNo ratings yet
- Quality Project Management: Part-2 Cost of QualityDocument40 pagesQuality Project Management: Part-2 Cost of Qualitytasneem isamNo ratings yet
- Quality Management - ShahnawazDocument16 pagesQuality Management - ShahnawazShahnawaz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- EM416 Cost of QualityDocument24 pagesEM416 Cost of QualityYao SsengssNo ratings yet
- SCORE Productivity Training Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: - Sustaining Competitive and Responsible EnterprisesDocument110 pagesSCORE Productivity Training Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: - Sustaining Competitive and Responsible EnterprisesAweke ZewduNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Quality Assurance in Textile IndustryDocument46 pagesQuality Control and Quality Assurance in Textile IndustryHabtamu SitotawNo ratings yet
- Topic 6.0: Quality Cost: Prepared By: Zainal Abidin Bin Ab. Kasim Noor Hapizah Binti AbdullahDocument12 pagesTopic 6.0: Quality Cost: Prepared By: Zainal Abidin Bin Ab. Kasim Noor Hapizah Binti AbdullahA LishaaaNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument21 pagesCost of Qualitymuneerpp100% (4)
- Managing quality and logisticsDocument75 pagesManaging quality and logisticsJoost VerheyenNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument33 pagesCost of QualitydrrajputNo ratings yet
- 3 QualityDocument45 pages3 QualityAyush KishoreNo ratings yet
- Quality, Quality Control and Quality ManagementDocument91 pagesQuality, Quality Control and Quality Managementsaurabh das100% (1)
- 1415J M - Sesi 09 10 - Akuntansi Manajemen - Topik KhususDocument58 pages1415J M - Sesi 09 10 - Akuntansi Manajemen - Topik KhususAnonymous yMOMM9bsNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management ExplainedDocument17 pagesTotal Quality Management Explainedsaniaiqbal6No ratings yet
- CH 6 Quality ManagementDocument44 pagesCH 6 Quality ManagementYaredNo ratings yet
- Operations Management and Quality: Instructor Lecture PowerpointsDocument71 pagesOperations Management and Quality: Instructor Lecture PowerpointstheintelligentgirlNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument1 pageCost of QualityanasNo ratings yet
- Software Quality AssuranceDocument30 pagesSoftware Quality AssuranceSYED SUMAIR AHMED JAFFRINo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management - OverviewDocument20 pagesProject Quality Management - Overviewbobby indaeyoNo ratings yet
- Quality+Statistical ProcessDocument173 pagesQuality+Statistical ProcessAyush KishoreNo ratings yet
- Quality Service DimensionsDocument22 pagesQuality Service DimensionsAlexAndriaVillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Quality Management FundamentalsDocument33 pagesQuality Management FundamentalsHabtamu SitotawNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Management For Continuous ImprovementDocument25 pagesQuality Management Management For Continuous ImprovementMahfuzulNo ratings yet
- Various Cost of QualityDocument36 pagesVarious Cost of Qualityiqac.ncbNo ratings yet
- Cost of Quality - TRG MatDocument36 pagesCost of Quality - TRG MatRohit Tripathi100% (1)
- Introduction to Quality Control and Customer SatisfactionDocument22 pagesIntroduction to Quality Control and Customer SatisfactionSakeena Naureen Ashraf100% (1)
- Cost of QualityDocument11 pagesCost of QualityZNo ratings yet
- Profitbaility Through QualityDocument27 pagesProfitbaility Through QualityAvantika SinghNo ratings yet
- 01 Quality Principles in Nutshell Part IDocument13 pages01 Quality Principles in Nutshell Part IKapildev100% (2)
- 5-Operations Management-Chapter SixDocument44 pages5-Operations Management-Chapter SixAbdiNo ratings yet
- Cost of Quality: Quality Costs and ProfitDocument5 pagesCost of Quality: Quality Costs and ProfitrahulNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management: Goal 2Document34 pagesTotal Quality Management: Goal 2Samuel ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cost of Quality in Healthcare - A Case Study in A Clinical LaboratoryDocument13 pagesCost of Quality in Healthcare - A Case Study in A Clinical Laboratoryloan.vuNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma - Session 7Document13 pagesSix Sigma - Session 7Ritu RajNo ratings yet
- 5S - Session 9Document19 pages5S - Session 9Ritu RajNo ratings yet
- 5S - Session 9Document19 pages5S - Session 9Ritu RajNo ratings yet
- Ucb Brand PerformanaceDocument23 pagesUcb Brand PerformanaceRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Final Compiled PPT BangleDocument21 pagesFinal Compiled PPT BangleRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Ucb Brand PerformanaceDocument23 pagesUcb Brand PerformanaceRitu RajNo ratings yet
- 5s Lean ToolDocument11 pages5s Lean ToolRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Final Compiled PPT BangleDocument21 pagesFinal Compiled PPT BangleRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma - Session 7Document13 pagesSix Sigma - Session 7Ritu RajNo ratings yet
- Brand Personality of Zara & H&MDocument2 pagesBrand Personality of Zara & H&MRitu Raj0% (1)
- 3.5B Liters of Water Saved: Since Introducing Water Less® in 2011Document3 pages3.5B Liters of Water Saved: Since Introducing Water Less® in 2011Ritu RajNo ratings yet
- Social Media StrategiesDocument10 pagesSocial Media StrategiesRitu RajNo ratings yet
- NIFT Patna assignment explores strategic management examplesDocument8 pagesNIFT Patna assignment explores strategic management examplesRitu RajNo ratings yet
- History of Indian Carpet IndustryDocument14 pagesHistory of Indian Carpet IndustryRitu Raj100% (1)
- Bhaglpuri Silk SareeDocument4 pagesBhaglpuri Silk SareeRitu RajNo ratings yet
- LevisDocument1 pageLevisRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Bhaglpuri Silk SareeDocument4 pagesBhaglpuri Silk SareeRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Excercise 1: Developing A Competitive Profile Matrix For My University PurposeDocument2 pagesExcercise 1: Developing A Competitive Profile Matrix For My University PurposeRitu RajNo ratings yet
- AMUL'S Every Function Involves Huge Human ResourcesDocument3 pagesAMUL'S Every Function Involves Huge Human ResourcesRitu RajNo ratings yet
- NIFT Patna assignment explores strategic management examplesDocument8 pagesNIFT Patna assignment explores strategic management examplesRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Excercise 1: Developing A Competitive Profile Matrix For My University PurposeDocument2 pagesExcercise 1: Developing A Competitive Profile Matrix For My University PurposeRitu RajNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis On State of West Bengal V. Anwar Ali Sarkar: Nivedita GulianiDocument9 pagesCase Analysis On State of West Bengal V. Anwar Ali Sarkar: Nivedita Gulianiamulya kaushikNo ratings yet
- Bcom - Part 1Document43 pagesBcom - Part 1Hamza Ali KhalidNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report InternshipDocument5 pagesWeekly Report InternshipKebe DeNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Val - Ed. Prof. Standards & Prof. EthicsDocument6 pagesQuiz-Val - Ed. Prof. Standards & Prof. EthicsJoyce Ann CortezNo ratings yet
- ICT in EducationDocument9 pagesICT in EducationIts ShaafNo ratings yet
- Playtime, Downtime, and Family Time: PDF For Elementary-Aged KidsDocument1 pagePlaytime, Downtime, and Family Time: PDF For Elementary-Aged KidsFoganholoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Pratice Worplace CommunicationDocument80 pages1.1 Pratice Worplace CommunicationEmelson VertucioNo ratings yet
- Client feedback improves DOLE servicesDocument1 pageClient feedback improves DOLE servicesAngelica Gallos - Madija0% (1)
- Altis Little Havana - UDRB Plan SetDocument63 pagesAltis Little Havana - UDRB Plan SetNone None None100% (2)
- Project Management Termination MethodsDocument12 pagesProject Management Termination MethodsQasim RehmanNo ratings yet
- 998 2296 1 PBDocument20 pages998 2296 1 PBAriestoni SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Commercial Air Transport OperationsDocument288 pagesCommercial Air Transport OperationsSam HoNo ratings yet
- A Brief Compendium of One Day History National Seminar:18-01-2019Document20 pagesA Brief Compendium of One Day History National Seminar:18-01-2019cbkNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric ArtDocument3 pagesPrehistoric ArtTin AcidreNo ratings yet
- The Case of Lester Coltman-Lilian WalbrookDocument115 pagesThe Case of Lester Coltman-Lilian WalbrookmichaelcadNo ratings yet
- Edup2132 - Tutorial Task Week 10Document8 pagesEdup2132 - Tutorial Task Week 10syeerNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet-EAPPDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet-EAPPJeanicar Culi - AsiñasNo ratings yet
- Community Service and Duval County Public Schools 10-16Document7 pagesCommunity Service and Duval County Public Schools 10-16mortensenkNo ratings yet
- Kenworth MotorDocument2 pagesKenworth MotorRizky WinandaNo ratings yet
- 2525 Final Families For Justice Submissions 07JAN2019Document58 pages2525 Final Families For Justice Submissions 07JAN2019suzan fraserNo ratings yet
- 1 An Evolving Map of Design Practice and Design ResearchDocument7 pages1 An Evolving Map of Design Practice and Design ResearchAna PeraltaNo ratings yet
- The Four Major Conceptional Blocks in Problem SolvingDocument10 pagesThe Four Major Conceptional Blocks in Problem Solvingapi-281199790No ratings yet
- Monitoring Learners ProgressDocument6 pagesMonitoring Learners ProgressIsrael BualNo ratings yet
- Rle Grade Sheet: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityDocument3 pagesRle Grade Sheet: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityZahra jane A.No ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World: Self and Peer AssessmentDocument9 pages21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World: Self and Peer AssessmentMarq Qo100% (5)
- Rya VHF SRC Radio Course Details v1Document11 pagesRya VHF SRC Radio Course Details v1d.srdjan6829No ratings yet
- Ten Characteristics Adults-LearnersDocument4 pagesTen Characteristics Adults-Learnersapi-353014166No ratings yet
- Internet Filtering FOIDocument130 pagesInternet Filtering FOITJ McIntyreNo ratings yet
- Prophet S Agenda The Divine Plan of The AgesDocument3 pagesProphet S Agenda The Divine Plan of The Agesbroadband_dryfter100% (1)
- Modello Risk and Issues Management ToolDocument6 pagesModello Risk and Issues Management ToolaNo ratings yet