Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Composite Climate
Uploaded by
Ratnesh Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views7 pagesOriginal Title
214100680-Composite-Climate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views7 pagesComposite Climate
Uploaded by
Ratnesh PatelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
HIGH
PERFORMANCE
BUILDING IN
COMPOSITE
CLIMATE
COMPOSITE
Ar. Kruti Desai
Master’s of Urban and Regional
Planning (cont.)
Factors affecting Climate
1) Latitude (distance from the equator),
2) Altitude (height above sea level),
3) Topography (surface features),
4) Distance from oceans and large lakes,
5) The circulation of the air.
Accordingly, there are 5 major types of climates:
1) Hot and Dry
2) Warm and Humid
3) Cold and Dry
4) Composite
5) Moderate
Composite climate
In India most of the
region falls under 2 types
of climate: composite
and hot and dry
The only difference
between and hot and dry
climate is Composite
regions experience
Composite higher humidity levels
during monsoons.
characteristics of the composite climate
1) Ambient Temperature: Summer: 32-43°C during day and 27-32°C at night
Winter: 10-25 °C during day and 4-10 °C at night.
2) Relative humidity: 20-25 % in dry periods and 55-95% in wet periods.
3) Precipitation: 500-1300mm Per year
4) Winds: Summer: Winds are hot and dusty
Winter: Dry cold winds from the north east
Monsoon: Strong winds from the south east
5) Sky condition: Summer: occasional haze;
Winter: clear;
Monsoon: overcast and dull
HIGH PERFORMANCE BUILDINGS
According to Energy Policy Act of 2005 (Public Law 109-058),
“High performance building” means a building that integrates and
optimizes all major high-performance building attributes, including
energy efficiency, durability, life-cycle performance, and occupant
productivity.
Basic needs for high performance building:
Climate sensitive architecture
Use of Eco friendly materials
Energy efficient design
Preservation of natural eco system
Use of renewable energy
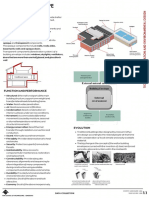
Design Features
Appropriate
Use
Walls
Roof
Thick
Pergolas
ofinsulation
Water and
walls/
treesglass
Courtyards,
bodies as
orientation
cavity
wind
wind
for surface
walls/
barriers
and
protected
andjali/
evaporative
towers shapehollow
by
of
cooling
other thebrick
building
openings walls
overhangs,
White or anyfins andcoloured
light trees exterior surface
Use of Passive means rather than active
means
Passive design strategies Indirect cooling includes
ventilation and stack effect and venture effect, roof pond,
earth air tunnel, courtyards and wind scoops and wind
towers.
You might also like
- Composite ClimateDocument7 pagesComposite ClimateManthan20% (5)
- 8.energy Effienct BuidingDocument7 pages8.energy Effienct BuidingmariyaNo ratings yet
- 1.intro To Climatology, Macro-Micro ClimateDocument25 pages1.intro To Climatology, Macro-Micro ClimateAsish Baraili100% (1)
- "The Purpose of A Building Is To Perform A Function " (Salvadori, 1990)Document15 pages"The Purpose of A Building Is To Perform A Function " (Salvadori, 1990)junnie boyNo ratings yet
- Design Strategies For Composite ClimateDocument13 pagesDesign Strategies For Composite Climatemariya100% (2)
- ARC 228 Building climat-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesARC 228 Building climat-WPS OfficeolajumokekvNo ratings yet
- Climatology NotesDocument13 pagesClimatology NotesolajumokekvNo ratings yet
- ClimatologyDocument23 pagesClimatologyShouryaGoswamiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Passive Design With ClimateDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Passive Design With ClimateZHI YI SOONo ratings yet
- Climatologypresentation 1 120116135348 Phpapp02Document26 pagesClimatologypresentation 1 120116135348 Phpapp02Sagar Arora100% (1)
- Roof Insulation SpecsDocument14 pagesRoof Insulation SpecsRajesh BalachanderNo ratings yet
- Establishing Thermal ComfortDocument12 pagesEstablishing Thermal ComfortShahruzi MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Exterior Wall Solutions For Hot Humid Climates PDFDocument12 pagesExterior Wall Solutions For Hot Humid Climates PDFBogdan MucenicaNo ratings yet
- The Climatological, Ecological, Solar and Wind Considerations, Day Lighting in Architectural DesignDocument25 pagesThe Climatological, Ecological, Solar and Wind Considerations, Day Lighting in Architectural DesignAr Frank EpeNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Design Strategies in Hot-Dry AreaDocument22 pagesEnergy Efficient Design Strategies in Hot-Dry AreaKapil AroraNo ratings yet
- ABT Chapter 4 FourDocument23 pagesABT Chapter 4 FourMicky AlemuNo ratings yet
- Uc in ConstructionDocument5 pagesUc in ConstructioncpcbsktNo ratings yet
- Macro and MicroDocument4 pagesMacro and Micronaina dakshNo ratings yet
- Lec - 2 - Buildings and ClimateDocument53 pagesLec - 2 - Buildings and ClimateLaila AlqaisiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Performance of Exposed Composed Roofs in Very Hot Dry Desert Region in Egypt (Toshky)Document11 pagesThermal Performance of Exposed Composed Roofs in Very Hot Dry Desert Region in Egypt (Toshky)Anas Khalid TahirNo ratings yet
- Micro ClimateDocument12 pagesMicro ClimateROSHANI TIWARINo ratings yet
- Unit I - Macroclimate and Microclimate PDFDocument27 pagesUnit I - Macroclimate and Microclimate PDFujjwal kaulNo ratings yet
- Siniat Whitepaper Ventilated Facade System and Rigid Air Barriers FinalDocument8 pagesSiniat Whitepaper Ventilated Facade System and Rigid Air Barriers FinalRobert WuNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro ClimateDocument35 pagesMacro and Micro ClimateKapil Arora100% (2)
- Building EnvelopeDocument56 pagesBuilding EnvelopehamnahricoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Climatology & It'S Effect On Shelter: Compiled byDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Climatology & It'S Effect On Shelter: Compiled bynikita100% (1)
- Warm Humid Moderate ClimateDocument58 pagesWarm Humid Moderate ClimateDeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation COMPOSITEDocument24 pagesPresentation COMPOSITEAashi SoniNo ratings yet
- High Performance Building in Composite Climate PDFDocument37 pagesHigh Performance Building in Composite Climate PDFrashmigodhaNo ratings yet
- Hvac GreenDocument201 pagesHvac GreenShiyamraj ThamodharanNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro ClimateDocument5 pagesMacro and Micro ClimateAman ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Conventional Planning Considerations On Solar Architecture Modification of Microclimate Through Landscape Elements For Energy ConservationDocument17 pagesImpact of Conventional Planning Considerations On Solar Architecture Modification of Microclimate Through Landscape Elements For Energy ConservationIna RoseNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 9 - Building Envelope With Green Building CodeDocument38 pagesLECTURE 9 - Building Envelope With Green Building CodeKhyverAndreiAmadorNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Landscaping Case Study - NCR HighDocument19 pagesEnergy Efficient Landscaping Case Study - NCR HighDheeshna DileepNo ratings yet
- Urban ClimateDocument32 pagesUrban ClimateRitika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Composite ClimateDocument40 pagesComposite ClimateVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Building EnvelopeDocument19 pagesBuilding EnvelopeDivyanshu ThakurNo ratings yet
- Artrodes Module #11 (General Concepts, Low-Rise Design) A) Locations On Slopes, Hills and in ValleysDocument17 pagesArtrodes Module #11 (General Concepts, Low-Rise Design) A) Locations On Slopes, Hills and in ValleysJamandre, Joseph M.No ratings yet
- Assingment 1 - Ria Gurbani 16031Document16 pagesAssingment 1 - Ria Gurbani 16031Ria GurbaniNo ratings yet
- SRIJANA GOJA SHRESTHA (079MSEEB016) Article To PrintDocument5 pagesSRIJANA GOJA SHRESTHA (079MSEEB016) Article To PrintSrijana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Composite ClimateDocument49 pagesComposite ClimateDhopesor hazarikaNo ratings yet
- RSW 1 TropicalDocument30 pagesRSW 1 TropicalArphy Renz Gavina MenesesNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects in Warm and Humid ClimateDocument50 pagesEnvironmental Aspects in Warm and Humid ClimateRafiq FitriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document34 pagesUnit 1Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- High Performance Building in Composite ClimateDocument37 pagesHigh Performance Building in Composite ClimateAarti Yadav92% (60)
- Macroclimate and MicroclimateDocument21 pagesMacroclimate and MicroclimateHello YouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Building Climatology - Chapter 11 - Design in The Zones OCR PDFDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Building Climatology - Chapter 11 - Design in The Zones OCR PDFsherin greenal100% (1)
- Climatic DesignDocument5 pagesClimatic DesignJoji BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Wind Loads of Structures: Figure 1: BuildingDocument6 pagesWind Loads of Structures: Figure 1: Buildingadeel raziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 (Prima DomusDocument34 pagesChapter 1-3 (Prima DomusMaire Joy E. AzañaNo ratings yet
- Composite Climate-Cost Effective ConstructionDocument33 pagesComposite Climate-Cost Effective ConstructionRiya Elizabeth Raju100% (1)
- Natural Cooling of Residential Buildings in Hot-Dry ClimateDocument11 pagesNatural Cooling of Residential Buildings in Hot-Dry ClimatePoojaManjunathNo ratings yet
- What Is Building Envelope ?: Function and PerformanceDocument7 pagesWhat Is Building Envelope ?: Function and PerformanceSumi MathewNo ratings yet
- Climate & Architecture: Prepared By: Prof.P.Eswara RaoDocument20 pagesClimate & Architecture: Prepared By: Prof.P.Eswara RaoBekkyNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Roofs For Warm Humid Climates - A Case Study in Residential Buildings in Madurai, Tamilnadu, IndiaDocument14 pagesSustainable Roofs For Warm Humid Climates - A Case Study in Residential Buildings in Madurai, Tamilnadu, Indiamadhu100% (1)
- Porous Paving: Advantages and LimitationsDocument7 pagesPorous Paving: Advantages and LimitationsmariyaNo ratings yet
- CLIMATEDocument8 pagesCLIMATERhona CantagoNo ratings yet
- Airtightness 1Document3 pagesAirtightness 1bhusalgeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal InsulationDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Thermal InsulationMUGHIL P - ANo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument8 pagesBeam DesignFaraaz FaisalNo ratings yet
- MCQs Consumer Behavior PDFDocument25 pagesMCQs Consumer Behavior PDFganeshital62% (13)
- ENGR 2140 Sign ConventionsDocument10 pagesENGR 2140 Sign ConventionsarjunNo ratings yet
- We Are Hiring - Deputy Project Manager (Structure) PDFDocument1 pageWe Are Hiring - Deputy Project Manager (Structure) PDFRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- WallfinishesDocument16 pagesWallfinishesRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Gamble (IC) Chapter 1Document34 pagesGamble (IC) Chapter 1MureinNo ratings yet
- 20203010-Programme Brochure-PGP-MECCC PDFDocument4 pages20203010-Programme Brochure-PGP-MECCC PDFRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Slab Design Excel SheetDocument8 pagesSlab Design Excel SheetRajat GargNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design Excel SheetDocument16 pagesConcrete Design Excel SheetCleth Hiren Santos25% (4)
- Aymen Mohamed Elmagalfta (KHK) (NN24) PDFDocument47 pagesAymen Mohamed Elmagalfta (KHK) (NN24) PDFChristian Daiva100% (2)
- Slab Design Excel SheetDocument8 pagesSlab Design Excel SheetRajat GargNo ratings yet
- Flooring - FinalllDocument63 pagesFlooring - FinalllRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- RCC Two Way Slab BS 8110Document9 pagesRCC Two Way Slab BS 8110sourabdaroch100% (1)
- Fee Structure 2020 2024 Batch - Final PDFDocument1 pageFee Structure 2020 2024 Batch - Final PDFRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Floor FinishesDocument20 pagesFloor FinishesRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Concrete Design Excel SheetDocument16 pagesConcrete Design Excel SheetCleth Hiren Santos25% (4)
- FileHandler PDFDocument48 pagesFileHandler PDFDeepak YadavNo ratings yet
- Finishing. MATERIALSDocument98 pagesFinishing. MATERIALSRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- MCQ For StructureDocument4 pagesMCQ For StructureRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument8 pagesBeam DesignFaraaz FaisalNo ratings yet
- Veneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardDocument23 pagesVeneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Finishing. MATERIALSDocument98 pagesFinishing. MATERIALSRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Flooring - FinalllDocument63 pagesFlooring - FinalllRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Certificate For Medical Fitness PDFDocument1 pageCertificate For Medical Fitness PDFSwaroop VasistaNo ratings yet
- Veneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardDocument23 pagesVeneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Floor FinishesDocument20 pagesFloor FinishesRatnesh Patel100% (1)
- Cladding: Ketan Anwesha Mohith Building Construction and MaterialsDocument26 pagesCladding: Ketan Anwesha Mohith Building Construction and MaterialsRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Wallfinishes2 150121010354 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument27 pagesWallfinishes2 150121010354 Conversion Gate01 PDFRatnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Ight Mitting Iodes: Presentation OnDocument34 pagesIght Mitting Iodes: Presentation OnsixfacerajNo ratings yet
- IMDSI22Document82 pagesIMDSI22Dang JinlongNo ratings yet
- Web-Based Attendance Management System Using Bimodal Authentication TechniquesDocument61 pagesWeb-Based Attendance Management System Using Bimodal Authentication TechniquesajextopeNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument29 pagesPreviewpdfSoemarlan ErlanNo ratings yet
- Coal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcreteDocument9 pagesCoal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcretexxqNo ratings yet
- John Wren-Lewis - NDEDocument7 pagesJohn Wren-Lewis - NDEpointandspaceNo ratings yet
- Rights of Parents in IslamDocument11 pagesRights of Parents in Islamstoneage989100% (2)
- Week - 2 Lab - 1 - Part I Lab Aim: Basic Programming Concepts, Python InstallationDocument13 pagesWeek - 2 Lab - 1 - Part I Lab Aim: Basic Programming Concepts, Python InstallationSahil Shah100% (1)
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousNatalia SalinasNo ratings yet
- Community Architecture Concept PDFDocument11 pagesCommunity Architecture Concept PDFdeanNo ratings yet
- Jpedal ManualDocument20 pagesJpedal ManualDamián DávilaNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Online TestingDocument6 pagesEmbedded Systems Online TestingPuspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Limitations of BEPDocument2 pagesBenefits and Limitations of BEPAnishaAppuNo ratings yet
- Guided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaDocument9 pagesGuided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Accounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesDocument7 pagesAccounting Students' Perceptions On Employment OpportunitiesAquila Kate ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationDocument28 pagesThe Body Shop Case Analysis. The Challenges of Managing Business As Holistic ConfigurationHanna AbejoNo ratings yet
- Loop Types and ExamplesDocument19 pagesLoop Types and ExamplesSurendran K SurendranNo ratings yet
- Animal Health ChecklistDocument4 pagesAnimal Health ChecklistcapsfastNo ratings yet
- G1000 Us 1014 PDFDocument820 pagesG1000 Us 1014 PDFLuís Miguel RomãoNo ratings yet
- International Freight 01Document5 pagesInternational Freight 01mature.ones1043No ratings yet
- 1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementDocument10 pages1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementrohaizadNo ratings yet
- Riqas Ri RQ9142 11aDocument6 pagesRiqas Ri RQ9142 11aGrescia Ramos VegaNo ratings yet
- Toshiba MotorsDocument16 pagesToshiba MotorsSergio Cabrera100% (1)
- 1500 Series: Pull Force Range: 10-12 Lbs (44-53 N) Hold Force Range: 19-28 Lbs (85-125 N)Document2 pages1500 Series: Pull Force Range: 10-12 Lbs (44-53 N) Hold Force Range: 19-28 Lbs (85-125 N)Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- RECYFIX STANDARD 100 Tipe 010 MW - C250Document2 pagesRECYFIX STANDARD 100 Tipe 010 MW - C250Dadang KurniaNo ratings yet
- A Teachers' Journey: Phenomenological Study On The Puritive Behavioral Standards of Students With Broken FamilyDocument11 pagesA Teachers' Journey: Phenomenological Study On The Puritive Behavioral Standards of Students With Broken FamilyNova Ariston100% (2)
- The Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (Document34 pagesThe Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (mark_schwartz_41No ratings yet
- [18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing CountriesDocument15 pages[18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing Countrieslohithsarath bethalaNo ratings yet
- Play ClawDocument2 pagesPlay ClawFrenda SeivelunNo ratings yet
- 160kW SOFT STARTER - TAP HOLE 1Document20 pages160kW SOFT STARTER - TAP HOLE 1Ankit Uttam0% (1)
- Multimedia System DesignDocument95 pagesMultimedia System DesignRishi Aeri100% (1)










































































































![[18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing Countries](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/422064728/149x198/344a5742a7/1565947342?v=1)


