Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Diarrheal
Uploaded by
shaitabligan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesAntidiarrheal drugs work to relieve diarrhea symptoms by several mechanisms: adsorbents bind to and neutralize toxins, antimotility agents slow intestinal movement, and probiotics interfere with pathogenic organisms. Examples of adsorbents include kaolin, pectin, and bismuth subsalicylate, while opioids like loperamide and anticholinergics are antimotility agents. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Saccharomyces boulardii compete with pathogens in the GI tract. Special considerations for these drugs include allergies, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and limited use during pregnancy.
Original Description:
Original Title
anti diarrheal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAntidiarrheal drugs work to relieve diarrhea symptoms by several mechanisms: adsorbents bind to and neutralize toxins, antimotility agents slow intestinal movement, and probiotics interfere with pathogenic organisms. Examples of adsorbents include kaolin, pectin, and bismuth subsalicylate, while opioids like loperamide and anticholinergics are antimotility agents. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Saccharomyces boulardii compete with pathogens in the GI tract. Special considerations for these drugs include allergies, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and limited use during pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesAnti Diarrheal
Uploaded by
shaitabliganAntidiarrheal drugs work to relieve diarrhea symptoms by several mechanisms: adsorbents bind to and neutralize toxins, antimotility agents slow intestinal movement, and probiotics interfere with pathogenic organisms. Examples of adsorbents include kaolin, pectin, and bismuth subsalicylate, while opioids like loperamide and anticholinergics are antimotility agents. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Saccharomyces boulardii compete with pathogens in the GI tract. Special considerations for these drugs include allergies, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and limited use during pregnancy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Anti-Diarrheal Drugs
Antidiarrheal drug, any drug that relieves symptoms of
diarrhea, the frequent passage of a watery loose stool. In
general, the antidiarrheal drugs may be divided into
different groups based on chemical or functional
similarities; these groups include adsorbents, antimotility
agents, and bacterial replacements (probiotics).
These agents are thought to work by binding to and thereby
neutralizing the actions of diarrhea-causing toxins that are
produced by infectious agents or by preventing the adherence
of infectious agents to the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
Examples of adsorbents used in the treatment of diarrhea
include kaolin, pectin, activated charcoal, attapulgite
(aluminum silicate), and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol).
Opioids, such as codeine and loperamide (Imodium), and anticholinergic drugs,
such as dicyclomine and atropine.
The opiate derivative diphenoxylate typically is given with atropine in a
combination marketed as Lomotil. Although opioids carry a risk of dependency
and addiction, codeine and the synthetic analogs diphenoxylate and loperamide
produce little dependence, and they have been used successfully for diarrhea.
Probiotics consist of harmless organisms that interfere with the colonization of
the gastrointestinal tract by pathogenic (disease-causing) organisms. Probiotics
commonly used in the treatment of diarrhea include commercial preparations of
the bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus and the yeast Saccharomyces boulardii.
Special Considerations
Before taking anti-diarrheal drugs, tell your doctor
if you are allergic to it.
Antibiotics may rarely cause a severe intestinal
condition(clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea)
During pregnancy, this medication should be used
only if clearly needed.
You might also like
- GI Effects IGDocument12 pagesGI Effects IGAngelo Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument38 pagesCoronary Artery Diseaseshaitabligan100% (2)
- ProbioticsDocument26 pagesProbioticsShnabay DaryaNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]From EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: DR Binod Raut MD Pharmacology KMCDocument44 pagesPharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: DR Binod Raut MD Pharmacology KMCAakash JhaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFDocument5 pagesDrug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFmeeraNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument28 pagesMyocardial Infarctionshaitabligan100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemDocument4 pagesPharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemZaira KimNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument33 pagesSeminarTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 13 ProbioticsDocument29 pages13 ProbioticsChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- 19 Probiotics PrebioticsDocument22 pages19 Probiotics PrebioticsGâtlan Lucian100% (1)
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument21 pagesBronchial AsthmashaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Prebiotic and ProbioticDocument5 pagesPrebiotic and ProbioticIshan GhaiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Drugs: Prof. Dr. Muhammad Ashraf Dean FBS Professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology UVAS, LahoreDocument33 pagesGastrointestinal Drugs: Prof. Dr. Muhammad Ashraf Dean FBS Professor of Pharmacology and Toxicology UVAS, LahoreMuhammad Shahid BilalNo ratings yet
- AntidiarrhoealDocument16 pagesAntidiarrhoealSuraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Workman: Understanding Pharmacology: Chapter 20: Drugs For Gastric Ulcers and Reflux Audio Key PointsDocument3 pagesWorkman: Understanding Pharmacology: Chapter 20: Drugs For Gastric Ulcers and Reflux Audio Key PointsMohammed AbusbeihNo ratings yet
- Taniya ChemDocument30 pagesTaniya ChemTaniyaNo ratings yet
- Anti DiarrheaDocument40 pagesAnti DiarrheaNofilia Citra CandraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Ulcer AgentsDocument8 pagesAnti-Ulcer AgentsKnight DevilNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDocument49 pagesGastrointestinal DrugsMae Antonette OrlinaNo ratings yet
- Git Pharmacology: Eduviere A.TDocument25 pagesGit Pharmacology: Eduviere A.TOmaraye JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Digestive Disorders PDFDocument41 pagesDrugs For Digestive Disorders PDFNoreak SokNo ratings yet
- Anti DiarrheaDocument3 pagesAnti DiarrheaGrijehNo ratings yet
- Zinobacilly Final TrainingDocument12 pagesZinobacilly Final TrainingShima ElshewyNo ratings yet
- Antidiarrheal DrugsDocument7 pagesAntidiarrheal Drugsmwaithira71682No ratings yet
- GIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument5 pagesGIT Drugs I. Drugs That Promote Upper Gastrointestinal MotilityEli Ezer SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Anti Diarrheal DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Diarrheal DrugsKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Antacid, Ulcer Healing Drugs and Ulcer Protective DrugsDocument42 pagesAntacid, Ulcer Healing Drugs and Ulcer Protective DrugsSuraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal, Endocrine and Renal SystemsDocument35 pagesDrugs Affecting Gastrointestinal, Endocrine and Renal SystemsJewel Ramos GalinatoNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument2 pagesDiarrheajanna_3No ratings yet
- GIT - Part IIDocument23 pagesGIT - Part IIDiyar ArifNo ratings yet
- GIT Part 2Document15 pagesGIT Part 2jjf4708No ratings yet
- Gi PharmacologyDocument54 pagesGi Pharmacologyyohanes fikaduNo ratings yet
- Management of ConstipationDocument3 pagesManagement of ConstipationFarah Balqis BaragbahNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry 3Document4 pagesPharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry 3DeepikaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Drugs: Dr. Nandit P BDocument34 pagesGastrointestinal Drugs: Dr. Nandit P BNandit BanawalikarNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Constipation and DiarrheaDocument40 pagesDrugs For Constipation and DiarrheagirgrayNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document16 pagesPharma 2gxmtzth6hmNo ratings yet
- Medication: Therapeutic UsesDocument2 pagesMedication: Therapeutic UsesShannonNo ratings yet
- 15th November 2016 - Phar01 - Drugs For The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument47 pages15th November 2016 - Phar01 - Drugs For The Gastrointestinal SystemRjDNo ratings yet
- Anti DiarrhoealsDocument37 pagesAnti DiarrhoealsCrome operatorNo ratings yet
- Causes of Peptic Ulcers:: Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori)Document4 pagesCauses of Peptic Ulcers:: Helicobacter Pylori (H. Pylori)jessie monroeNo ratings yet
- 1 The Definition of ProbioticsDocument11 pages1 The Definition of ProbioticsMohd Shuaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Classification Generic Name Brand NameDocument42 pagesClassification Generic Name Brand NameMARIA ROWENA VIA J. LUCENANo ratings yet
- Medications of The SystemsDocument39 pagesMedications of The SystemsNicole DouglasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Dr. Haji Bahadar, Pharmd, PHD (Pharmacology) Assistant Professor, Ipms-KmuDocument21 pagesPharmacology: Dr. Haji Bahadar, Pharmd, PHD (Pharmacology) Assistant Professor, Ipms-KmuMuhammad KaleemNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal SystemJerica Jaz F. Vergara100% (1)
- Pharmacology AssignmentDocument9 pagesPharmacology AssignmentSaud AlamNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument20 pagesPeptic UlcerSINDHOOR S MNo ratings yet
- Bowel Disorder DRUGS: 29: Prof. Lopez NUR 210: PharmacologyDocument22 pagesBowel Disorder DRUGS: 29: Prof. Lopez NUR 210: PharmacologyLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- Management of DiarrhoeaDocument16 pagesManagement of Diarrhoeasunday danielNo ratings yet
- Lecturer 5Document19 pagesLecturer 5Doaa gamalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases - 2Document63 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases - 2Varunavi SivakanesanNo ratings yet
- FK UB Modul Drug Used in Gastrointestinal Disorders StudentDocument9 pagesFK UB Modul Drug Used in Gastrointestinal Disorders StudentEli Ezer SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pagesChemistry ProjectRhythm's PathakNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Diseases and Therapy NotesDocument19 pagesDigestive System Diseases and Therapy NotesMbah GapinbissiNo ratings yet
- 10 Agents Affecting Digestive Organs FunctionDocument62 pages10 Agents Affecting Digestive Organs FunctionAaghaz SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Antacids Are Used To Chemically React With and NeuDocument4 pagesAntacids Are Used To Chemically React With and Neunipheyy dananNo ratings yet
- Antinutrional FactorsDocument36 pagesAntinutrional FactorsHemanth Kumar JNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GitDocument119 pagesDrugs Acting On GitNathaniel Mbiu Tim100% (1)
- Obat Anti DiareDocument12 pagesObat Anti DiareYessy Dwi OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Christine Drug StudyDocument4 pagesChristine Drug StudyAmari BillNo ratings yet
- Trends Affecting NSG PracticeDocument22 pagesTrends Affecting NSG PracticeshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic DrugsDocument21 pagesAntiemetic DrugsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Anti-Spasmodic DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti-Spasmodic DrugsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Proclamation No. 499Document21 pagesProclamation No. 499shaitabliganNo ratings yet
- AnthelminticsDocument8 pagesAnthelminticsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Cephalosphorins 3rd Gen 4rt GenDocument24 pagesCephalosphorins 3rd Gen 4rt GenshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Anti-Malarial DrugDocument6 pagesAnti-Malarial DrugshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmunary DiseaseDocument39 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmunary DiseaseshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- PenicillinDocument5 pagesPenicillinshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Action OF Antifungal AgentsDocument5 pagesMechanisms of Action OF Antifungal AgentsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial CombinationsDocument21 pagesAntibacterial CombinationsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
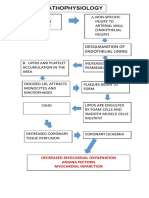
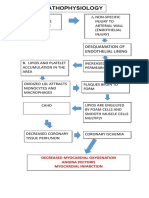
- Pathophys of CADDocument1 pagePathophys of CADshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Risk FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Risk FactorsshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: EpidemiologyDocument6 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: EpidemiologyshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Burgers DiseaseDocument21 pagesBurgers DiseaseshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- AnginaDocument4 pagesAnginashaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Management ProcessDocument12 pagesManagement ProcessshaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology: Arrhythmia/DysrhythmiaDocument6 pagesEpidemiology: Arrhythmia/DysrhythmiashaitabliganNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Management Sample QuestionsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Management Sample QuestionsshaitabliganNo ratings yet



![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)