Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measuring Metal Temperature & Hardness
Uploaded by
Md Arifuzzaman ArifOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measuring Metal Temperature & Hardness
Uploaded by
Md Arifuzzaman ArifCopyright:
Available Formats
Temperature measurement
Radiation pyrometer 4 4
𝑇 = 𝑒𝑡 𝑇
𝑎
A standard radiating source or blackbody
Radiation pyrometers are calibrated to indicate blackbody or true
temperatures
According to Stefan-Boltzmann law, the rate of radiant energy from a
blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature
No upper temperature limit but lower limit is 1000°F
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Temperature measurement
Radiation pyrometer
𝑏
𝐸 𝑚𝑓 =𝐾 𝑇
Thermocouple
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Temperature measurement
Optical pyrometer
In radiation pyrometer, all wavelengths are considered and also known as total
radiation pyrometer
Only difference between radiation pyrometer and optical pyrometer is that
optical pyrometer considers only single wavelength or a narrow band of
wavelengths in the visible part of the spectrum.
Brightness of light emission from a body is compared with a standard body
A red filter is used for color comparison
Red filter only allows wavelength of red radiation
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Temperature measurement
Optical pyrometer
Temperature range
1400 to 2400°F
This limit can be
extended to 10,000°F
by using various
absorption screens
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Metallography
The study of the structural characteristics of metals and alloys
Grain size and the size, shape and distribution of various phases may be
determined
The microstructure can talk about mechanical and thermal treatment of
metals
Sometimes it is possible to predict the behavior of metals and alloys under
given conditions
Microscopic study greatly depends on specimen preparation
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Metallography
Steps of preparing the specimens for metallography
1. Sampling
2. Rough grinding
3. Mounting
4. Intermediate polishing
5. Fine polishing
6. Etching
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Metallurgical Microscopes
Magnification can be
Maximum extended by using
magnification is short wavelength
about 2000X radiation, such as
ultraviolet radiation
Total magnification is Magnification power
the product of the may be extended
magnifications of the drastically by using
objective and eyepiece electron microscope
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Metallurgical Microscopes:
Electron Microscope
• High velocity
electrons • Must be kept
behaves like in vacuum
light of very • Lenses are
short magnetic field
wavelength • Replica of the
nearly 100,000 surface to be
times shorter produced
than visible • Maximum
light. magnification
• High power is about
needed to 200,000X
produce and
control electron
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
beam
Test for mechanical properties
Destructive tests
and
Non-destructive tests
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
The various hardness tests may be divided into three categories:
1. Elastic Hardness
2. Resistance to cutting or abrasion
3. Resistance to indentation
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Diamond tip hammer
1. Elastic Hardness
Measured by scleroscope
It is really a measure of the resilience
of a material that is the energy it can
absorb in the elastic range
Specimen
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
2. Resistance to cutting or abrasion
Scratch test (ten standard minerals
numbered 1 - 10)
File test (a file of known hardness)
Heat treat until the material is file hard
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
3. Resistance to Indentation
Brinell Hardness Test
Rockwell Hardness Test
Vickers Hardness Test
Microhardness Test
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Brinell Hardness Test
Hardened steel ball indenter is forced into the specimen
Standard ball diameter is 10 mm and force 3000 kg for ferrous
metals and 500 kg for non-ferrous metals
Indentation time is 10s for ferrous metals and 30s for non-ferrous
metals
Indentation diameter is measured by microscope with ocular scale
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Brinell Hardness Test 75 HB 10/500/30
The Brinell hardness number (HB)
Measuring limit is
500 HB
Can be measured up to
650 HB by using
tungsten carbide ball
Tables are available based on indentation
diameter
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Rockwell Hardness Test
The principle is based on differential depth measurement
Initially fixed minor load is applied on the specimen (10kg for
normal tester and 3 kg for superficial tester)
Then major load is applied (60, 100 and 150 kg for normal and 15,
30 and 45 for superficial tester)
Order of numbers are reversed on the scale (large impression
gives low hardness number and vise versa)
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Rockwell Hardness Test
A variety of indenters and loads are used and each combination
determines a particular Rockwell scale (A, B, C etc.)
Indenters are hard steel ball (1/16, 1/8, 1/4, and 1/2 in. dia and a
120° conical diamond)
Rockwell hardness number 75 measured on
75 HRB
Rockwell scale “B” (1/16 in. ball and 100kg)
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Vickers Hardness Test
Square based diamond pyramid indenter with included angle 136°
Load range 1-120kg
Basic principle is same as Brinell hardness tester
Impression in the surface is square
The length of diagonal is measured
Can be used to measure hardness of thin sheets
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Vickers Hardness Test
Vickers hardness number
(HV)
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Microhardness Test
Test loads are between 1 and 1,000 gm
Two types of indenters (136° square base Vickers diamond
pyramid and elongated knop diamond indenter)
Hardness number is the load per unit area of impression
Vickers hardness number (HV)
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Destructive tests: Hardness
Microhardness Test
Test loads are between 1 and 1,000 gm
Two types of indenters (136° square
base Vickers diamond pyramid and
elongated knoop diamond indenter)
Hardness number is the load per unit
area of impression
Knoop diamond pyramid
indenter
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
Next class
MORE ON DESTRUCTIVE TESTS
Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KUET, Khulna
You might also like
- Pass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewFrom EverandPass Ultrasound Physics Exam Study Guide ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- ME3215 - L3 MetallographyDocument9 pagesME3215 - L3 MetallographyABID ANJAMNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument37 pagesSpectrosKiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document38 pagesPresentation 1Kiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Radiography TestingDocument98 pagesRadiography TestingKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: CHM 303 Instrumental Method of Analysis-2UnitsDocument12 pagesLecture Notes: CHM 303 Instrumental Method of Analysis-2UnitsAnurak OnnnoomNo ratings yet
- Radiation Pyrometre NaveenaDocument27 pagesRadiation Pyrometre NaveenaRahul RaaghavNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Radiography Testing TechniquesDocument98 pagesModule 5 - Radiography Testing TechniquesRicky SarkarNo ratings yet
- Detection of Light: PhotodetectorsDocument48 pagesDetection of Light: PhotodetectorsFilston RukerandangaNo ratings yet
- CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES: Infrared spectroscopy fundamentalsDocument17 pagesCHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES: Infrared spectroscopy fundamentalsRaman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Lab V.10 07102020 - CompressedDocument2 pagesSolar Energy Lab V.10 07102020 - CompressedMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 BCHY101L TH VL2021220106627 Reference Material I 24-12-2021 EC Module 6 - MARDocument66 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 BCHY101L TH VL2021220106627 Reference Material I 24-12-2021 EC Module 6 - MARHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic PDFDocument5 pagesUltrasonic PDFHarsh DarjiNo ratings yet
- IR Training - LIDIDocument52 pagesIR Training - LIDInigussu temesganeNo ratings yet
- Xray Training Anx - PPSXDocument54 pagesXray Training Anx - PPSXkhurshedlakhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Introduction of Optical InstrumentDocument71 pagesChapter 2 - Introduction of Optical Instrumentnurinadlina.jpkmawarNo ratings yet
- L1-for-mondayDocument37 pagesL1-for-mondayHavana, Keren Anne M.No ratings yet
- Class: Integrated Physics: 6 .: 18532030019: Incharge: Mrs. Anshul Uppal Topic: FTIR and Vibrational Analysis of LabdaneDocument23 pagesClass: Integrated Physics: 6 .: 18532030019: Incharge: Mrs. Anshul Uppal Topic: FTIR and Vibrational Analysis of LabdaneArthansh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform InfraRed Spectroscopy 1Document22 pagesFourier Transform InfraRed Spectroscopy 1Uma kNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 1pDocument12 pagesChemistry Module 1pRiyazNo ratings yet
- 3 CC1Document6 pages3 CC1marianNo ratings yet
- EM Waves and Spextrum PDFDocument45 pagesEM Waves and Spextrum PDFJoanna SeproNo ratings yet
- Radiative Energy Transfer ExplainedDocument37 pagesRadiative Energy Transfer ExplainedAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2D - Infrared SpectrosDocument37 pagesTopic 2D - Infrared SpectrosLoh JiayeeNo ratings yet
- Advanced PH Analyses Lec 1 IntroDocument50 pagesAdvanced PH Analyses Lec 1 Introknowlegebook6No ratings yet
- Scanning Probe MicrosDocument22 pagesScanning Probe MicrosWinta BreaNo ratings yet
- Ti:sapphire Laser Properties and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesTi:sapphire Laser Properties and ApplicationsSap HarelNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrosDocument4 pagesInfrared SpectrosGabriel VazquezNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Analytical Methods and InstrumentationDocument74 pagesWeek 4 Analytical Methods and Instrumentationpuno ric0% (1)
- FTIR - Polymer AnalysisDocument20 pagesFTIR - Polymer AnalysisberkahNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesjosephrandalldeiparineNo ratings yet
- Subject:: Database Management Information System & Applications of Remote Sensing and GISDocument21 pagesSubject:: Database Management Information System & Applications of Remote Sensing and GISAmir Ahmed BaigoNo ratings yet
- Damping Capacity of Materials-Metals, Ceramics & MMCsDocument12 pagesDamping Capacity of Materials-Metals, Ceramics & MMCsArjun Satheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec Module 1 Pharm AnalysisDocument20 pagesLec Module 1 Pharm AnalysisJonas BorjNo ratings yet
- 26-Module 6a and 6B-02-06-2022Document21 pages26-Module 6a and 6B-02-06-2022krishna sanapala2003No ratings yet
- NIR Spectroscopy Techniques and ApplicationsDocument13 pagesNIR Spectroscopy Techniques and ApplicationsSunil RatheeNo ratings yet
- Radiations Lect1Document36 pagesRadiations Lect1Muhammad Nouman RashidNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy: Saptarshi BasuDocument18 pagesFourier Transform IR Spectroscopy: Saptarshi BasuDAMNiningNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy: Saptarshi BasuDocument18 pagesFourier Transform IR Spectroscopy: Saptarshi BasuDAMNiningNo ratings yet
- Helios-Quartz IR-LAMPS EngDocument24 pagesHelios-Quartz IR-LAMPS EngAlbertoNo ratings yet
- 4th Seminar - MicrowavesDocument54 pages4th Seminar - MicrowavesmonikaNo ratings yet
- Components of Optical Instruments: Skoog - Chapter 7Document40 pagesComponents of Optical Instruments: Skoog - Chapter 7jpmaurya77No ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument25 pagesSpectrosanuj phalswalNo ratings yet
- FTIRDocument79 pagesFTIRshruti shahNo ratings yet
- Surgical Lasers PDFDocument89 pagesSurgical Lasers PDFSammie PingNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Seminar on Ultra-Violet & Visible SpectroscopyDocument21 pagesSpectroscopy Seminar on Ultra-Violet & Visible SpectroscopyMounik RoutNo ratings yet
- NDT Radiography Training GuideDocument88 pagesNDT Radiography Training GuideMakhfud EdyNo ratings yet
- BY P.Sravanthi M.pharmacy 1styear-Pharmaceutical Analysis TRINITY College of Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument32 pagesBY P.Sravanthi M.pharmacy 1styear-Pharmaceutical Analysis TRINITY College of Pharmaceutical SciencesanithaNo ratings yet
- 8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesDocument3 pages8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesRamananNo ratings yet
- Unit1pptnotes 210823071031Document65 pagesUnit1pptnotes 210823071031SAMPATH ANo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDF Ultrasonic TestingDocument61 pagesModule 4 PDF Ultrasonic Testingjesna mohammedNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument3 pagesSpectro Photo Me TryAshley Nicole DelizoNo ratings yet
- Int +Spectroscopy+&+UVDocument40 pagesInt +Spectroscopy+&+UVTahsin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation of Uv Spectrophotometer: - Pranav Kumar Singh M.Sc.-Applied Chemistry (Third Semester)Document32 pagesInstrumentation of Uv Spectrophotometer: - Pranav Kumar Singh M.Sc.-Applied Chemistry (Third Semester)Kevin Gilberto S�nchez Ch�vezNo ratings yet
- Thermal ImagingDocument21 pagesThermal ImagingKaustubh Rajwade100% (5)
- Lasers in ProsthodonticsDocument27 pagesLasers in ProsthodonticsPremshith CpNo ratings yet
- What Is SpectrosDocument26 pagesWhat Is SpectrosMelvin Pogi138No ratings yet
- Vidthiya M FSN 105Document25 pagesVidthiya M FSN 105SELVI ANo ratings yet
- 9.1radiographic Testing-Part1Document20 pages9.1radiographic Testing-Part1Mohanad AlmalahNo ratings yet
- Laser Beam Machining GuideDocument33 pagesLaser Beam Machining GuidePPSwainNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain: σ = F/A F FDocument11 pagesStress and Strain: σ = F/A F FMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- Test For Mechanical Properties: Destructive Tests Non-Destructive TestsDocument18 pagesTest For Mechanical Properties: Destructive Tests Non-Destructive TestsMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- ME 3215 Engineering Metallurgy: Course ContentsDocument16 pagesME 3215 Engineering Metallurgy: Course ContentsMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- Online Routine PDFDocument1 pageOnline Routine PDFMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- CV of Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman Mechanical Engineering ProfessorDocument5 pagesCV of Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman Mechanical Engineering ProfessorMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- CV of Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman Mechanical Engineering ProfessorDocument5 pagesCV of Dr. Md. Arifuzzaman Mechanical Engineering ProfessorMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- KUET Professor Applies for Interest-Free Computer LoanDocument1 pageKUET Professor Applies for Interest-Free Computer LoanMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- Australian Federal Police National Police CheckDocument2 pagesAustralian Federal Police National Police CheckMd Arifuzzaman ArifNo ratings yet
- Expt 6 - Chemical KineticsDocument5 pagesExpt 6 - Chemical KineticsNeil Tangara100% (2)
- 1 s2.0 S0022024813002820 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0022024813002820 Main PDFSamah SamahNo ratings yet
- ACS Periodic Table PDFDocument1 pageACS Periodic Table PDFRyan Christopher MartinezNo ratings yet
- E400-Withdrawn 25013Document6 pagesE400-Withdrawn 25013Yeilly Buitrago ManriqueNo ratings yet
- MNR Decay Heat Estimates ReportDocument12 pagesMNR Decay Heat Estimates ReportUdit OjhaNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Homework on Entropy and Free EnergyDocument2 pagesAP Chemistry Homework on Entropy and Free EnergyOlsa NdoshaNo ratings yet
- Formula Summary: Monday, 5 April 2021 2:15 PMDocument19 pagesFormula Summary: Monday, 5 April 2021 2:15 PMJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Improved Nuclear Matter Calculations From Chiral Low-Momentum InteractionsDocument6 pagesImproved Nuclear Matter Calculations From Chiral Low-Momentum InteractionsKristian MalauNo ratings yet
- EOCQ - Ans - 17 2Document1 pageEOCQ - Ans - 17 2Куаныш ЖанадилNo ratings yet
- MarcottingDocument2 pagesMarcottingChristopherNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2E: V U As V BDocument7 pagesExercise 2E: V U As V BPetro SoudahNo ratings yet
- Single Electron Tunneling DevicesDocument16 pagesSingle Electron Tunneling DevicesDebapriya Basu RoyNo ratings yet
- Spherical Sand SeparatorDocument2 pagesSpherical Sand SeparatorKapwell LimitedNo ratings yet
- DuPont Personal Protection CatalogDocument52 pagesDuPont Personal Protection CatalogiuliaNo ratings yet
- Solomons Frsolomons-Fryhlesyhles Organic Chemistry For Iit JeeDocument2 pagesSolomons Frsolomons-Fryhlesyhles Organic Chemistry For Iit JeeFazle Rahman Ejazi50% (4)
- Physical Vs Chemical Change AnswersDocument3 pagesPhysical Vs Chemical Change AnswersLaili LeliNo ratings yet
- The Project RESelyserDocument40 pagesThe Project RESelyserJesús Javier Antuña CouceiroNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingIOCL SHUTDOWNNo ratings yet
- FCM Ec2-25Document51 pagesFCM Ec2-25Coil98No ratings yet
- Physical Science GRADE 10 STEP AHEAD LEARNER SUPPORT DOCUMENT 2022Document41 pagesPhysical Science GRADE 10 STEP AHEAD LEARNER SUPPORT DOCUMENT 2022TsheguhNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fibre in The Body of A Formula 1 Racing CarDocument4 pagesCarbon Fibre in The Body of A Formula 1 Racing CarAlex LoughlanNo ratings yet
- MercerizationDocument141 pagesMercerizationkreeshnuNo ratings yet
- Benzofused HeterocyclesDocument6 pagesBenzofused HeterocyclesMohini Bajaj50% (2)
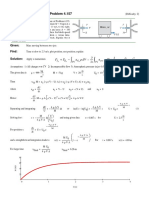
- Problem 4.157 momentum change time plotDocument1 pageProblem 4.157 momentum change time plotPaulo OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Blown Film Presentation PDFDocument14 pagesBlown Film Presentation PDFnitinmuthaNo ratings yet
- European Tracked Micro-Rover For Planetary SurfaceDocument9 pagesEuropean Tracked Micro-Rover For Planetary SurfaceSuryank JoshiNo ratings yet
- Database MSDSDocument4 pagesDatabase MSDSRinto SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (TKJ3302) Lecture Notes - 4 Energy Analysis of Closed SystemsDocument18 pagesThermodynamics (TKJ3302) Lecture Notes - 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systemsmamat88100% (2)
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Quantitative PCR An Introduction - 2010 - Molecular DiagnosticsDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Quantitative PCR An Introduction - 2010 - Molecular Diagnosticskorg123No ratings yet