Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation On Ecg: K. Vani MSC (N) Iind Year
Presentation On Ecg: K. Vani MSC (N) Iind Year
Uploaded by
vani reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views46 pagesThis document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG). It discusses the history and development of ECG, from the first recordings in the late 1800s to Willem Einthoven's Nobel Prize-winning development of the electrocardiograph in the early 1900s. The document also describes the electrical activity of myocardial cells during the depolarization and repolarization cycle and introduces the concept of electrocardiographic leads used to record the heart's rhythm.
Original Description:
Original Title
Presentation 15.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG). It discusses the history and development of ECG, from the first recordings in the late 1800s to Willem Einthoven's Nobel Prize-winning development of the electrocardiograph in the early 1900s. The document also describes the electrical activity of myocardial cells during the depolarization and repolarization cycle and introduces the concept of electrocardiographic leads used to record the heart's rhythm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views46 pagesPresentation On Ecg: K. Vani MSC (N) Iind Year
Presentation On Ecg: K. Vani MSC (N) Iind Year
Uploaded by
vani reddyThis document provides an overview of electrocardiography (ECG). It discusses the history and development of ECG, from the first recordings in the late 1800s to Willem Einthoven's Nobel Prize-winning development of the electrocardiograph in the early 1900s. The document also describes the electrical activity of myocardial cells during the depolarization and repolarization cycle and introduces the concept of electrocardiographic leads used to record the heart's rhythm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 46
PRESENTATION
ON
ECG
k. vani
Msc (N) IInd year
This Photo by Unknown author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND.
INTRODUCTION
ECG is a three-letter acronym for electro cardiography.
The word is derived from electro (Greek for electricity), cardio (Greek for
heart) and graph (Greek root meaning to write).
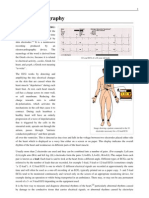
It Is a transthoracic interpretation of the electricity activity of the heart over
time captured and extremally recorded by skin electrodes.
The device used to produce this noninvasive record is called the
electrocardiograph. ECG is the gold standard for the non-invasive diagnosis
of cardiac diseases and may occasionally be the only marker for the presence
of heart disease.
ELECTROCARDIOGRPAHY TIMELINE:
1872: Alexander Muirhead attached wires to a feverish patient's wrist to obtain a
record of the patients' heartbeat's Bartholomew's Hospital.
1887: British physiologist Augustus D. Waller of St Marys' Medical School,
London publishes the first human electrocardiogram. The trace from the heartbeat
was projected onto a photographic plate which was itself fixed to a toy train
1893: Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven introduces the term
electrocardiogram at a meeting of the Dutch Medical Association.
1895: Willem Einthoven distinguishes five deflections which he names P, Q, R, S
and T.
1902: Einthoven publishes the first electro -cardiogram recorded
on a string galvanometer.
1912: Einthoven addresses the Chelsea Clinical Society in
London and describes an equilateral triangle formed by his
standard leads I, II and III later called Einthoven's triangle.
1924: Willem Einthoven wins the Nobel prize for inventing
the electrocardiograph.
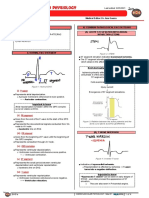
ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY OF MYCOCARDIAL CELLS
The depolarization-repolarization cycle consists of the
following phases:
Phase 0: Sodium (Na+) moves rapidly into cell.
Rapid depolarization Calcium (Ca++) moves slowly into cell.
Phase 1: Sodium channels close.
Early repolarization
Phase 2: Calcium continues to flow in.
Plateau phase Potassium (K+) continues to flow out.
Phase 3: Calcium channels close.
Rapid repolarization Potassium flows out rapidly.
Phase 4: Cell membrane is impermeable to sodium.
Resting phase Potassium moves out of the cell.
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
ELECTRO
CARDIOGAPHIC
LEADS
THE HEART RHYTHM
You might also like
- ECG Library PDFDocument98 pagesECG Library PDFJayden WaveNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Electrocardiography by Burch (Chr. Zywietz)Document10 pagesA Brief History of Electrocardiography by Burch (Chr. Zywietz)Laura Isop100% (1)
- Schiller MT101 MT200 User Manual PDFDocument96 pagesSchiller MT101 MT200 User Manual PDFgilalulaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument5 pages1 PBamirnamouchi1997No ratings yet
- Physiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyDocument42 pagesPhysiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument16 pagesElectrocardiogramjames garciaNo ratings yet
- E.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDocument36 pagesE.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentAch ThungNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument62 pagesECGSanju TanwarNo ratings yet
- Tentiran Basic Ecg Perawat Dr. Gun EditDocument104 pagesTentiran Basic Ecg Perawat Dr. Gun EditYoland CornelisNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesElectrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapayments8543No ratings yet
- Ecg PresentationDocument42 pagesEcg PresentationAnwar SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- CVS ElectrocardiogramDocument167 pagesCVS ElectrocardiogramSheral AidaNo ratings yet
- Centenary of Tele-Electrocardiography and TelephonocardiographyDocument3 pagesCentenary of Tele-Electrocardiography and Telephonocardiographymohamed hemdanNo ratings yet
- Tentiran Basic Ecg CoassDocument104 pagesTentiran Basic Ecg Coassbagus anantaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: Willis J. TompkinsDocument31 pagesElectrocardiography: Willis J. TompkinsLisCarrionSarmientoNo ratings yet
- 4 07introtoecg PDFDocument16 pages4 07introtoecg PDFPatricia SanchezNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review History To Understand Fundamentals of ElectrocardiographyDocument6 pagesA Brief Review History To Understand Fundamentals of ElectrocardiographyAbdullah AbdurrehmanNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiographyDocument13 pagesElectrocardiographymuditanatomyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDocument76 pagesElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography HistoryDocument115 pagesElectrocardiography HistoryRicardo QuinteiroNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cardiology ImagesDocument65 pagesPaediatric Cardiology ImagesEmy JacobNo ratings yet
- Lifs1902 11 4Document41 pagesLifs1902 11 4Gary TsangNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument50 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMamitava2010No ratings yet
- REAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALDocument15 pagesREAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALSHANKARNo ratings yet
- ECGramDocument24 pagesECGramZied TMARNo ratings yet
- ECG All LeadsDocument25 pagesECG All LeadsVIJAYKUMAR ANo ratings yet
- History of Electrocardiography, From The Past To The PresentDocument37 pagesHistory of Electrocardiography, From The Past To The PresentОксана ЗвягинаNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography - WikipediaDocument18 pagesElectrocardiography - WikipediaAkhil WaliaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Cen01 2019Document13 pagesDetailed Cen01 2019ChanNo ratings yet
- SPDX Electrocardiography-EcgDocument6 pagesSPDX Electrocardiography-Ecgdumppotato24No ratings yet
- ECGDocument15 pagesECGJegathese BaskerNo ratings yet
- HP 2Document12 pagesHP 2api-3756609100% (2)
- The Wiring Diagram of The HeartDocument4 pagesThe Wiring Diagram of The Heartgurneet kourNo ratings yet
- EchocardiographyDocument3 pagesEchocardiographyJanine Alicia VargasNo ratings yet
- Review: ECG Diagnosis of Acute Ischaemia and Infarction: Past, Present and FutureDocument12 pagesReview: ECG Diagnosis of Acute Ischaemia and Infarction: Past, Present and FutureArunKumar ManiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleDocument39 pagesMechanical and Electrical Events of The Cardiac CycleEdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- 05 - ElektrokardiogramDocument39 pages05 - ElektrokardiogramNauval Zilal FananyNo ratings yet
- The Physiological Basis of The EkgDocument87 pagesThe Physiological Basis of The EkgYS NateNo ratings yet
- Cardio Assignment On Electrocardiography (ECG)Document14 pagesCardio Assignment On Electrocardiography (ECG)s.sheikhh000No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 pagesElectrocardiogram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRaJeev K SookunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGDocument39 pagesIntroduction To ECGSingey LhendupNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan EKGDocument51 pagesPerkembangan EKGevhyajahNo ratings yet
- ECG MorphologyDocument36 pagesECG MorphologyMr Joko100% (2)
- Electrical Hazards in Cardiac Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument2 pagesElectrical Hazards in Cardiac Diagnosis and TreatmentRajuNo ratings yet
- SPDX311 LEC - 03 ElectrocardiographyDocument6 pagesSPDX311 LEC - 03 Electrocardiographywootzu1No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- CH 013Document11 pagesCH 013bubu.raiseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document24 pagesClinical Demonstration: Topic: Electrocardiogram (ECG)soniya josephNo ratings yet
- Delta Wave - LITFL Medical Blog - ECG Library BasicsDocument9 pagesDelta Wave - LITFL Medical Blog - ECG Library Basicssilver silvaNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiologyofheart PDFDocument99 pagesElectrophysiologyofheart PDFsahar awaisNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectrophysiologyDocument18 pagesBasic ElectrophysiologyCarlo Domingo LadieroNo ratings yet
- Presented By-: ElectrocardiographyDocument18 pagesPresented By-: ElectrocardiographyArnab Guin100% (1)
- Topic:: Performing and Interpreting Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document137 pagesTopic:: Performing and Interpreting Electrocardiogram (ECG)Tiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document25 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)Laraib KanwalNo ratings yet
- (PHY) 3.02A ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pages(PHY) 3.02A ElectrocardiogramMarilou de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramDocument2 pagesExercise 7.2 - ElectrocardiogramKevin F. CortesNo ratings yet
- 009 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular - EKG SDocument4 pages009 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular - EKG SSWATHIKA LNo ratings yet
- 1621324573PHYSIOLOGY, SEM-2 - K-Sembulingam-Essentials-Of-Medical-PhysiologyDocument7 pages1621324573PHYSIOLOGY, SEM-2 - K-Sembulingam-Essentials-Of-Medical-PhysiologyAyoola BolajiNo ratings yet
- Basics ECGpediaDocument6 pagesBasics ECGpediaCarina SuarezNo ratings yet
- الوحده الثالثهDocument8 pagesالوحده الثالثهHUAWEI HUAWEI100% (1)
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Ward TeachingDocument23 pagesWard Teachingvani reddyNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument47 pagesDiabetesvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Child DevelopmentDocument7 pagesChild Developmentvani reddyNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument29 pagesCardiologyvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Inservice EducatrionDocument28 pagesInservice Educatrionvani reddyNo ratings yet
- The Referral System Revised: DisclaimerDocument33 pagesThe Referral System Revised: Disclaimervani reddyNo ratings yet
- Types of FeverDocument10 pagesTypes of Fevervani reddyNo ratings yet
- Identify The Problems of The Speciality Units To Develop Plan of Action by Using Problem Solving AppraoachDocument19 pagesIdentify The Problems of The Speciality Units To Develop Plan of Action by Using Problem Solving Appraoachvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument35 pagesCystic Fibrosisvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Approach Topic WordDocument20 pagesProblem Solving Approach Topic Wordvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Tetrallogy of FallotDocument33 pagesPresentation ON Tetrallogy of Fallotvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Jhpiego Pinktober OutlineDocument1 pageJhpiego Pinktober Outlinevani reddyNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing MSC (N) 1 ST YEAR (2019-2021) Research Proposal PresentationsDocument4 pagesGovernment College of Nursing MSC (N) 1 ST YEAR (2019-2021) Research Proposal Presentationsvani reddy100% (1)
- Administrative Flow Chart: Health Care System in IndiaDocument4 pagesAdministrative Flow Chart: Health Care System in Indiavani reddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Tetralogy of FallotDocument36 pagesPresentation ON Tetralogy of Fallotvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis, Bone Tumors, and Muscular DystrophyDocument85 pagesOsteomyelitis, Bone Tumors, and Muscular Dystrophyvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Augmentation and IOLDocument22 pagesAugmentation and IOLvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis LectureDocument16 pagesCystic Fibrosis Lecturevani reddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title 2/11/20XXDocument18 pagesPresentation Title 2/11/20XXvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cystic Fibrosis & Its ManagementDocument54 pagesOverview of Cystic Fibrosis & Its Managementvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON BroncitisDocument24 pagesLesson Plan ON Broncitisvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Seminar 1Document38 pagesMeningitis Seminar 1vani reddyNo ratings yet
- Telangana Health Medical and Family Welfare Annual Report 2018 19Document47 pagesTelangana Health Medical and Family Welfare Annual Report 2018 19vani reddyNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetics DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Emetics Drugsvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Disorders of AortaDocument25 pagesDisorders of Aortavani reddyNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial DiseasesDocument34 pagesPeripheral Arterial Diseasesvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Competencies: Mrs. Satyapriya M.Sc. Nursing (Community Health Nursing) Lecturer Government College of NursingDocument16 pagesPrescribing Competencies: Mrs. Satyapriya M.Sc. Nursing (Community Health Nursing) Lecturer Government College of Nursingvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Satyapriya Madam Topic 2Document16 pagesSatyapriya Madam Topic 2vani reddyNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Pulmonary HypertensionDocument12 pagesSeminar On Pulmonary Hypertensionvani reddyNo ratings yet
- 2020 NHSN Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) ChecklistDocument5 pages2020 NHSN Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Checklistvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Ebstein Anomaly in The Adult PatientDocument11 pagesEbstein Anomaly in The Adult PatientRJMNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of 3-Lead ECG Machine For Rural MedificationDocument7 pagesDesign and Implementation of 3-Lead ECG Machine For Rural Medificationlibya freeNo ratings yet
- Nihon Kohden 9010K Service ManualDocument130 pagesNihon Kohden 9010K Service ManualjojaaNo ratings yet
- New Catalogue 2018Document7 pagesNew Catalogue 2018Haliun AltangerelNo ratings yet
- EC 2021 - ME Question Bank 2015Document24 pagesEC 2021 - ME Question Bank 2015Rajendran JhansiNo ratings yet
- Mosbys Paramedic Textbook 4th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesMosbys Paramedic Textbook 4th Edition Ebook PDFdenise.sweeney729100% (39)
- Development of A Smart Garment For The Assessment of Cardiac Mechanical Performance and Other Vital Signs During Sleep in MicrogravityDocument9 pagesDevelopment of A Smart Garment For The Assessment of Cardiac Mechanical Performance and Other Vital Signs During Sleep in MicrogravitynarykNo ratings yet
- ADS1298 FE User GuideDocument61 pagesADS1298 FE User GuideArio FitriantoNo ratings yet
- Ecg Basics - NAVEENDocument65 pagesEcg Basics - NAVEENNaveen MathieuNo ratings yet
- Naccarelli 2012 Electrocardiography of Arrhythmias A Comprehensive ReviewDocument1 pageNaccarelli 2012 Electrocardiography of Arrhythmias A Comprehensive Reviewraul gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cardiology-5 DysrhythmiaDocument16 pagesCardiology-5 DysrhythmiaMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Teaching PackageDocument9 pagesCardiology Teaching PackageRicy SaiteNo ratings yet
- SUM 198 2386 13-NMUC-SpecsheetDocument17 pagesSUM 198 2386 13-NMUC-SpecsheetConrad WaluddeNo ratings yet
- EBB111E0Document96 pagesEBB111E0Mohammed Taha ALyafeiNo ratings yet
- Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia in Infants and Children: Ranjit I. Kylat MD - Ricardo A. Samson MDDocument8 pagesJunctional Ectopic Tachycardia in Infants and Children: Ranjit I. Kylat MD - Ricardo A. Samson MDCatherine MorrisNo ratings yet
- EI8073 BMI QN BankDocument8 pagesEI8073 BMI QN BankKeerthana SahadevanNo ratings yet
- C30 User ManualDocument146 pagesC30 User ManualKiattisak PrajongsinNo ratings yet
- Cardioperfect Pro Ecg Recorder - User Manual: Regulatory Affairs Representative Welch Allyn, IncDocument25 pagesCardioperfect Pro Ecg Recorder - User Manual: Regulatory Affairs Representative Welch Allyn, Incjostin2007No ratings yet
- Pharmacology RevisedDocument59 pagesPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- LiFEGAIN CU-HD1Document5 pagesLiFEGAIN CU-HD1Sandro RebecNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyali sarjunipadangNo ratings yet
- FCPS Pretest Series - CVS Physiology PDFDocument130 pagesFCPS Pretest Series - CVS Physiology PDFFatima Habib JajjaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography I C P: N Linical RacticeDocument57 pagesElectrocardiography I C P: N Linical RacticewidyamarisNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care Algorithms For Rural Settings 2018 PDFDocument67 pagesEmergency Care Algorithms For Rural Settings 2018 PDFGbariel100% (1)
- ECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersDocument7 pagesECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersAANo ratings yet
- Lifs1902 11 4Document41 pagesLifs1902 11 4Gary TsangNo ratings yet
- Cerner Resource GuideDocument87 pagesCerner Resource GuideAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardioline Ar600 - User ManualDocument36 pagesCardioline Ar600 - User ManualDavid SanchezNo ratings yet
- Xducers & P-MonitorsDocument22 pagesXducers & P-MonitorschanlalNo ratings yet