Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Kingdom
Uploaded by
Angel Mary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views13 pagesThis document provides information on the expected learning outcomes, basis of classification of animals, and characteristics of invertebrates and vertebrates. It outlines the levels of hierarchy in classification from kingdom to species. It also includes tables comparing the features of invertebrates, such as their germ layers, body symmetry, and examples; and compares the characteristics of vertebrate classes including their habitats, respiratory systems, and modes of reproduction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Animal Kingdom Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the expected learning outcomes, basis of classification of animals, and characteristics of invertebrates and vertebrates. It outlines the levels of hierarchy in classification from kingdom to species. It also includes tables comparing the features of invertebrates, such as their germ layers, body symmetry, and examples; and compares the characteristics of vertebrate classes including their habitats, respiratory systems, and modes of reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views13 pagesAnimal Kingdom
Uploaded by
Angel MaryThis document provides information on the expected learning outcomes, basis of classification of animals, and characteristics of invertebrates and vertebrates. It outlines the levels of hierarchy in classification from kingdom to species. It also includes tables comparing the features of invertebrates, such as their germ layers, body symmetry, and examples; and compares the characteristics of vertebrate classes including their habitats, respiratory systems, and modes of reproduction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Expected Learning Outcome
Brief the Basis of classification.
List out the hierarchy of classification of
animals.
Tabulate the characteristic features of
invertebrates and vertebrates.
BASIS OF CLASSIFICATION
Level of organization – unicellular & multicellular.
Symmetry- Radial –Animal-cut from central axis in any direction it can
be divided into similar halves.eg hydra.
Bilateral - Animal-cut from central axis in any direction it can be
divided into identical halves.eg frog Body parts arranged along the central axis.
Germ layers –diploblastic-ecto and endoderm.
Triploblastic –ecto,meso and endoderm .
Coelom-fluid filled body cavity-separates the digestive track from the
body wall.
acoelomates- no body cavity eg tapeworm
pseudocoelomate- false body cavity eg roundworm
eucoelomate or coelomate true body cavity eg earthworm, frog
ANIMAL KINGDOM
Classification of Living Organisms
Kingdom – have same fundamental characters. Eg microorganisms,
animals & plants
• Phylum – Classes of different animals [have notochord/back bone]
• Class – Share some common features[ mammary gland, skin]
• Order – Possess some common characters- monkeys, apes man,
baboons
• Family – Group have several common characters-cat [Felidae]
• Genus – Closely related species – wolf, jackal –Canis
• Species – Lowest category [Indian parakeet diff-green parrot.
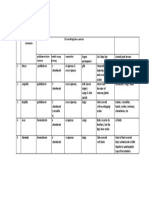
INVETEBRATES
PHYLUMSeper SPECIAL Germ layer coelom symmetr No of Reproducti
ate NAMES y cell on
Protozoan First Animal - - - Uni Sexual&ase
xual
Porifera Pore Bearers - - - Multi Sexual&ase
xual
Coelenterata Cnidaria diploblastic radial Multi Sexual&ase
xual
Platyhelminthe Paracitic triploblastic acoelomat bilateral Multi hermaphrod
s e ites
Aschelminthes Free Living triploblastic Pseudocoe bilateral Multi Separate
Soil Forms lomate
Annelida Segmented triploblastic coelomate bilateral Multi Hermaphrod
Body ites
Arthropoda Jointed Foot triploblastic coelomate bilateral Multi Moulting
Separate
Mollusca Soft Bodied triploblastic coelomate bilateral Multi Seperate
Animals
Echinodermata Calcareous triploblastic coelomate radial Multi Asexual
Ossicles
PROCHORDATA
Phyllum Notochord Habitat Skull Example
Hemichordate No Marine Absent Balanoglossus
Acrania- do
not have skull
Urochordate No Marine Absent Ascidian
Acrania- do
not have skull
Cephalochord present Marine Absent Amphioxus
ate Acrania- do
not have skull
CHORDATA
Phylum Habitat Chamb Respirati Body Locomoti Fertilizat Special
ers in on covering on ion features
the through
heart
Pisces Aquatic 2 Gills Epidermal Fins Mostly Poikilothe
scales internal rmic
Some
have
internal
Amphibia Aquatic 3 Water- Moist skin Webbed External
n as well as moist skin Feet &
land Land- Leap
lungs
Reptilia Dry land 3 Lungs Epidermal Limbs Internal homeothe
Crocodi scales rmic
le has 4
Aves Aerial 4 Lungs Epidermal Wings External Homeothe
feathers rmic
Hollow
bones
Mammali Mostly 4 Lungs Epidermal Limbs Internal Homeothe
a live on fur or hair rmic
land heteroden
Summary
Today we learnt about the Basis of
classification in detail.
Also, we learnt about the hierarchy of
classification of animals.
The characteristic features of invertebrates and
vertebrates
You might also like
- Lab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ADocument8 pagesLab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ASITI NUR AQILAH ASRULNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus Forms 3-4Document88 pagesBiology Syllabus Forms 3-4Malack Chagwa100% (6)
- Unit 1 4º Living Things PDFDocument28 pagesUnit 1 4º Living Things PDFVanessaLopez100% (1)
- Genetics HandoutDocument69 pagesGenetics HandoutIrene JavierNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle HBRDocument42 pagesCell Cycle HBRMaliha TasnimNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi Genetics: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument35 pagesUnit - Vi Genetics: Very Short Answer QuestionsRK YeleswarapuNo ratings yet
- Arts 8Document36 pagesArts 8Analee Regalado LumadayNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument17 pagesPlantsAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument37 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsCza VerwinNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument252 pagesAnimal KingdomBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesPlant Structure and FunctionsahiNo ratings yet
- Proverbs and Adages MatchDocument2 pagesProverbs and Adages Matchjomabi67% (3)
- Waves and Light Unit Exam Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesWaves and Light Unit Exam Practice QuestionsobaidaaljoboryNo ratings yet
- Proverbs Worksheet MatchDocument2 pagesProverbs Worksheet MatchAndrés FarfánNo ratings yet
- GENETICS ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENETICS ReviewerMargarita RosarioNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 - 2nd Sem - Ps - m2 - UamDocument8 pagesSci 9 - 2nd Sem - Ps - m2 - UamMark John Paul CablingNo ratings yet
- Punnet SquareDocument26 pagesPunnet SquarePrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Function PDFDocument2 pagesPlant Structure and Function PDFPT.Susan Angwyn Gemilang 8No ratings yet
- Parallel and Series CircuitDocument13 pagesParallel and Series CircuitsafaNo ratings yet
- Monohybrid CrossDocument67 pagesMonohybrid Crossapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Endangered and ExtinctDocument23 pagesEndangered and Extincthengst librandoNo ratings yet
- Presentado Por: Oscar Vallejo Caterine Montalvo Paola ObandoDocument11 pagesPresentado Por: Oscar Vallejo Caterine Montalvo Paola ObandoLuis Felipe MontalvoNo ratings yet
- Sea Floor Spreading and Plate TectonicsDocument26 pagesSea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonicsbking bbNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Short QuizDocument2 pagesShort QuizAnonymous MGMgUWNo ratings yet
- Renewable & Non - Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument53 pagesRenewable & Non - Renewable Energy ResourcesSheejaVargheseNo ratings yet
- Gymnosperms and AngiospermsDocument38 pagesGymnosperms and AngiospermsMeah PachecoNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: Identifying Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesStates of Matter: Identifying Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Learning ObjectivesChito DoctoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Review PowerpointDocument21 pagesElectricity Review PowerpointDoomofthehillsNo ratings yet
- Comets and AsteroidsDocument42 pagesComets and AsteroidsEd TapuroNo ratings yet
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Practice KeyDocument4 pagesNon-Mendelian Practice KeyJopit O. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesDigestive SystemImneil Jeanne Melendres-PerezNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeMohamad Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- S-B-2-3 - Energy Pyramid Worksheet KEYDocument1 pageS-B-2-3 - Energy Pyramid Worksheet KEYNatalee SalcidoNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument23 pagesGroup 3: Kingdom AnimaliabrettNo ratings yet
- Look at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareDocument26 pagesLook at The Picture On The Side.: Think-Pair-ShareCharo Nudo PongasiNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Molecules: One Mark QuestionsDocument11 pagesAtoms and Molecules: One Mark QuestionsSrividhya ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Patterns of InheritanceDocument26 pagesPatterns of InheritanceVidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Tools: Constructi0N Material and TestingDocument43 pagesTools: Constructi0N Material and TestingKemuel TabamoNo ratings yet
- Weather LectureDocument60 pagesWeather LecturenagtipunanNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationships (Final) 1Document14 pagesSymbiotic Relationships (Final) 1Jane PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Archaebacteria: Group MembersDocument30 pagesArchaebacteria: Group MembersMr MNo ratings yet
- Green Minimal Simple School Environmental Science Geography Project PresentationDocument13 pagesGreen Minimal Simple School Environmental Science Geography Project PresentationPro ThamNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric LascauxDocument25 pagesPrehistoric LascauxRAHUL163980% (1)
- 25 VertebratesDocument41 pages25 Vertebratespurple crocNo ratings yet
- Grade7science 180122081417Document37 pagesGrade7science 180122081417Anonymous SpjVHfNpqNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument28 pagesInterior of The EarthjayantnainiwalNo ratings yet
- Metric Lab ActivityDocument11 pagesMetric Lab Activityapi-365636101No ratings yet
- DLL BNC Q2W3 4Document3 pagesDLL BNC Q2W3 4ainabelleNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument21 pagesSCIENCEAbello BadayosNo ratings yet
- Microscope CareDocument5 pagesMicroscope CareKate BlahblahNo ratings yet
- Classifying Organisms: 1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2011Document25 pagesClassifying Organisms: 1 of 33 © Boardworks LTD 2011huzaifa mobusherNo ratings yet
- AnimaliaDocument68 pagesAnimaliaNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Non-Chordates AnimalDocument58 pagesNon-Chordates AnimalToushik Ahamed MollaNo ratings yet
- Asysyifa Arinilhaq Modjo x-5: Kelompok Vertebrata Ciri Morfologi Dan AnatomiDocument1 pageAsysyifa Arinilhaq Modjo x-5: Kelompok Vertebrata Ciri Morfologi Dan AnatomiAsysyifa Arini ModjoNo ratings yet
- AnimalDocument42 pagesAnimalanwar zahwanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE YEAR 4 (19.05.2021) Vertebrates and Invertebrates: AnimalsDocument2 pagesSCIENCE YEAR 4 (19.05.2021) Vertebrates and Invertebrates: AnimalsAten KenangaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Subphylum Vertebrata Class IXDocument1 pageAnimal Kingdom Subphylum Vertebrata Class IXNandishwara ThonthanalNo ratings yet
- Chordate Classification:: Lecture Two Assit - Lect.Maha MustafaDocument6 pagesChordate Classification:: Lecture Two Assit - Lect.Maha Mustafanareman hassanNo ratings yet
- Six Kingdoms of Living Things Teacher NotesDocument4 pagesSix Kingdoms of Living Things Teacher NotesAshraful AlamNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledJaime MaestreNo ratings yet
- A1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Document3 pagesA1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2018 Question Paper Solution Set 1Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2018 Question Paper Solution Set 1Angel MaryNo ratings yet
- Plague: Roshan A Xi-D Roll No. 23Document1 pagePlague: Roshan A Xi-D Roll No. 23Angel MaryNo ratings yet
- Che 11thDocument1 pageChe 11thAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Consent Form For Reopening of School 20-21Document1 pageConsent Form For Reopening of School 20-21Angel MaryNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Question Bank 2020-21Document3 pagesAnimal Kingdom Question Bank 2020-21Angel MaryNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Invertebrate Diversity: Chapter ObjectivesDocument15 pagesThe Evolution of Invertebrate Diversity: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Classification of AnimalsDocument47 pagesClassification of AnimalsReylen MaderazoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Breathing Organs of Animals Learning Standard: Pupils Are Able ToDocument4 pages3.1 Breathing Organs of Animals Learning Standard: Pupils Are Able ToZulkifly Md AlwayiNo ratings yet
- CSJMU MSC Zoology SyllabusDocument7 pagesCSJMU MSC Zoology SyllabusAbdul WassayNo ratings yet
- 7 Classify Animals Based On Their Characteristics 1Document17 pages7 Classify Animals Based On Their Characteristics 1Reylen MaderazoNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates: September 1,2008Document51 pagesVertebrates and Invertebrates: September 1,2008superwee100No ratings yet
- Sample 7E Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSample 7E Lesson PlanJan BajeNo ratings yet
- Science - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Document18 pagesScience - Form - 2 1 27 10 27Gan Wei ShengNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity Take Home TestDocument7 pagesAnimal Diversity Take Home TestPaolo MackayNo ratings yet
- Classification of Animals.: BiodiversityDocument17 pagesClassification of Animals.: BiodiversityIffah Nurain ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- BOOKLET 4th - 2024Document88 pagesBOOKLET 4th - 2024marielapriscoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Quarter 2 Periodical Test in ScienceDocument37 pagesReviewer - Quarter 2 Periodical Test in ScienceCalay StagramNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Invertebrate AnimalsDocument46 pagesCharacteristics of Invertebrate AnimalsNiel FelicildaNo ratings yet
- Classify Each of The Organisms by Writing Their Names in The Correct LocationDocument2 pagesClassify Each of The Organisms by Writing Their Names in The Correct LocationJuju ZenemijNo ratings yet
- Caris Nebb - Comparing Features of Invertebrates 2Document2 pagesCaris Nebb - Comparing Features of Invertebrates 2api-407073637No ratings yet
- Science 6 Q2Document2 pagesScience 6 Q2AnaNo ratings yet
- 22 ZoologyDocument33 pages22 ZoologyMalsawmkima Maski-aNo ratings yet
- Science and Health: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education CurriculumDocument31 pagesScience and Health: (Philippine Elementary Learning Competencies) Basic Education Curriculumirish-tuazon-411294% (17)
- Chap1 4Document690 pagesChap1 4Avinash DahaleNo ratings yet
- Bio 211Document132 pagesBio 211MehmetŞahinNo ratings yet
- g3 U2 RDR WebDocument168 pagesg3 U2 RDR WebVindu ViharamNo ratings yet
- 10 Animal Kingdom: (General Accounts & Non-Chordates)Document17 pages10 Animal Kingdom: (General Accounts & Non-Chordates)Ekta Manglani100% (1)
- Answers of ScienceDocument135 pagesAnswers of ScienceAdil AtifNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, InvertebratesDocument4 pagesUnit 1, InvertebratesnatalescorNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Animal Systematic I - Activity 2 - 20202021-1Document3 pagesWork Sheet Animal Systematic I - Activity 2 - 20202021-1Anang Yanuar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- BSC Zoology SyllabusDocument5 pagesBSC Zoology SyllabusUmar BagbanNo ratings yet
- Alec Leitman Jcu CVDocument4 pagesAlec Leitman Jcu CVapi-655595943No ratings yet