Professional Documents
Culture Documents
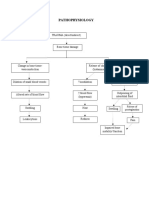
Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Response
Uploaded by
Deo Factuar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
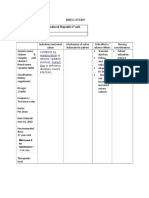
309 views1 pageThe inflammatory response involves the release of chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, and leukocyte migration. This leads to hyperemia, exudate formation, and leukocytosis as neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes are attracted to the injured area. The leaked fluid and cells cause pain, swelling, and heat as the body walls off the injured tissue and clears debris via phagocytosis to promote healing.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Response
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe inflammatory response involves the release of chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, and leukocyte migration. This leads to hyperemia, exudate formation, and leukocytosis as neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes are attracted to the injured area. The leaked fluid and cells cause pain, swelling, and heat as the body walls off the injured tissue and clears debris via phagocytosis to promote healing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
309 views1 pagePathophysiology of Inflammatory Response
Uploaded by
Deo FactuarThe inflammatory response involves the release of chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, and leukocyte migration. This leads to hyperemia, exudate formation, and leukocytosis as neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes are attracted to the injured area. The leaked fluid and cells cause pain, swelling, and heat as the body walls off the injured tissue and clears debris via phagocytosis to promote healing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
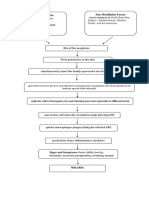
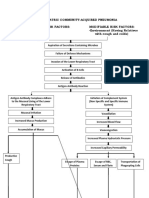
Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Response
Etiology: Infection/ Mechanical Damage/
Ischemia/ Nutritional Deprivation/ Extremes Tissue Injury
Temperature/ Radiation/ etc.
Release of chemical
mediators (histamine, Release of
complement, kinins, leukocytosis-inducing
prostaglandins) factors
Vasodilation Increased Attract neutrophils,
capillary Leukocytosis
of arterioles monocytes & lymphocyte to
permeability area (chemotaxis) (increased of WBC
in blood stream)
Local hyperemia Capillaries leak
fluid (exudate Migration to
formation) injury area
Heat Redness
Increased Blood flow
oxygen & Leaked protein-rich slows
Leaked
Increased nutrients fluid in tissue Margination
clothing
temperature spaces (leukocytes cling to
proteins
increases metabolic capillary walls)
rate of cells
Pain Swelling
Walling-off process(blood clots Diapedesis (leukocytes pas
wall off area to prevent injury to through capillary walls)
surrounding area
Possible temporary limitation
of joint movement
Phagocytosis of pathogen & dead
Temporary fibrin tissue cells (by neutrophils, short
patch forms term; by macrophages, long term)
scaffolding for
repair Pus may
Area cleared of form
debris
Prepared by:
Czarina Sales, RN Healing
Student Name
You might also like
- Savage Worlds of Shadowrun FinalDocument29 pagesSavage Worlds of Shadowrun Finaljasonstierle100% (4)
- Gmat Clinic Course Notes PDFDocument213 pagesGmat Clinic Course Notes PDFDavid ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism Concept MapDocument1 pageHypothyroidism Concept MapMonica Ugarte Treta100% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- 2500 Supreme IO&M ManualDocument36 pages2500 Supreme IO&M Manualadrianram1No ratings yet
- 2.08 Surg - Wound Healing (Dr. Jayme 2020)Document13 pages2.08 Surg - Wound Healing (Dr. Jayme 2020)DETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- Case Study AscariasisDocument60 pagesCase Study AscariasisRijane Tabonoc OmlangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Uterine FibroidsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Uterine FibroidsJurilyne Rose TundagNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Module: Powerful Software Featuring Intuitive WorkflowDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Module: Powerful Software Featuring Intuitive WorkflowMuhammadAviCennaNo ratings yet
- Galeo Wa430-6 PDFDocument1,612 pagesGaleo Wa430-6 PDFWalter100% (1)
- Hirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesDocument3 pagesHirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPathophysiologyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- CKD - For Concept MappingDocument7 pagesCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Hyperparathyroidism Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism Concept MapDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Aghora and Tantra: Using Hawan To Appease Indra and YamaDocument3 pagesAghora and Tantra: Using Hawan To Appease Indra and YamaMahesh BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Cho Chon FatsDocument26 pagesCho Chon FatsKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Edwin A. Winckler. Political AnthropologyDocument87 pagesEdwin A. Winckler. Political AnthropologyGabriela Herrera MonrroyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PostpartumDocument6 pagesDrug Study PostpartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Aids/HivDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Aids/HivAdha100% (1)
- MYOMA PathoDocument1 pageMYOMA Pathobsn2011100% (1)
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pages3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthShanealle Athaliah Magsalay CuaNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- A Family Nursing Care Plan OnDocument14 pagesA Family Nursing Care Plan OnMonique LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNo ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDocument52 pagesHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunitySaira SucgangNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- Self-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)Document2 pagesSelf-Care Deficit Related To Inability To Perceive Body Part (Bathing)lilpeabea100% (1)
- FNCPDocument2 pagesFNCPNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- Computer Generated Nursing Care Plans OutlineDocument1 pageComputer Generated Nursing Care Plans OutlineEstelle RhineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification Evaluationanette katrinNo ratings yet
- Learning Derived (Lysha)Document1 pageLearning Derived (Lysha)Choy DavidNo ratings yet
- FNCP PoorsanitationmarwahDocument3 pagesFNCP PoorsanitationmarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- NCP of Endometrical CancerDocument2 pagesNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainjrilleraNo ratings yet
- FNCP Unplanned PregnancyDocument1 pageFNCP Unplanned PregnancyASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy Across The LifespanDocument34 pagesDrug Therapy Across The LifespanJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Why Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinDocument4 pagesWhy Do Human Cells Rely Far More On Glucose and Fat For The Energy Than On ProteinHamda HassanNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Support for Insufficient Milk ProductionDocument4 pagesBreastfeeding Support for Insufficient Milk ProductionYeng MangilitNo ratings yet
- How to treat and prevent breast engorgementDocument1 pageHow to treat and prevent breast engorgementkurniaNo ratings yet
- Action Plan - Inadequate IncomeDocument2 pagesAction Plan - Inadequate IncomeBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- TYPOLOGY OF FAMILY NURSING PROBLEMS HandoutDocument5 pagesTYPOLOGY OF FAMILY NURSING PROBLEMS HandoutMaxime EllaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of mesenchymal chondrosarcomaDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of mesenchymal chondrosarcomaMaria Grace Raquel Ormeneta100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDocument1 pageBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Sample (Concept Map)Document1 pageSample (Concept Map)NMDNMSSDNo ratings yet
- Guide in Making The FCA 1Document18 pagesGuide in Making The FCA 1Zedrake CaraanNo ratings yet
- Differentiate a Schultze and Duncan PlacentaDocument16 pagesDifferentiate a Schultze and Duncan PlacentaMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- 4 ConceptDocument1 page4 ConceptStacey GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalsDocument4 pagesDrug Study FinalsKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathoDocument2 pagesPcap PathoLardel CarayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Care Plan New BornDocument10 pagesPostpartum Care Plan New BornUche Edwards-ShahidNo ratings yet
- Casestudy Makato 2nd Pre EclampsiaDocument7 pagesCasestudy Makato 2nd Pre EclampsiaRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLANDocument3 pagesFAMILY NURSING CARE PLANSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDocument42 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Case StudyGelah DacanayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesDocument13 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 pagesICS Pedia Wardsweet061991No ratings yet
- NCP Readiness RevisionDocument3 pagesNCP Readiness RevisionimnasNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Notes - Inflammation and HealingDocument6 pagesPathophysiology Notes - Inflammation and HealingKateNo ratings yet
- LASER BaganDocument1 pageLASER BaganannisayaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology FractureDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology Fracturecsy123No ratings yet
- CF Covid Ards PathoDocument3 pagesCF Covid Ards PathoDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Medical Examination Report SummaryDocument18 pagesMedical Examination Report SummaryDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Medical Examiner's Certificate: Form MCSA-5876 Public Burden StatementDocument1 pageMedical Examiner's Certificate: Form MCSA-5876 Public Burden StatementDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Sodium Carbonate SDS Safety SummaryDocument9 pagesSodium Carbonate SDS Safety SummaryDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Medical Examination Report Form: SECTION 1. Driver Information (To Be Filled Out by The Driver)Document11 pagesMedical Examination Report Form: SECTION 1. Driver Information (To Be Filled Out by The Driver)Deo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Nursing Management: Postoperative Care Key Points AsthmaDocument6 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Nursing Management: Postoperative Care Key Points AsthmaDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Caustic Soda Pels (Axiall) SDSDocument4 pagesCaustic Soda Pels (Axiall) SDSDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Snowflake Crystal (Sod Sesqui) SDSDocument7 pagesSnowflake Crystal (Sod Sesqui) SDSDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Nursing Management: Postoperative Care Key Points AsthmaDocument6 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Nursing Management: Postoperative Care Key Points AsthmaDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory ProblemsDocument3 pagesUpper Respiratory ProblemsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- CF Covid Ards PathoDocument3 pagesCF Covid Ards PathoDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDocument1 pageACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism Care MapDocument1 pageHypoparathyroidism Care MapDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment - Endocrine System - Nurse KeyDocument13 pagesNursing Assessment - Endocrine System - Nurse KeyDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma Proposal - Deo FactuarDocument12 pagesLean Six Sigma Proposal - Deo FactuarDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Sleep and Sleep Disorders Key Points SleepDocument4 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Sleep and Sleep Disorders Key Points Sleepsophia onu100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6sophia onuNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDocument3 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Value Stream Map - Deo FactuarDocument1 pageValue Stream Map - Deo FactuarDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Diabetes Mellitus Key PointsDocument6 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Diabetes Mellitus Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Endocrine Problems Key PointsDocument7 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Endocrine Problems Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Depreciation ActivityDocument4 pagesDepreciation ActivityDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Inflation ActivityDocument3 pagesInflation ActivityDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Co Existence of Low and High Heat Flow Anomalies On The South Balearic Margin and Algerian Oceanic BasinsDocument19 pagesCo Existence of Low and High Heat Flow Anomalies On The South Balearic Margin and Algerian Oceanic BasinsmariaNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument33 pagesInternship Reportstreamingmedia786No ratings yet
- EVERBUILD® EVERFLEX® 565 Clean Room Silicone: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesEVERBUILD® EVERFLEX® 565 Clean Room Silicone: Product Data Sheetsamira bashirvandNo ratings yet
- Diagram PLTA SLJDocument4 pagesDiagram PLTA SLJMEi Cuiet Luph-LuPhNo ratings yet
- Swiss ReDocument9 pagesSwiss ReTuxedo1982No ratings yet
- BD-90 75 Dekanter DE-EN 905-738-1 02-16Document4 pagesBD-90 75 Dekanter DE-EN 905-738-1 02-16RasoolKhadibiNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestIonescu Cristina-LucianaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Ipe Review ModuleDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Ipe Review ModuleDarren Ian MaalihanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Gold Petroleum's Performance and SuccessesDocument2 pagesLiquid Gold Petroleum's Performance and SuccessesShubham DawleNo ratings yet
- Mswin 9Document388 pagesMswin 9KZNo ratings yet
- Solid Free Form:: Quilt Flatten Quilt QuiltDocument3 pagesSolid Free Form:: Quilt Flatten Quilt QuiltNaganthrakumar RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Song of The Ancients Lyrics (English)Document1 pageSong of The Ancients Lyrics (English)Keith-Yves Rayden VonLiktinstine SiroisNo ratings yet
- LG Rotary Compressor GuideDocument32 pagesLG Rotary Compressor Guideวรศิษฐ์ อ๋อง33% (3)
- Probability As A General Concept Can Be Defined As The Chance of An Event OccurDocument14 pagesProbability As A General Concept Can Be Defined As The Chance of An Event OccurMuhammad Adnan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Zoom Basic Functions - FinalDocument31 pagesZoom Basic Functions - FinalWenshy LavadorNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Document6 pagesLightweight Slab Shoring System - ROYALFRAME50Renji Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- How To Do Chromatography With Candy and Coffee FiltersDocument4 pagesHow To Do Chromatography With Candy and Coffee FiltersSuharti HartiNo ratings yet
- Technical Sheet: Choline Chloride 60% VegetalDocument3 pagesTechnical Sheet: Choline Chloride 60% VegetalAnice CharafNo ratings yet
- LA36300 Circuit Breaker Data SheetDocument2 pagesLA36300 Circuit Breaker Data SheetALEJANDRO DOMINGUEZNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 & 11: Presented By: Group 4Document55 pagesExperiment 7 & 11: Presented By: Group 4Julliane JuanNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design Solution Manual 7th Edition PDFDocument5 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Solution Manual 7th Edition PDFEdmond Orena BautistaNo ratings yet
- Rice Today Vol. 13, No. 3 One Rice, Thousand GoldDocument2 pagesRice Today Vol. 13, No. 3 One Rice, Thousand GoldRice TodayNo ratings yet
- RTC Invoice 2965 Gj29es2223100505Document1 pageRTC Invoice 2965 Gj29es2223100505Alok PandeyNo ratings yet