Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Graphs - Part 3
Uploaded by
Jagdish Makwana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThe document discusses key concepts related to lines and linear equations in math and graphs. It defines lines with positive slope as having a direct relationship between x and y variables, and lines with negative slope as having an inverse relationship. Perfect complements are defined as lines where y=x, and perfect substitutes as lines where y=c-x. The document also discusses horizontal and vertical lines, shifts and rotations of lines, elasticity, intersections and equilibrium points, and calculating y values above or below a linear equation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts related to lines and linear equations in math and graphs. It defines lines with positive slope as having a direct relationship between x and y variables, and lines with negative slope as having an inverse relationship. Perfect complements are defined as lines where y=x, and perfect substitutes as lines where y=c-x. The document also discusses horizontal and vertical lines, shifts and rotations of lines, elasticity, intersections and equilibrium points, and calculating y values above or below a linear equation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 3
Uploaded by
Jagdish MakwanaThe document discusses key concepts related to lines and linear equations in math and graphs. It defines lines with positive slope as having a direct relationship between x and y variables, and lines with negative slope as having an inverse relationship. Perfect complements are defined as lines where y=x, and perfect substitutes as lines where y=c-x. The document also discusses horizontal and vertical lines, shifts and rotations of lines, elasticity, intersections and equilibrium points, and calculating y values above or below a linear equation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
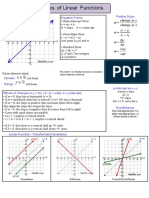
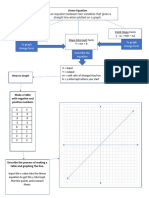
Graphs Lines
Math and Graph Refresher • Linear Equations
Lines (contd.) • Intercepts
• Horizontal Lines
• Positive Slope (+M) line is when X and Y react Perfect • Vertical Lines
Complim
positively with each other. E.g. Supply line… more ents • Positive Slope
the price more quantity supplied. • Perfect
• E.g. Y = C + MX, X = 5Y – 7 Y=X Compliment
• Phenomena like compliments show this • Negative Slope
behavior. As price increases quantity • Perfect Substitute
increases and vice versa.
• Shifts (Parallel
• Y = X (Slope M =+1, C = 0) means perfect
compliment i.e. for each additional unit of
Lines)
X we get one additional unit of Y. • Rotations (angle
lines)
• Negative Slope (-M) is when X and Y react • Elasticity and
Perfect
inversely to each other E.g. Demand line… more Substitutes implications of
the price lesser the demanded quantity. slope
• E.g. Y = C – MX, X = 7 – 5Y Y = 20 – X • Intersection and
• Phenomena like substitution show this Equilibrium
behavior. One goes for cheaper good (less • Maxima and
price) for higher quantity and vice versa. Minima of straight
• Y = C-X (Slope M = -1) means perfect
line regions
substitution i.e. one unit of X can be let go
of for an additional unit of Y until limit C.
• Sometimes the linear equations are interested to
know every value above or below a linear
equation … this means the output value Y should
be calculated above the equality value or below
the equality value.
• E.g. Y = 3X + 5 …
• if we want to know Y >= 3X + 5 then it’s the
value of Y above the line and Y <= 3X + 5 would
mean all Y values below the line.
You might also like
- Ext2 Maths Terry Lee PDFDocument415 pagesExt2 Maths Terry Lee PDFkev60% (5)
- Introduction To Fashion StylingDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Fashion StylingShefali Patel100% (3)
- FormatDocument9 pagesFormatMcjflores Villaruel BitaNo ratings yet
- Atm - Screen - Flow STD Chrted BankDocument11 pagesAtm - Screen - Flow STD Chrted BankJayavant MaliNo ratings yet
- Colgate - Palmolive LTD.: Brand Promotional ActivityDocument38 pagesColgate - Palmolive LTD.: Brand Promotional Activitysnehaldoddamani0% (1)
- Linear Graphs - PArt 6Document1 pageLinear Graphs - PArt 6Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 2Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 2Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear GraphsDocument1 pageLinear GraphsJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 5Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 5Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicDocument4 pagesFUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicTito AgooNo ratings yet
- ITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesDocument3 pagesITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 4Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 4Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterDocument12 pagesFunctions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterMohammed O IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Algebra I Unit 5 RelationshipsDocument8 pagesAlgebra I Unit 5 Relationshipsapi-287816312No ratings yet
- ITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesDocument3 pagesITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesEfraim KasinoNo ratings yet
- Cubic FunctionDocument19 pagesCubic Functionjoshua balansagNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions and Mathematical Modeling in The Port of Long BeachDocument77 pagesLinear Functions and Mathematical Modeling in The Port of Long BeachPort of Long BeachNo ratings yet
- Digital June KB Class-10Document34 pagesDigital June KB Class-10Uma MishraNo ratings yet
- M KPK X KVW: # of Roses (X) 3 4 5 6 9 Cost (Y) 45 60 75 90 135Document1 pageM KPK X KVW: # of Roses (X) 3 4 5 6 9 Cost (Y) 45 60 75 90 135MJ Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Crib Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCrib Sheet PDFHadarNo ratings yet
- MGMT 221 Ch. 1Document13 pagesMGMT 221 Ch. 1kebron100% (1)
- 4A Introduction To Rectangular HyperbolaDocument20 pages4A Introduction To Rectangular Hyperbolachuo.chengNo ratings yet
- Chapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationDocument12 pagesChapter One - Linear Equations and Its Interpretive ApplicationTewodrose Teklehawariat BelayhunNo ratings yet
- Rewriting and Solving EquationsDocument15 pagesRewriting and Solving Equationsman downNo ratings yet
- Working in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsDocument1 pageWorking in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- Alg+1+SOL+a 8+12 1+Inverse+Variation+Notes+PDFDocument2 pagesAlg+1+SOL+a 8+12 1+Inverse+Variation+Notes+PDFHARB Learning CentreNo ratings yet
- Example Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageExample Graphic Organizerapi-529122496No ratings yet
- Kidmath - Introduction To Geometry: Notation: We Name Points by Capital Letters. Two Points A and B DetermineDocument4 pagesKidmath - Introduction To Geometry: Notation: We Name Points by Capital Letters. Two Points A and B DetermineJames WigtonNo ratings yet
- Business MathesDocument152 pagesBusiness MathesBelay MezgeboNo ratings yet
- Lines in Coordinate Plane SummaryDocument10 pagesLines in Coordinate Plane Summaryyatharth.pitchourwayNo ratings yet
- 08 Lines and Linear ModelsDocument12 pages08 Lines and Linear ModelsharshilNo ratings yet
- By: Yap Khun Yee NG Woei Jian Khu Ing Ching Mok Shien ChengDocument18 pagesBy: Yap Khun Yee NG Woei Jian Khu Ing Ching Mok Shien ChengCoco YapNo ratings yet
- MC Bus Slope 2009 1Document2 pagesMC Bus Slope 2009 1redzuan.hajaraNo ratings yet
- Transformations 1Document32 pagesTransformations 1KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations and Its Application: Chapter One EquationDocument13 pagesLinear Equations and Its Application: Chapter One EquationWudneh AmareNo ratings yet
- Week-4 - MathsofDemandSupply - FarrukhWKhan - Spring2021Document20 pagesWeek-4 - MathsofDemandSupply - FarrukhWKhan - Spring2021Muddasir Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Ebe1133 Lu2 2022Document53 pagesEbe1133 Lu2 2022M.Musirah Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- Core RevisionDocument2 pagesCore RevisionMaasa AliNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialDocument18 pagesDerivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialJust SleepingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StudentDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Studentgerearegawi721No ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: 3 Miniterm, Nov-Dec 2004Document32 pagesComputer Graphics: 3 Miniterm, Nov-Dec 2004api-3799599100% (1)
- Exploring Fractional IndicesDocument15 pagesExploring Fractional IndicesLuly G.No ratings yet
- Straight Line Practice Booklet 1Document7 pagesStraight Line Practice Booklet 1jeevan gowdaNo ratings yet
- 11self Theory-Straight LineDocument5 pages11self Theory-Straight Lineرافت باصهيNo ratings yet
- UPenn Intro To Models - Lect 1Document1 pageUPenn Intro To Models - Lect 1SicklesNo ratings yet
- A Pair of ST - LinesDocument28 pagesA Pair of ST - LinesRajesh PurohitNo ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations, Functions and Their Applicationsyonas100% (1)
- As MathematicsDocument17 pagesAs Mathematicsjupe01No ratings yet
- Linear EquationDocument4 pagesLinear EquationthatweirdchildpNo ratings yet
- Maths Graphs PosterDocument1 pageMaths Graphs PosterHilary Louise LinNo ratings yet
- Functions and The Vertical Line Test: X y X y X yDocument3 pagesFunctions and The Vertical Line Test: X y X y X ylkjNo ratings yet
- CurvesDocument12 pagesCurveskandarpNo ratings yet
- Trigo Q3W7and8Document21 pagesTrigo Q3W7and8Leoniz VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationsDocument11 pagesChapter 1. Linear Functions & EquationstemedebereNo ratings yet
- ch1 PDFDocument27 pagesch1 PDFerakiuydfoiawudNo ratings yet
- MIF Textbook HSC Maths 2 Units PDFDocument412 pagesMIF Textbook HSC Maths 2 Units PDFHIMMZERLAND100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsashNo ratings yet
- Rate of Change and SlopeDocument1 pageRate of Change and SlopeVeranda PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 AsymptotesDocument21 pagesChapter-10 AsymptotesNitish PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse FunctionsDocument9 pagesMathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse Functionsdonz69914No ratings yet
- Ch1 Geometry 2Document47 pagesCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123No ratings yet
- ADDING FrameworkDocument1 pageADDING FrameworkJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Business Marketing - Precise Software: DescriptionDocument3 pagesBusiness Marketing - Precise Software: DescriptionJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Commercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum PumpDocument3 pagesCommercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum PumpJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 4Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 4Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Fiancial Summary - !Document232 pagesFiancial Summary - !Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- India: Environmental Issues: BriefingDocument4 pagesIndia: Environmental Issues: BriefingJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Laws and Regulations Related To Volkswagen Violations - Volkswagen Light Duty Diesel Vehicle Violations For Model Years 2009-2016 - US EPADocument2 pagesLaws and Regulations Related To Volkswagen Violations - Volkswagen Light Duty Diesel Vehicle Violations For Model Years 2009-2016 - US EPAJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Choice and Utility: Basic MicroeconomicsDocument25 pagesConsumer Choice and Utility: Basic MicroeconomicsSergio ConjugalNo ratings yet
- Service Quality Models A ReviewDocument45 pagesService Quality Models A ReviewVadim Lopotenco0% (1)
- Iast ResearchDocument10 pagesIast Researchnica pidlaoanNo ratings yet
- Competition Act 2002 (NYP)Document13 pagesCompetition Act 2002 (NYP)nitesh tekriwalNo ratings yet
- M Commerce NotesDocument16 pagesM Commerce NotesSalmon Prathap SinghNo ratings yet
- Asignar SCB Indicatores PDFDocument2 pagesAsignar SCB Indicatores PDFFernandoRieraJuradoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Economics PracticeDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Economics PracticeJoe StoneNo ratings yet
- Barber Shop AnalysisDocument5 pagesBarber Shop Analysisnantoine42924No ratings yet
- Media File Booz&Co GMA Shopper Marketing 4.0Document32 pagesMedia File Booz&Co GMA Shopper Marketing 4.0stephenjpomeroyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On FMCG IndustryDocument7 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On FMCG IndustryBhumika JainNo ratings yet
- LuxDocument4 pagesLuxBinaya Pradhan100% (2)
- Digital Marketing Companies in DubaiDocument3 pagesDigital Marketing Companies in DubaiDENNIS KIHUNGINo ratings yet
- Mid Semester CB 2020Document3 pagesMid Semester CB 2020Hemali KapadiyaNo ratings yet
- 65% Consumer Products Sold in Pakistan Are FakeDocument3 pages65% Consumer Products Sold in Pakistan Are FakeHuzaifa Bin SaeedNo ratings yet
- Construction LTD.: Strategic Business PlanDocument14 pagesConstruction LTD.: Strategic Business PlanAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- LPG Domestic Cooking Gas Customers: AttentionDocument1 pageLPG Domestic Cooking Gas Customers: AttentionBachchan MishraNo ratings yet
- Bolt Business Plan PDFDocument4 pagesBolt Business Plan PDFAnonymous 9DCXb7lBsNo ratings yet
- JeansDocument7 pagesJeansAniket KatariaNo ratings yet
- Market Basket Analysis 2 PDFDocument8 pagesMarket Basket Analysis 2 PDFabhishekniiftNo ratings yet
- Nickel and Dime AnsweresDocument6 pagesNickel and Dime Answeresalbo355No ratings yet
- 2019 11 30 Netflix and BlockbusterDocument12 pages2019 11 30 Netflix and BlockbusterAndrew AkakoNo ratings yet
- MC DonaldDocument2 pagesMC DonaldAatif Soomro100% (2)
- Actividad 6 Punto 4 Inlges Plan of DistributionDocument7 pagesActividad 6 Punto 4 Inlges Plan of DistributionSANDRA TARAZONANo ratings yet
- Kiran - Synopsis - 1Document4 pagesKiran - Synopsis - 1umeshrathoreNo ratings yet
- Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyDocument14 pagesCreating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and LoyaltyJosette Christine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument3 pagesNational Income AccountingTRIZIE CHENGNo ratings yet