Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Graphs - Part 2
Uploaded by
Jagdish Makwana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13K views1 pageThis document provides a summary of key concepts related to lines and linear equations in mathematics including:
1) Different types of linear equations where X and Y can appear on the same or different sides with constant or variable coefficients.
2) Lines that pass through the origin with no intercepts when in the form of Y=MX.
3) Horizontal and vertical lines where the slope is 0 for horizontal and undefined for vertical, with the corresponding intercept also being undefined.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a summary of key concepts related to lines and linear equations in mathematics including:
1) Different types of linear equations where X and Y can appear on the same or different sides with constant or variable coefficients.
2) Lines that pass through the origin with no intercepts when in the form of Y=MX.
3) Horizontal and vertical lines where the slope is 0 for horizontal and undefined for vertical, with the corresponding intercept also being undefined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13K views1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 2
Uploaded by
Jagdish MakwanaThis document provides a summary of key concepts related to lines and linear equations in mathematics including:
1) Different types of linear equations where X and Y can appear on the same or different sides with constant or variable coefficients.
2) Lines that pass through the origin with no intercepts when in the form of Y=MX.
3) Horizontal and vertical lines where the slope is 0 for horizontal and undefined for vertical, with the corresponding intercept also being undefined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
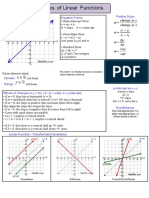
Graphs Lines
Math and Graph Refresher • Linear Equations
Lines (contd.) • Intercepts
Complimentary • Horizontal Lines
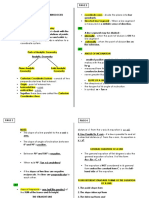
• Sometimes the formula has both X and Y on behavior • Vertical Lines
same side of the equation (say LHS), in which • Positive Slope
X – 2Y = 0
case the other side of equation (RHS) can X/2 = Y • Perfect
have a constant or X or Y term itself. Compliment
• 25 = X + Y, 25X = X + Y, 25Y = X + Y, X – • Negative Slope
2Y = 0.
• Perfect Substitute
• When the simplified F(X) form is Y = MX, the • Shifts (Parallel
line passes through the origin (0,0) with no X Lines)
or Y intercept. Among above examples (25X • Rotations (angle
= X + Y, 25Y = X + Y, X – 2Y = 0) are all of Horizontal Line lines)
this form. Here X and Y are called as linear Y = 10 • Elasticity and
compliments. Slope M = 0 implications of
X-Intercept slope
• When either X or Y component is missing in = Undefined
• Intersection and
the equation the line could be Horizontal or
Equilibrium
Vertical respectively.
• Maxima and
• In case of horizontal line M (slope) is Minima of straight
ZERO. X intercept is undefined. Vertical Line
line regions
• In case of vertical line M (slope) is infinity. X=4
Y intercept is undefined Slope M = Infinity
Y-Intercept
= Undefined
You might also like
- Ombined Footing Design Calculation in Excel SpreadsheetDocument12 pagesOmbined Footing Design Calculation in Excel SpreadsheetfelipeNo ratings yet
- 1 GR 11 Functions Graphs and Exercise Questions AnswersDocument12 pages1 GR 11 Functions Graphs and Exercise Questions AnswersWalter Mazibuko100% (1)
- Universitext Siegfried Bosch Algebraic Geometry and Commutative PDFDocument508 pagesUniversitext Siegfried Bosch Algebraic Geometry and Commutative PDFYusuf Berk AKÇAYNo ratings yet
- Optical Engineering FundamentalsDocument292 pagesOptical Engineering Fundamentalseduardo0% (1)
- Measurement of Focal Spots of Industrial X-Ray Tubes by Pinhole ImagingDocument7 pagesMeasurement of Focal Spots of Industrial X-Ray Tubes by Pinhole ImagingERNESTO ENRIQUE FERNANDEZ BAPTISTANo ratings yet
- Linear GraphsDocument1 pageLinear GraphsJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 5Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 5Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - PArt 6Document1 pageLinear Graphs - PArt 6Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 3Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 3Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicDocument4 pagesFUNCTIONS - Linear, Quadratics and CubicTito AgooNo ratings yet
- Working in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsDocument1 pageWorking in The Cartesian Plane: KeywordsEmrah ozkanNo ratings yet
- 4A Introduction To Rectangular HyperbolaDocument20 pages4A Introduction To Rectangular Hyperbolachuo.chengNo ratings yet
- Lines in Coordinate Plane SummaryDocument10 pagesLines in Coordinate Plane Summaryyatharth.pitchourwayNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 4Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 4Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Practice Booklet 1Document7 pagesStraight Line Practice Booklet 1jeevan gowdaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15-Increasing & Decreasing Functions Concavity Point of Inflection Relative ExtremaDocument17 pagesLesson 15-Increasing & Decreasing Functions Concavity Point of Inflection Relative ExtremaJhonnel CapuleNo ratings yet
- Algebra I Unit 5 RelationshipsDocument8 pagesAlgebra I Unit 5 Relationshipsapi-287816312No ratings yet
- Ebe1133 Lu2 2022Document53 pagesEbe1133 Lu2 2022M.Musirah Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- ITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesDocument3 pagesITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Digital June KB Class-10Document34 pagesDigital June KB Class-10Uma MishraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse FunctionsDocument9 pagesMathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse Functionsdonz69914No ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- ITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesDocument3 pagesITM401S Unit 3.7.4 Exponential and Logarithmic CurvesEfraim KasinoNo ratings yet
- 11self Theory-Straight LineDocument5 pages11self Theory-Straight Lineرافت باصهيNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Exploring Properties of Parent Functions PDFDocument5 pages1.3 Exploring Properties of Parent Functions PDFLevin JackNo ratings yet
- Functions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterDocument12 pagesFunctions and Line in Coordinate: University of Kirkuk Civil Engineering Department 1 Stage, 1 SemsterMohammed O IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Function 1Document12 pagesFunction 1tahosin jusiNo ratings yet
- Rewriting and Solving EquationsDocument15 pagesRewriting and Solving Equationsman downNo ratings yet
- A Pair of ST - LinesDocument28 pagesA Pair of ST - LinesRajesh PurohitNo ratings yet
- Straght LineDocument23 pagesStraght LineCHIA POH HOOI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 29, 2024Document9 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 29, 2024k.v.v.satyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument23 pagesDefinitionashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry TerminologiesDocument3 pagesAnalytic Geometry TerminologiesMariell TabanaoNo ratings yet
- Slope of Lines V5Document7 pagesSlope of Lines V5Windy CarlesNo ratings yet
- Day-4-UPCAMP-2018Document40 pagesDay-4-UPCAMP-2018afunabermudezNo ratings yet
- Linear Functions and Mathematical Modeling in The Port of Long BeachDocument77 pagesLinear Functions and Mathematical Modeling in The Port of Long BeachPort of Long BeachNo ratings yet
- 4B The TruncusDocument7 pages4B The Truncuschuo.chengNo ratings yet
- 16 Martie - Asimptote - Teorie + QuizDocument5 pages16 Martie - Asimptote - Teorie + Quizdm.jebeleanNo ratings yet
- XI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESDocument47 pagesXI - Maths - Chapter 10 - STRAIGHTLINESStephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Project Review Third Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesMath 8 Project Review Third Quarter NotesaliyahsduNo ratings yet
- Maths 04 1Document19 pagesMaths 04 1Komal mushtaqNo ratings yet
- As MathematicsDocument17 pagesAs Mathematicsjupe01No ratings yet
- Module 5: Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocument4 pagesModule 5: Introduction To Linear ProgrammingJan JanNo ratings yet
- Iitjee Notes by Dipesh Sir Straight LineDocument6 pagesIitjee Notes by Dipesh Sir Straight LineKakakaunNo ratings yet
- Maths Graphs PosterDocument1 pageMaths Graphs PosterHilary Louise LinNo ratings yet
- Slide Chapter 1Document74 pagesSlide Chapter 1Sagar ChaulagaiNo ratings yet
- 18 Mathematics Straight LineDocument17 pages18 Mathematics Straight LineArunava BasuNo ratings yet
- Monomial and Polynomial: Polynomials. Each of The MonomialsDocument66 pagesMonomial and Polynomial: Polynomials. Each of The MonomialsMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeDocument37 pagesChapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeNitish PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer Second QuarterDocument6 pagesMath Reviewer Second Quarterwjohn6182No ratings yet
- Straight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDocument27 pagesStraight Line: AIEEE SyllabusDeepali KotaryNo ratings yet
- CurvesDocument12 pagesCurveskandarpNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For GeometryDocument2 pagesReviewer For GeometryAlice AsmodeusNo ratings yet
- Transformations 1Document32 pagesTransformations 1KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry Mind MapDocument42 pagesCoordinate Geometry Mind MapOm SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineDocument1 pageLinear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineNoor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Pair of LinesDocument58 pagesPair of LinesKahaan KakabaliaNo ratings yet
- Simple and Multiple Linear RegressionDocument91 pagesSimple and Multiple Linear Regressionkomal kashyapNo ratings yet
- Limit and ContinuityDocument8 pagesLimit and ContinuityAsadullah ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Tracing of CurvesDocument15 pagesTracing of CurvesKRISHNA CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- The ABC's of Mathematics Concepts: Prepared By: Trisha Bujalance, Jazel Zoilo and Blademeir JavaDocument19 pagesThe ABC's of Mathematics Concepts: Prepared By: Trisha Bujalance, Jazel Zoilo and Blademeir JavaTrisha Mae Ebrada BujalanceNo ratings yet
- Wjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 Algebra and Functions BDocument1 pageWjec Gce Mathematics Unit 3 Algebra and Functions Bginrosmom1No ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument8 pagesLimits and Continuityprince12No ratings yet
- ADDING FrameworkDocument1 pageADDING FrameworkJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Business Marketing - Precise Software: DescriptionDocument3 pagesBusiness Marketing - Precise Software: DescriptionJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Commercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum PumpDocument3 pagesCommercializing The Kunst 1600 Dry Piston Vacuum PumpJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphs - Part 4Document1 pageLinear Graphs - Part 4Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Fiancial Summary - !Document232 pagesFiancial Summary - !Jagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- India: Environmental Issues: BriefingDocument4 pagesIndia: Environmental Issues: BriefingJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Laws and Regulations Related To Volkswagen Violations - Volkswagen Light Duty Diesel Vehicle Violations For Model Years 2009-2016 - US EPADocument2 pagesLaws and Regulations Related To Volkswagen Violations - Volkswagen Light Duty Diesel Vehicle Violations For Model Years 2009-2016 - US EPAJagdish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Nuclear Medicine - Edited Version)Document65 pagesLecture Notes in Nuclear Medicine - Edited Version)Jestia Lyn EngracialNo ratings yet
- VC.11: 3D Flow Along LiteracyDocument9 pagesVC.11: 3D Flow Along LiteracySri RaghavanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 - THE LAWS OF PHYSICS-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesMODULE 6 - THE LAWS OF PHYSICS-WPS OfficePsychopompNo ratings yet
- The Gartner Hype Cycle For MetamaterialsDocument3 pagesThe Gartner Hype Cycle For MetamaterialsJānis BērziņšNo ratings yet
- Yarn Formation - Spinning - AymanDocument125 pagesYarn Formation - Spinning - AymanTamer Farouk KhalifaNo ratings yet
- FSK ScopeDocument4 pagesFSK ScopeHope DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Class: XII Session: 2020-2021 Subject: Physics Sample Question Paper (Theory)Document10 pagesClass: XII Session: 2020-2021 Subject: Physics Sample Question Paper (Theory)Hritik JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 3621 11403 1 PB PDFDocument8 pages3621 11403 1 PB PDFAlifah PutriNo ratings yet
- 1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveDocument2 pages1588244806UPHTE-601 Unit3.7 JU - Hysteresis CurveMihir RanaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Document4 pagesAP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Dheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiography Procedure RNDTDocument27 pagesRadiography Procedure RNDTrashmibetuNo ratings yet
- A Design Handbook For Phase Change Thermal Control and Energy Storage DevicesDocument256 pagesA Design Handbook For Phase Change Thermal Control and Energy Storage DevicesProfessor MichelNo ratings yet
- Propagation and Attenuation Characteristics of Various Ground VibrationsDocument12 pagesPropagation and Attenuation Characteristics of Various Ground VibrationsTony Christian Canahua ChoquezaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document27 pagesLec 4KuthuraikaranNo ratings yet
- Iwa Mpt-1 - Chemistry - Que. & Sol.Document5 pagesIwa Mpt-1 - Chemistry - Que. & Sol.Prajwal PawarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior of Materials: Lecture 4: Elasticity by Dr. Yumna QureshiDocument38 pagesMechanical Behavior of Materials: Lecture 4: Elasticity by Dr. Yumna QureshiArslanNo ratings yet
- Pipette CalibrationDocument9 pagesPipette CalibrationMaame Efua NeizerNo ratings yet
- NLM 6Document3 pagesNLM 6Ramesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Phsics Newton's LawDocument145 pagesPhsics Newton's LawMontazer WorkNo ratings yet
- Measurement of SolidsDocument7 pagesMeasurement of SolidsWasim AkramNo ratings yet
- ATOM Flashcut EASY Series Models 222 888 BrochureDocument2 pagesATOM Flashcut EASY Series Models 222 888 BrochureBowpack EngineerNo ratings yet
- Steel Lecture - 1Document131 pagesSteel Lecture - 1vinodh159No ratings yet
- 06-Combined FootingDocument12 pages06-Combined FootingHusein El MazloumNo ratings yet
- Composite Book CatalogueDocument8 pagesComposite Book CatalogueYash ShahNo ratings yet
- Design and Evaluation of Residential Building Alongwith Floating ColumnDocument4 pagesDesign and Evaluation of Residential Building Alongwith Floating ColumnSivaAgathamudiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document5 pagesLecture 2RishitaNo ratings yet