Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instrument Identification and Line Symbols
Uploaded by
Talha Imtiaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views32 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views32 pagesInstrument Identification and Line Symbols
Uploaded by
Talha ImtiazCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
Instrument identification
and line symbols
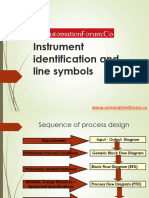
Sequence of process design
Stoichiometry Input - Output Diagram
Preliminary Process Conditions Generic Block Flow Diagram
Block Flow Diagram (BFD)
Preliminary Material Balance
Material, Energy Balances +
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
Equipment Specifications
Mechanical & Instrumentation
Piping and Instrument Diagram
Information
(PID)
Block flow diagram
It consists of simple block elements that are connected with an arrow. It
describes following information’s,
Each block represents a process function which in reality may consist of
several pieces of equipment.
Gives a clear overview uncluttered by details.
Effective for conceptualizing a new process or a PFD.
Major flow lines shown with arrows giving direction of flow.
Critical information unique to the process supplied.
Provides preliminary material balance.
Ammonia
Urea Prills Bagging
Air Ammonia Urea &
Carbon Dioxide
Unit Unit Shipping
Fuel Gas Utility
Utility
Unit
Unit
Process flow diagram
It is a diagram of fluid flow system showing the equipment items connected
by major process pipes and containing data on essential process control
circuits or major process requirements. It would include following details.
Process piping
Major equipment names
Major equipment numbers
Major equipment identification numbers
Control valves
Interconnection with other system
Major bypass and circulation lines
System rating and operational values as maximum, minimum and normal flow
Process parameters i.e. temperature and pressure
Composition of fluids
Process flow diagram
A process flow diagram does not include following details,
Pipe class
Isolation and shutoff valves
Maintenance vents and drains
Relief and safety valves
Code class information
Seismic class information
Instruments
Process flow diagram
A process flow diagram does not following details,
Pipe class
Isolation and shutoff valves
Maintenance vents and drains
Relief and safety valves
Code class information
Seismic class information
Instruments
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram
It is a schematic representation of functional relationship of piping,
instrumentation and system equipment components. It is termed as final
step of process design. It includes following information’s,
Instrumentation and their designation along with indicators, recorders and
controllers
All equipments with their names and particular numbers
All valves and their corresponding numbers
Piping related to its size, schedule, material of construction and insulation
Miscellaneous - vents, drains, special fittings, sampling lines, reducers,
increasers and swaggers
Permanent start-up and flush lines
Directions of flow
Interlinked references
Control inputs and outputs, interlocks
Quality standard
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram
Computer control system input
Vendor and contractor interfaces
Identification of components and subsystems delivered by others
Intended physical sequence of the equipment
All utilities with identification related to inputs and outputs
It doesn’t include following parameters,
Route valves for instruments
Control relays
Manful switches
Equipment rating or capacity
Pressure, temperature and flow data
Elbows, tees and its related standard fitting
Extensive explanatory notes
Instrument identification tags
PI&D Exercise
Line types
Process/Instrument line connections
Instrument bubbles
Process valve types
Valve actuator types
Liquid level measurement devices
Flow measurement devices (flowing left-to-right)
Flow measurement devices (flowing left-to-right)
Process equipment
Process equipment
Reactor Symbol
Reactor Symbol
Introduction to applied process
control
Prof. M A Tahir
( Page 201 – 216 )
You might also like
- Substation Automation Systems: Design and ImplementationFrom EverandSubstation Automation Systems: Design and ImplementationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Instrument_identification_and_line_symbols_1710347067Document32 pagesInstrument_identification_and_line_symbols_1710347067himanshu manoriNo ratings yet
- P&ID SeminarDocument66 pagesP&ID Seminar蔡蕲82% (11)
- Automatic Instruments and Measuring Systems: Jones' Instrument TechnologyFrom EverandAutomatic Instruments and Measuring Systems: Jones' Instrument TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- P&ID - Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocument5 pagesP&ID - Piping and Instrumentation DiagramEngr Shahid ZafarNo ratings yet
- Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants: Volume 1From EverandApplied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants: Volume 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- List of P&ID Items: Process IndustryDocument3 pagesList of P&ID Items: Process IndustryNur Fatin AwanisNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers: A Practical Approach to IEC 61131-3 using CoDeSysFrom EverandProgrammable Logic Controllers: A Practical Approach to IEC 61131-3 using CoDeSysNo ratings yet
- Pid 01Document41 pagesPid 01Dung Thu Le100% (1)
- Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocument8 pagesPiping and Instrumentation DiagramSourirajan BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationFrom EverandThe Handbook of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) for Design and ImplementationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lecture 4 - ISA Standards and Line SymbolsDocument23 pagesLecture 4 - ISA Standards and Line SymbolsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power Valves & Hose Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandFluid Power Valves & Hose Fittings World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) 2.4 Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)Document34 pages2.3 Process Flow Diagram (PFD) 2.4 Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)Sofea Izyan100% (1)
- Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocument2 pagesPiping and Instrumentation DiagramJejomar DantesNo ratings yet
- P&ID AnalysisDocument104 pagesP&ID AnalysisSaz ZasNo ratings yet
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)Document13 pagesPiping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)mohamad ashaziq100% (8)
- Process and Control System (General)Document16 pagesProcess and Control System (General)Sang Duong VanNo ratings yet
- P & ID PresentationDocument104 pagesP & ID PresentationShaheer Shabbir100% (17)
- Notes Process DiagramDocument42 pagesNotes Process DiagramDinesh guhanNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD) & Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&id)Document29 pagesProcess Flow Diagram (PFD) & Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&id)Mohd Nor Ariffin100% (2)
- P&ID Diagram ExplainedDocument4 pagesP&ID Diagram ExplainedmirvaiskhanNo ratings yet
- Process Symbol and Process DiagramDocument6 pagesProcess Symbol and Process DiagramRukanuzzaman RaselNo ratings yet
- Process Unit 2B Module 1Document27 pagesProcess Unit 2B Module 1Zabdi Paulina Pérez UrquietaNo ratings yet
- P&ID Process Diagram GuideDocument5 pagesP&ID Process Diagram GuideMOHAMMAD HASHIM KHANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To P&Id: Types of Chemical Process DiagramsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To P&Id: Types of Chemical Process DiagramsAldrick Lance HernandezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics PFD and P&IDDocument36 pagesEngineering Graphics PFD and P&IDeja70No ratings yet
- Essential P&ID guide with symbols and usesDocument5 pagesEssential P&ID guide with symbols and useslochoadauk53No ratings yet
- Chapter 04 InstrumentDocument20 pagesChapter 04 InstrumentRushanth ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- KSP Instrument DrawingDocument15 pagesKSP Instrument DrawingZulfequar R. Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- AICHE - PFD - PID - Lectura No 1 EGOYP 2015Document8 pagesAICHE - PFD - PID - Lectura No 1 EGOYP 2015Yuldor LopezNo ratings yet
- P&ID - Piping and Instrumentation Diagram ExplainedDocument2 pagesP&ID - Piping and Instrumentation Diagram ExplainednoxleekNo ratings yet
- Introduction To P&ID Reading & DesignDocument45 pagesIntroduction To P&ID Reading & DesignJaime Segura100% (1)
- Designing A Process Flowsheet-Mayo 2009 PDFDocument7 pagesDesigning A Process Flowsheet-Mayo 2009 PDFKathy SandovalNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About Piping and Instrumentation DiagramDocument4 pagesBasic Knowledge About Piping and Instrumentation DiagramsorbariNo ratings yet
- P & I DiagramsDocument20 pagesP & I DiagramsYash PatelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Design and Engineering Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFDocument7 pagesDetailed Design and Engineering Deliverable List (Sample) - The Project Definition PDFPeter Bridge100% (1)
- HAZOP Study Guide for Process SafetyDocument61 pagesHAZOP Study Guide for Process SafetyAmritRoshniKaurNo ratings yet
- 02 P&ID Guide PDFDocument9 pages02 P&ID Guide PDFcharleselitb92No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument104 pagesUntitledEvans HopeNo ratings yet
- PFDDocument8 pagesPFDDurgaRaoVutlaNo ratings yet
- Input Details and Reference DocumentsDocument8 pagesInput Details and Reference DocumentsJULIUS CAEZAR CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- 46495402733Document2 pages46495402733Abd El-Kader IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lecture PFD & P &idDocument46 pagesLecture PFD & P &idsanjaykumarkadam2289100% (1)
- PID LectureDocument42 pagesPID Lecturekathrin_jazz2695% (20)
- Process Flow Diagram Definition and UsesDocument1 pageProcess Flow Diagram Definition and UsesNurul Anna GoaNo ratings yet
- P&id - 1Document5 pagesP&id - 1dasubhai100% (1)
- P&IDDocument34 pagesP&IDHabibNo ratings yet
- 10a Piping Diagrams and DrawingsDocument8 pages10a Piping Diagrams and DrawingsAnonymous lswzqloNo ratings yet
- Instrument and Control System Documents ListDocument4 pagesInstrument and Control System Documents ListbaigprodNo ratings yet
- Process Diagrams Flow Sheet SynthesisDocument44 pagesProcess Diagrams Flow Sheet SynthesisAdeel Hussain ManjNo ratings yet
- Pre CommissioningDocument10 pagesPre CommissioningRajesh100% (2)
- PFD & PID Eng Toolbox InternetDocument21 pagesPFD & PID Eng Toolbox InternetFransiska Adelia FroggersNo ratings yet
- P&ID Diagram Guide: Symbols, Loops & How to Read Piping Instrumentation DiagramsDocument34 pagesP&ID Diagram Guide: Symbols, Loops & How to Read Piping Instrumentation Diagramsalejandro inostrozaNo ratings yet
- P&ID ManualDocument35 pagesP&ID Manualdharan kumarNo ratings yet
- Differences Between PFD, P&ID and BFD DiagramsDocument3 pagesDifferences Between PFD, P&ID and BFD DiagramsAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrument DiagramDocument23 pagesPiping & Instrument Diagramanon_770350620No ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram (Introduction)Document3 pagesProcess Flow Diagram (Introduction)Hassan M KhanNo ratings yet
- Paint ArticlesDocument1 pagePaint ArticlesTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Document13 pages3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Farnaz Va Ali MohammadlouNo ratings yet
- Antonym: Word Urdu Meaning Antonym Urdu MeaningDocument1 pageAntonym: Word Urdu Meaning Antonym Urdu MeaningTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Document13 pages3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Farnaz Va Ali MohammadlouNo ratings yet
- 2015-Tackling Difficult Mixing ProblemsDocument8 pages2015-Tackling Difficult Mixing Problemsjuan sepulvedaNo ratings yet
- 3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Document13 pages3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Farnaz Va Ali MohammadlouNo ratings yet
- Table For PU SERIESDocument1 pageTable For PU SERIESTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument19 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument16 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument18 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument18 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument19 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Document13 pages3 E7 AD6 A0 D 01Farnaz Va Ali MohammadlouNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument6 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Liaison ScrapTechDocument9 pagesLiaison ScrapTechTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument16 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Power House:: 2. Participating Teams Are Expected To Bring Their Own 2 PVC COCA COLA BOTTLES (1.5Document1 pagePower House:: 2. Participating Teams Are Expected To Bring Their Own 2 PVC COCA COLA BOTTLES (1.5Talha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Ambassador Liaison WTT17Document5 pagesAmbassador Liaison WTT17Talha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 3 SunnahDocument26 pages3 SunnahWafiy AkmalNo ratings yet
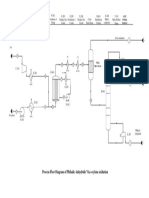
- Process Flow Diagram of Phthalic Anhydride Via O-Xylene OxidationDocument1 pageProcess Flow Diagram of Phthalic Anhydride Via O-Xylene OxidationTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- 3 SunnahDocument26 pages3 SunnahWafiy AkmalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document28 pagesLecture 13Talha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document10 pagesLecture 12Talha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Optimize Batch Reactor PerformanceDocument10 pagesOptimize Batch Reactor PerformancewaqaskhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document19 pagesLecture 11Talha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument25 pagesProcess Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- HastelloyDocument24 pagesHastelloyTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument32 pagesProcess Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Process ControlDocument33 pagesChemical Plant Process ControlTalha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Fluent TutorialDocument23 pagesFluent TutorialYashad KasarNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of Ramjet: Thermophysics and Aeromechanics, 2009, Vol. 16, No. 2Document11 pagesExergy Analysis of Ramjet: Thermophysics and Aeromechanics, 2009, Vol. 16, No. 2alexNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment BernoulliDocument13 pagesLab Experiment BernoulliAmoluck BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Pump Cavitation and How To Avoid ItDocument5 pagesPump Cavitation and How To Avoid Itfawmer61No ratings yet
- Aga 8 Part 1Document62 pagesAga 8 Part 1Leandro SantanaNo ratings yet
- CEI Graduate Diploma SyllabusDocument257 pagesCEI Graduate Diploma Syllabuse--cityandguilds100% (8)
- Xfab SCH FB GN Icfms 004Document1 pageXfab SCH FB GN Icfms 004VchengNo ratings yet
- Pump System Analysis and SizingDocument157 pagesPump System Analysis and Sizingtachet100% (1)
- Hydraulic Caluculation ReportDocument16 pagesHydraulic Caluculation ReportbecpavanNo ratings yet
- ABB Handbook - Flowmeters (Ingles)Document55 pagesABB Handbook - Flowmeters (Ingles)Eduardo ZapataNo ratings yet
- Isentropic Flow - Area VariationDocument11 pagesIsentropic Flow - Area VariationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Ace FMDocument146 pagesAce FMMr Perfect100% (1)
- CE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020Document42 pagesCE-UG-2018 Spring FEB-JUN 2020SalmanNo ratings yet
- The Aoki Katashi Award: T-Rex16 T-Rex22 T-Rex32 T-Rex45Document4 pagesThe Aoki Katashi Award: T-Rex16 T-Rex22 T-Rex32 T-Rex45Munekatsu KamiyaNo ratings yet
- VTU Tribology QuestionsDocument9 pagesVTU Tribology QuestionsTHRISHAN SINGH R LNo ratings yet
- Blast Furnace Aero Dynamics NewDocument36 pagesBlast Furnace Aero Dynamics NewSandeepNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ActuatorsDocument32 pagesHydraulic ActuatorsNilesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ahu 2Document5 pagesAhu 2SADJI RachidNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of Marine Surface Vessel Dynamics: DR Tristan Perez Professor Thor I FossenDocument16 pagesModelling and Simulation of Marine Surface Vessel Dynamics: DR Tristan Perez Professor Thor I FossenBENHNo ratings yet
- AFX8010 Combine Belts, Chains, Filters and ValvesDocument1,077 pagesAFX8010 Combine Belts, Chains, Filters and Valvesvut73 aNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of FluidsSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- CEP Refresher Problem Set3Document7 pagesCEP Refresher Problem Set3Alyssa Camille Malig-onNo ratings yet
- Effects of Venturi Meter Orientation and Pressure Drop Location for CalibrationDocument4 pagesEffects of Venturi Meter Orientation and Pressure Drop Location for CalibrationWilliam Arthur Mackloren0% (1)
- Experiment No. 5 Demonstration of Continuity Equation: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 5 Demonstration of Continuity Equation: I. ObjectivesMark B. Barroga100% (1)
- Hydraulic Calculation For FFDocument2 pagesHydraulic Calculation For FFAnsari1918No ratings yet
- Tugas Remidi Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik 2015Document8 pagesTugas Remidi Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik 2015RezaNo ratings yet
- (Epstein P. S.) On The Air Resistance of Projectil (BookFi)Document16 pages(Epstein P. S.) On The Air Resistance of Projectil (BookFi)eki dwiNo ratings yet
- Halliburton PLTDocument16 pagesHalliburton PLTbahmangNo ratings yet
- Pump Energy Efficiency Calculation ToolDocument8 pagesPump Energy Efficiency Calculation Toolqwerty_conanNo ratings yet