Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME-213 Mechanics of Solids: Dr. Khalid Rahman Ph:2351 Email: Khalid - Rehman@giki - Edu.pk
Uploaded by
Murtaza RashdiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME-213 Mechanics of Solids: Dr. Khalid Rahman Ph:2351 Email: Khalid - Rehman@giki - Edu.pk
Uploaded by
Murtaza RashdiCopyright:
Available Formats
ME-213
MECHANICS OF
SOLIDS
Dr. Khalid Rahman
Ph:2351
Email: khalid.rehman@giki.edu.pk
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
• Instructor: Dr. Khalid Rahman
Room No. G05 (FME Faculty Lobby)
Email: khalid.rehman@giki.edu.pk
• Teaching Assistant: Engr. Salman
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Books
• Text book:
– “Mechanics of Materials”, by F.P. Beer, E.R. Johnston, John T. Dewolf &
David F. Mazurek, 7th Edition
• Reference book:
• “Mechanics of Materials”, by R.C. Hibbeler, 8th Edition
MecMovies 2.0
http://web.mst.edu/~mecmovie/
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Grading Policy
• Assignment 10%
• Quizzes (announced) 5%
• Project Assignment 10%
• Midterm Exam 30%
• Final 45%
– No make-up quiz, assignment session or exam
– Attendance requirement as per institute’s policy
– Min. 35% score to pass the course or (Average – 1.5 Stnd. Dev.)
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Pre-requisite
• ME-211 “Statics”
– Classification and equivalence of Force system
– Free body diagrams
– Twisting Moment (Torque)
– Mending moment and shear force diagram (Beams)
– Moments of Areas
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
ME-211 “Statics”
• Surface Forces
– Concentrated forces (F)
– Linear distributed forces (F/L)
– Distributed forces (F/L2)
• Body Forces
– Force due to gravity (F)
– (Acts through the centroid of the body.)
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
ME-211 “Statics”
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
ME-211 “Statics”
Types of Supports
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
ME-211 “Statics”
•
•
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
ME-211 “Statics”
• Question:
– In Statics, what useful means did you use to show all the
forces or moments?
• Answer:
– Free-body diagrams (FBD) are used to show all the
forces and moments acting at a joint or on a member.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
As an Engineer, two questions you want to answer whenever you
design something.
1. Is the material strong enough?
2. Is the material stiff enough?
We will learn to answer these questions in this course
Main objective of course is to provide the engineering methods of
analyzing various machines and structures
Design and analysis of a given structure involve the determination
of stresses and deformation
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Application of Statics to Mechanics of Solids
• In Statics, you determined external loadings acting
on a body.
• Knowing the external loads does not tell us if the
member can safely carry the loads.
• For Mechanics of Solids, we will determine internal
forces which are the loadings acting within a body.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Determining Internal Force (IF)
• Cut a convenient section though the body where the IF are
to be determined.
• •Sketch free-body diagram showing all the external loads
and the IF acting both normal and parallel to the section.
Directions of IF are assumed.
• Compute the magnitudes and the directions of the IF.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Magnitudes and Directions of IFs
• Question:
– How can you determine the magnitudes and directions of the
internal forces?
• Answer:
– Use equilibrium equations to compute the resultant internal
forces.
– If the resultant is negative, the assumed direction is incorrect.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Example
b a
b a
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Example
If the pipe is fixed to the wall at A, determine the resultant internal loadings acting
on the cross section at B.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
• Question:
– Is it sufficient to determine the magnitudes and directions of the
internal forces acting on a section?
• Answer:
– It is not sufficient. You need to know the intensity of the resulting
forces associated with internal forces.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Definition of Mechanics of Solids
• Study of the interactions between bodies and the forces acting on them.
Description of Mechanics of Solids
• Derive relationships between applied loads and internal load intensities
and deformations
• Study the stresses and deformations that result when mechanical
components and structures are loaded by external forces.
• Study failure mechanisms, material behavior, complex structure and
advanced topics.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
•Stress
Stress is the intensity of internal forces. It can also be defined as force per
unit area , or intensity of the force distributed over a given section
SI Units
1 kPa 103 Pa 103 N/m2
1 MPa 106 Pa 106 N/m2
1 GPa 109 Pa 109 N/m2
British Units
1 psi 1 lb/in2
1 ksi 1000 lb/in2 Kip/in2
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Course Outline
Normal and shear stress, Strain, Material, Factor of safety,
Stress concentration. Pressurized thinwalled cylinder,
Simple loading tension, torsion and bending, Deflection
with simple loading, Super position techniques,
Statistically indeterminate member, Thermal stresses,
Combined stresses, Mohr circle, Combined loading,
Failure Criterion.
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
The purpose of the course is to provide students with the means of
analyzing and designing various machine and load bearing
structures.
CLO Statement Blooms Taxonomy
CLO No PLO
Upon the completion of the course the student should be able to:
Apply fundamental concepts of stress, strain and elastic behavior of
materials on mechanical structural members subject to various PLO_1
CLO1 Engineering C3 (Application)
loading(s).
Knowledge
Analyze principal stresses produced by combined loads in mechanical
PLO_2
CLO2 structure(s) C4 (Analysis)
Problem Analysis
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS
Lect.
OF SOLIDS Topics Week
No.
Chapter 1 “Introduction – Concept of Stress”
1 Introduction – Static Review
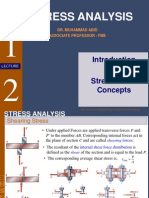
2 Force and Stresses, Axial Loading: Normal Stress, Shearing Stress 1
3 Bearing Stresses in Connection, Application to the Analysis and Design of Simple
Structures, Method of Problem Solution
4 Stress on an Oblique Plane, Under Axial Loading
5 Stress Under General Loading Conditions; Components of Stress, Design Considerations 2
6 Problems related to Chapter 1
Chapter 2 “Stress and Strain – Axial Loading”
7 Introduction, Normal Strain Under Axial, Loading, Stress-Strain Diagram, Hooke’s Law;
Modulus of Elasticity, Elastic versus Plastic Behavior of a Material,
8 Repeated Loadings; Fatigue, Deformations of Members Under Axial Loading, 3
9 Statically Indeterminate Problems, Problems Involving Temperature Changes
10 Poisson’s Ratio, Generalized Hooke’s Law, Shearing Strain
11 Further Discussions of Deformations Under Axial Loading, Saint-Venant’s Principle, 4
12 Stress Concentrations, Problems related to Chapter 2
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Lect. Topics Week
No.
Chapter 3 “Torsion”
13 Introduction, Stresses in a Shaft, Deformations in a Circular Shaft
14 Stresses in the Elastic Range, Angle of Twist in the Elastic Range 5
15 Statically Indeterminate Shafts,
16 Design of Transmission Shafts, Problem related to Chapter 3
Chapter 4 “Pure Bending”
17 Introduction, Symmetric Member in Pure Bending, Deformations in a Symmetric Member 6
in Pure Bending,
18 Stresses and Deformations in the Elastic Range, Deformations in a Transverse Cross Section
19 Bending of Members Made of Several Materials
20 Eccentric Axial Loading in a Plane of Symmetry, 7
21 Unsymmetric Bending
22 General Case of Eccentric Axial Loading
8
23 ~24 Revision and Problem solving
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Lect. Topics Week
No.
Chapter 5 “Analysis and Design of Beams for Bending”
25 Shear Force & Bending Moment Diagrams
26 Shear Force & Bending Moment Diagrams 9
27 Design of Prismatic Beams for Bending
Chapter 6 “Shearing Stress in Beam and Thin-Walled Members”
28 Shear on the Horizontal Face of a Beam Element, Determination of the Shearing Stresses in a
Beam,
29 Shearing Stresses in Common Types of Beams 10
30 Longitudinal Shear on a Beam
31 Shearing Stresses in Thin-Walled Members
Chapter 9 “Deflection of Beams”
11
32 Deformation of a Beam under Transverse Loading, Equation of the Elastic Curve
33 Equation of the Elastic Curve
34 Statically Indeterminate Beams
12
35 Application of Superposition to Statically Indeterminate Beams
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
Lect. No. Topics Week
Chapter 7 “Transformations of Stress and Strain”
36 Introduction, Transformation of Plane Stress 12
37 Principal Stresses; Maximum Shearing Stress
38 Mohr’s Circle for Plane Stress, 13
39 General State of Stress, Application of Mohr’s Circle to the Three-Dimensional Analysis of
Stress
40 Stresses in Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels
Chapter 8 “Principal Stresses Under a Given Loading”
14
41 Principal Stresses in a Beam
42 Design of a Transmission Shafts
43 Stresses under Combined Loadings
15
44 ~ 45 Revision and Problem solving
Office Visit Time
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday
10:00 ~ 12:30 10:00~12:30 10:00~12:30 10:00~12:30
GIK Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology
You might also like
- Stress Analysis (ME-416) 1Document47 pagesStress Analysis (ME-416) 1Anas AsifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 2Document40 pagesLecture 1 2Zeeshan ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document62 pagesModule 1Nazim ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- EM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFDocument180 pagesEM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFJoshua RajNo ratings yet
- Course Handbook Mech 1054 2011-2012Document10 pagesCourse Handbook Mech 1054 2011-2012Ahmar RazaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Civil Engg. New SyllabusDocument25 pages3rd Sem Civil Engg. New SyllabusSubhashree SahooNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19KSghNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 4Mehul MunshiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFParesh NimodiyaNo ratings yet
- ME 206 Mechanics of Materials: Mechatronics Engineering DepartmentDocument42 pagesME 206 Mechanics of Materials: Mechatronics Engineering DepartmentTahoor AsimNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Strength of MaterialsAli SalehNo ratings yet
- E GN 3331 Strength Mat LsDocument1 pageE GN 3331 Strength Mat LsDominic GograNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesEngineering MechanicsAbdul Rafey NawazNo ratings yet
- CE-101 Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesCE-101 Engineering MechanicsAbdul Rafey NawazNo ratings yet
- The Master of EngineeringDocument17 pagesThe Master of Engineeringaurea_yansikuNo ratings yet
- S8 Elective V SyllabusDocument21 pagesS8 Elective V SyllabusnafidfdNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Level 3Document17 pagesCivil Engineering Level 3Rega SaputraNo ratings yet
- MIE222 Syllabus 2015Document3 pagesMIE222 Syllabus 2015Sourabh DasNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis: Dr. Muhammad Abid Associate Professor - FmeDocument29 pagesStress Analysis: Dr. Muhammad Abid Associate Professor - FmeHusnain SikandarNo ratings yet
- SAI SyllabusDocument4 pagesSAI SyllabusSnehal YagnikNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument17 pages1 IntroLloyd KangNo ratings yet
- Computer Aidded Structural Engineering 05 CE 60XXDocument61 pagesComputer Aidded Structural Engineering 05 CE 60XXwhiteelephant93No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2 3Document63 pagesChapter 1 2 3Arnab DipraNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument34 pagesEngineering Mechanicsgotu123No ratings yet
- Strength of MateriaLS Course Outline For Civil Engineer, TarchaDocument3 pagesStrength of MateriaLS Course Outline For Civil Engineer, TarchaKebede HaileNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Civil Engineering With Specialization in Specialization in Computer Aided StructuralDocument21 pagesVdocuments - MX - Civil Engineering With Specialization in Specialization in Computer Aided StructuralandersonvallejosfloresNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Behavior IDocument33 pagesMechanical Behavior IVidushi MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Outline - SM-I (CL301)Document21 pagesTutorial Outline - SM-I (CL301)kakkar kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Tcbe 2101Document153 pagesLecture Notes Tcbe 2101musinguzi robertNo ratings yet
- CE 537 SPRSVDocument5 pagesCE 537 SPRSVCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- ALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuDocument67 pagesALL-CIVIL ENGINEERING - S3 - 2019-Scheme-Syllabus - Ktu StuMeghaNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument11 pagesFracture MechanicsDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- National University: of Computer & Emerging SciencesDocument2 pagesNational University: of Computer & Emerging SciencesHamzaNo ratings yet
- School of Architecture and Design Architecture Department Fall 2020-2021Document3 pagesSchool of Architecture and Design Architecture Department Fall 2020-2021death armyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 1Document32 pagesUnit 1 Part 1ramamurthiNo ratings yet
- Fracture 1Document43 pagesFracture 1seenulegendNo ratings yet
- Ebook t357 Block1 Part5 E2i1 n9780749252632 l1Document93 pagesEbook t357 Block1 Part5 E2i1 n9780749252632 l1Bobby extramoneyguyNo ratings yet
- 20180728144951D3419 Session1 IntroductionDocument47 pages20180728144951D3419 Session1 Introductionlola angela teterissaNo ratings yet
- Course SubjectsDocument12 pagesCourse SubjectsNoriele Paul CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan DOMEDocument3 pagesLesson Plan DOMEMamoon SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Obe Reports Hec - Report Section OutlineDocument2 pagesObe Reports Hec - Report Section OutlineDanish EjazNo ratings yet
- CSE30301Document436 pagesCSE30301彭宇鑫No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingDocument40 pagesMechanics of Solids: Stress and Strain - Axial LoadingKHAKSARNo ratings yet
- Course File SOM-IDocument11 pagesCourse File SOM-IKashyap ChintuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ME215 Spring 2012Document2 pagesSyllabus ME215 Spring 2012Anwär AlmöjarkeshNo ratings yet
- Ce-309 Sa-IiiDocument4 pagesCe-309 Sa-IiiAbdul Rafey NawazNo ratings yet
- EE 3111 SyllabusDocument25 pagesEE 3111 SyllabusKenNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Mechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument11 pagesModule 4 Mechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsChristopher NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Design Lab (18MEL77) Updated ManualDocument57 pagesDesign Lab (18MEL77) Updated ManualSagar SagNo ratings yet
- W-1 Lec-1 2022 01 18Document20 pagesW-1 Lec-1 2022 01 18Zain ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument56 pagesLecture 1 PDFonkod1No ratings yet
- Course Outline: Meng6302 Advanced Mechanics of SolidsDocument7 pagesCourse Outline: Meng6302 Advanced Mechanics of SolidsKKDhNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Manual-DengDocument3 pagesLab 2 Manual-DengDavid ChenNo ratings yet
- Machine Design II (ME-3217)Document12 pagesMachine Design II (ME-3217)Somnath SomadderNo ratings yet
- Mekanika TeknikDocument42 pagesMekanika TeknikNovan ArdhiyanggaNo ratings yet
- Course Plan-WO110Document2 pagesCourse Plan-WO110itsmekrishna2006No ratings yet
- Design Criteria For RCCDocument7 pagesDesign Criteria For RCCAtifkhan132No ratings yet
- ME3491 Course PlanDocument9 pagesME3491 Course Planmanoj1316kumar_63152No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: Pure BendingDocument42 pagesMechanics of Solids: Pure BendingMurtaza RashdiNo ratings yet
- Beermom Ism c01Document90 pagesBeermom Ism c01박송환No ratings yet
- 2 Axial LoadingDocument38 pages2 Axial LoadingNavian NadeemNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: TorsionDocument31 pagesMechanics of Solids: TorsionMurtaza RashdiNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument28 pages1 IntroductionZabid UllahNo ratings yet
- Structural Use of Bamboo: Part 4: Element Design EquationsDocument10 pagesStructural Use of Bamboo: Part 4: Element Design EquationsJevillyn Daniel TugboNo ratings yet
- 1 - Design of Purlins Engr. S. Olarte Cesd 443: Structural Design 2 (Steel and Timber Cesd 443: Structural Design 2 (Steel and Timber)Document9 pages1 - Design of Purlins Engr. S. Olarte Cesd 443: Structural Design 2 (Steel and Timber Cesd 443: Structural Design 2 (Steel and Timber)Amihan De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- European Design Guide For Footbridge Vibration: Christoph HEINEMEYER Markus FELDMANNDocument14 pagesEuropean Design Guide For Footbridge Vibration: Christoph HEINEMEYER Markus FELDMANNAbdullah NajjarNo ratings yet
- Joint Evaluation Report: Roseburg Forest Products CoDocument7 pagesJoint Evaluation Report: Roseburg Forest Products ComurdicksNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Analysis and Design Fundamentals 2nd Ed CAP 11 PDFDocument82 pagesPrestressed Concrete Analysis and Design Fundamentals 2nd Ed CAP 11 PDFCarlos Alberto Pacheco Sierra100% (1)
- Syllabus For Junior Engineer - Civil-WatermarkedDocument3 pagesSyllabus For Junior Engineer - Civil-WatermarkedLaxmanNo ratings yet
- ZAPATASDocument115 pagesZAPATASCarolina Aguirre ANo ratings yet
- Dive Deep Into Revit Structure Analytical ToolsDocument27 pagesDive Deep Into Revit Structure Analytical ToolsFractosNo ratings yet
- 645Document2 pages645Elmon Ray JuratilNo ratings yet
- Two Way Joist Concrete Waffle Slab Floor Design DetailingDocument86 pagesTwo Way Joist Concrete Waffle Slab Floor Design DetailingHung NguyentheNo ratings yet
- Filigree Slabs TestingDocument6 pagesFiligree Slabs Testingmulti5torpeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Design of Prestresed Concrete BridgesDocument28 pagesCHAPTER 7 Design of Prestresed Concrete BridgesLittleRedNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Beams With Openings - 5c27a460097c47e9468b4615Document230 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Beams With Openings - 5c27a460097c47e9468b4615FerSalviaNo ratings yet
- T12M 03 PDFDocument19 pagesT12M 03 PDFpechugonisNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Structures Using Struds SoftwareDocument3 pagesAnalysis and Design of Structures Using Struds SoftwareRamachandra SahuNo ratings yet
- ENES 220 - Mechanics of Materials Spring 2001 April 20, 2001 Exam #2Document4 pagesENES 220 - Mechanics of Materials Spring 2001 April 20, 2001 Exam #2Ehsan WasimNo ratings yet
- Design of Superstructure ElementsDocument44 pagesDesign of Superstructure ElementsZyril Besto100% (1)
- 11.15.03 - Design and Construction of Reinforced Concrete Foundations and StructuresDocument23 pages11.15.03 - Design and Construction of Reinforced Concrete Foundations and Structuresawie1982100% (2)
- Bridge Deck FormworkDocument8 pagesBridge Deck Formworkedgarabraham100% (1)
- Roro Ramp CalDocument2 pagesRoro Ramp CalBoyNo ratings yet
- (Paper) Void Formers For SlabDocument10 pages(Paper) Void Formers For SlabShaileshRastogiNo ratings yet
- KosoDocument4 pagesKosoamar100% (1)
- Beer Chapter 1Document90 pagesBeer Chapter 1amarilis100% (2)
- RCC SlabDocument2 pagesRCC SlabprakashNo ratings yet
- C V of Professor P C PandeyDocument65 pagesC V of Professor P C PandeyMohammad SaaduddinNo ratings yet
- RC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument29 pagesRC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Stab 2 en Temporary 23.04.2016Document51 pagesStab 2 en Temporary 23.04.2016Oana StanNo ratings yet
- Double Reinforced BeamDocument4 pagesDouble Reinforced BeamCE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNo ratings yet
- Ras Al Khair Warehouse - Calculations - Rev.02Document102 pagesRas Al Khair Warehouse - Calculations - Rev.02Feroz Khan Patthan100% (1)
- Wind Load On EtabsDocument103 pagesWind Load On EtabsWaqar Ahmed100% (1)