0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views12 pagesCore Design 1
This document defines building cores and discusses their design. Cores are the central parts of buildings that house utilities, elevators, stairwells, and other shared functions. They act as structural supports that provide stability. Cores can be located off-center, central, or multiple cores may be used. Reinforced concrete is commonly used due to its fire resistance, though steel is also used. Cores must be designed to resist lateral forces and enable flexibility in floor plans.
Uploaded by
syed AffanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views12 pagesCore Design 1
This document defines building cores and discusses their design. Cores are the central parts of buildings that house utilities, elevators, stairwells, and other shared functions. They act as structural supports that provide stability. Cores can be located off-center, central, or multiple cores may be used. Reinforced concrete is commonly used due to its fire resistance, though steel is also used. Cores must be designed to resist lateral forces and enable flexibility in floor plans.
Uploaded by
syed AffanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
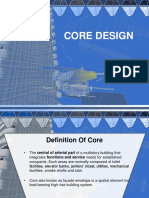
CORE DESIGN
Definition Of Core
• The central of arterial part of a multistory building that
integrates functions and service needs for established
occupants. Such areas are normally composed of toilet
facilities, elevator banks, janitors’ closet, utilities, mechanical
facilities, smoke shafts and stair.
• Core also known as facade envelope is a spatial element for
load-bearing high-rise building system.
Characteristic
• Shape of core
• Number of cores
• Location of cores
• Arrangement of cores
• Geometry of building as generator of core
form
Function
• Tying the building together to act as a unit
• To maximize flexibility in layout
• As shear wall systems to provide the
necessary lateral stability for the building
• Resist lateral forces from any direction
• Carries gravity loads
Elements
• Electrical & Telephone
• Piping and risers
• Transportation
• Fans room
• Toilets
PLACEMENT
Advantages and Disadvantages
• Off Center
– Advantages
• All window or building perimeter space to be used for
offices
• More flexibility in maximum depth and arrangement of
spaces
• Affords the opportunity of developing small secluded space
in the relatively narrow portion of the floor plan where the
core is closes to the exterior walls.
– Disadvantages
• Present some problems of access
• Less flexibility of tenant distribution
• Remote and thus less convenient to the far sides and
corners of the building
CENTRAL CORE
• Central
– Advantages
• Allows all window all window space to be utilized as rental of the
building plan will permit offices of verging depths to receive natural
light
• Extremely convenient of access and in some cases may be
equidistant for all side
• Simplifies area division & provides good flexibility of tenant
distribution in the some way
• Horizontal utility runs may also relatively equidistant from the core
• Combine with a square building plan, bearing exterior & core walls,
this location permits a floor plan tree of columns and thus totally
flexible for office layout
• Disadvantages
• The central interior location limits the depth of offices in the mid-
zone of each floor
• It requires an access corridor around its perimeter
MATERIAL
• Reinforced concrete
– large net tension forces exist can negate the inherent efficiency
of concrete in compression resistance
– Walls become thick
• Concrete
– Fire-resistance, in particular of lift and piping shafts, is good
– Execution is efficient
– Lateral forces can be transmitted employing the surrounding skeleton
– sufficient stiffness
• Steel
– Large and costly
– achieve its lateral stability.
– necessary core stiffness
– relatively rapid assemblage of the prefabricated members.
– Enclose space, no extra consideration need to be given to fire proofing.
– Lack of ductility
– Respect to earth quake loading
Structure
• Cantilever floor
• Hanging floor
• Core-in-r.c frame
• Bunched hanging floors
• Bunched cantilever floors
• Composite
• Core-in-steel frame
System
• Core-in-frame
• Cantilever-core
• Composite
• Core-cable
• CONTINUE CORE 2