Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Darcy's Law
Darcy's Law
Uploaded by
tom meetei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesDarcy's law describes the flow of fluid through a porous medium and defines hydraulic conductivity. It states that the flow rate is proportional to the hydraulic gradient and the cross-sectional area, and inversely proportional to the length of the flow path. The document then discusses different laboratory and field methods for determining hydraulic conductivity, including constant head tests and falling head tests which can be used to measure hydraulic conductivity of consolidated or unconsolidated formations based on measuring flow rates and head changes over time.
Original Description:
Introduction
Original Title
2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDarcy's law describes the flow of fluid through a porous medium and defines hydraulic conductivity. It states that the flow rate is proportional to the hydraulic gradient and the cross-sectional area, and inversely proportional to the length of the flow path. The document then discusses different laboratory and field methods for determining hydraulic conductivity, including constant head tests and falling head tests which can be used to measure hydraulic conductivity of consolidated or unconsolidated formations based on measuring flow rates and head changes over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesDarcy's Law
Darcy's Law
Uploaded by
tom meeteiDarcy's law describes the flow of fluid through a porous medium and defines hydraulic conductivity. It states that the flow rate is proportional to the hydraulic gradient and the cross-sectional area, and inversely proportional to the length of the flow path. The document then discusses different laboratory and field methods for determining hydraulic conductivity, including constant head tests and falling head tests which can be used to measure hydraulic conductivity of consolidated or unconsolidated formations based on measuring flow rates and head changes over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Darcy’s Law
where
Also, Q=AV
Or, v=Q/A
Then,
Here, v is called Darcy velocity or specific discharge. K is hydraulic conductivity(m/day).
Negative sign indicates the flow of water is in the direction of decreasing head. This velocity
here assumes that flow occurs through the entire cross section of the material without regard
to solids and pores. But, the flow is limited only to the pore space.
Then, average interstitial velocity, Where, α is effective porosity.
Determination of Hydraulic Conductivity
1.Laboratory Methods
2.Tracer test
3.Auger hole
4.Pumping test of wells
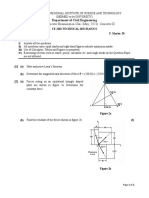
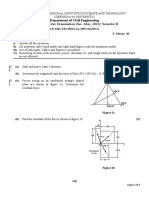
Laboratory Methods: a. Constant Head b. Falling Head
Constant Head: It can measure HC of consolidated or unconsolidated formations
under low heads. Water enters the medium cylinder from the bottom and is collected
as overflow after passing upward through the material. By Darcy’s law,
Falling Head: Water is added to the tall tube, it flows upward through the cylindrical
sample and is collected as overflow. Test consists of measuring rate of fall of water
level in the tube. Hydraulic conductivity can be obtained by noting that the flow rate
Q in the tube must be equal to the flow rate through the sample.
𝑑h2
Flow rate Q in the tube, 𝑄=𝜋 𝑟 𝑡
𝑑𝑡
h
2
Flow rate through the sample by Darcy’s law = 𝜋 𝑟 𝐾 𝐿 𝑐
Equating and integrating,
You might also like
- Experiment 9 Measurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Granular SoilsDocument12 pagesExperiment 9 Measurement of Hydraulic Conductivity of Granular SoilsAllyssa SuyatNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Darcy's LawDocument51 pagesFluid Mechanics and Darcy's LawUche Ukpai100% (5)
- GroundwaterDocument4 pagesGroundwatertom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Extensions of Darcy's LawDocument28 pagesLecture 2 - Extensions of Darcy's LawMonique AldanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 GW MovtDocument76 pagesChapter 3 GW MovtBelete Destaw100% (1)
- Geology Beng (Part B)Document18 pagesGeology Beng (Part B)Syafiqah AimanNo ratings yet
- M.SC IV Sem. Geology Hydrogeology Darcy Law by Dr. Mohammad RizwanDocument5 pagesM.SC IV Sem. Geology Hydrogeology Darcy Law by Dr. Mohammad RizwandeshmukhgeolNo ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument65 pagesPERMEABILITYMuhangi ChristopherNo ratings yet
- PERMEABILITYDocument8 pagesPERMEABILITYSaroo BastkyNo ratings yet
- DARCYs Law and Fluidised BedDocument2 pagesDARCYs Law and Fluidised Bedprakhar mishraNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law & FlowDocument19 pagesDarcy's Law & FlowmaulikpanchalNo ratings yet
- Soil Moisture, Permeability and StressesDocument52 pagesSoil Moisture, Permeability and Stressesanon_917763370No ratings yet
- Mal1033: Groundwater Hydrology: Principles of Groundwater FlowDocument53 pagesMal1033: Groundwater Hydrology: Principles of Groundwater Flowomed muhammadNo ratings yet
- ECG426 - Week 3 - I - PermeabilityDocument25 pagesECG426 - Week 3 - I - PermeabilityNur SyahiraNo ratings yet
- Permeability of SoilDocument7 pagesPermeability of SoilAbhishek BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversityDocument31 pagesDarcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversityMeron MogesNo ratings yet
- Basic Reservoir 5Document2 pagesBasic Reservoir 5ashraff09No ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - GW HydrologyDocument32 pagesLecture 15 - GW Hydrologynasir saleemNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Permeability - New PPTsDocument112 pagesModule 3 Permeability - New PPTsSahil WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3/ Reservoir Engineering: The Fundamentals of Fluid Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law)Document21 pagesLecture 3/ Reservoir Engineering: The Fundamentals of Fluid Flow Through Porous Medium (Darcy's Law)منتظر ال سلمانNo ratings yet
- Darcy's LawDocument5 pagesDarcy's LawEKWUE ChukwudaluNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversityDocument31 pagesDarcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversitySilveira VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversityDocument31 pagesDarcy's Law and Flow: Civil and Environmental Engineering Rice UniversitybrianlaksonoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Linear&Radial Liquid Phase Flow - Mod6Document46 pages4 - Linear&Radial Liquid Phase Flow - Mod6Jorge JiménezNo ratings yet
- Darcy-Law (Rock)Document9 pagesDarcy-Law (Rock)Maqsood IqbalNo ratings yet
- Darcy's Law & ApplicationsDocument10 pagesDarcy's Law & ApplicationsEmad AamerNo ratings yet
- Handout - Continuity EquationDocument2 pagesHandout - Continuity Equationkristine amerNo ratings yet
- V Is Superficial Flow Velocity (M/S) ,: Groundwater HydraulicsDocument1 pageV Is Superficial Flow Velocity (M/S) ,: Groundwater HydraulicskirbeyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Parameters 978-3-642-60117-0 - 2Document2 pagesHydraulic Parameters 978-3-642-60117-0 - 2TonyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Groundwater FlowDocument36 pagesUnit 4 Groundwater FlowdaanaahishmaelsNo ratings yet
- Petrophysics Application of Darcy's Law: DR - Falan SrisuriyachaiDocument20 pagesPetrophysics Application of Darcy's Law: DR - Falan SrisuriyachaiAnuchit ThanasrisurbwongNo ratings yet
- Ground Water Movement: 3.1 Darcy'S LawDocument19 pagesGround Water Movement: 3.1 Darcy'S LawAzman AzmanNo ratings yet
- 2.05 Darcy's Law - Flow in A Porous MediumDocument6 pages2.05 Darcy's Law - Flow in A Porous MediumAlfurjani AbubakrNo ratings yet
- Discussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling HeadDocument2 pagesDiscussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling HeadAzizi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Flujo SubterraneoDocument72 pagesFlujo SubterraneoWilliams León MenachoNo ratings yet
- Flow of Water in Soil Permeability and SeepageDocument24 pagesFlow of Water in Soil Permeability and SeepageahmadNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument29 pagesAttachmenttedy yidegNo ratings yet
- PermeabilityDocument30 pagesPermeabilityDarshak Sakhreliya100% (1)
- 04 Konsep DarcyDocument10 pages04 Konsep DarcyAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Moisture in The Phreatic ZoneDocument12 pagesMoisture in The Phreatic ZoneCzarina Kimberly GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rock & Rock-Fluid Properties: Permeability & Relative PermeabilityDocument43 pagesRock & Rock-Fluid Properties: Permeability & Relative PermeabilityJorge Jiménez100% (1)
- PermeabilityDocument18 pagesPermeabilityrashed kabbaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two. Groundwater MovementDocument44 pagesChapter Two. Groundwater MovementBonsa HailuNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Eng Geol 07Document58 pagesGroundwater Eng Geol 07Raymart BulagsacNo ratings yet
- CH2 Part2Document60 pagesCH2 Part2sertsemariammamushet2No ratings yet
- Darcy's LawDocument5 pagesDarcy's Lawwyath14No ratings yet
- Aquifer: Aquifers Provide Two Important FunctionsDocument6 pagesAquifer: Aquifers Provide Two Important FunctionsDjHanna OlShopsNo ratings yet
- CIVE 2004: PermeabilityDocument15 pagesCIVE 2004: PermeabilityAkshay BundhooNo ratings yet
- Hidrogeologi Lanjutan: Ir. Moh Sholichin, MT., PHDDocument43 pagesHidrogeologi Lanjutan: Ir. Moh Sholichin, MT., PHDAulia Rahmawati100% (1)
- Well HydraulicsDocument25 pagesWell HydraulicsFArzand E Gul100% (1)
- Week 1 Fluid Flow in PipesDocument14 pagesWeek 1 Fluid Flow in PipesAngelica Losares100% (1)
- Lecture 19w Groundwater 1 Darcy PowerpointDocument19 pagesLecture 19w Groundwater 1 Darcy PowerpointAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Flow-Chapter3FYDocument73 pagesGroundwater Flow-Chapter3FYTemesgen workiyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two. Groundwater MovementDocument9 pagesChapter Two. Groundwater MovementBonsa HailuNo ratings yet
- A New Navier-Stokes and Darcy's Law Combined Model For Fluid Flow in Crossflow Filtration Tubular MembranesDocument11 pagesA New Navier-Stokes and Darcy's Law Combined Model For Fluid Flow in Crossflow Filtration Tubular MembranesMohammad Shafaet JamilNo ratings yet
- 2 Physical Properties and PrinciplesDocument66 pages2 Physical Properties and PrinciplesAna Beatriz Rubio ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Permeability ConceptDocument54 pagesPermeability ConceptJohn Kevin de CastroNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Tables; The Elements Of Gagings And The Friction Of Water Flowing In Pipes, Aqueducts, Sewers, Etc., As Determined By The Hazen And Williams Formula And The Flow Of Water Over The Sharp-Edged And Irregular Weirs, And The Quantity DischargedFrom EverandHydraulic Tables; The Elements Of Gagings And The Friction Of Water Flowing In Pipes, Aqueducts, Sewers, Etc., As Determined By The Hazen And Williams Formula And The Flow Of Water Over The Sharp-Edged And Irregular Weirs, And The Quantity DischargedNo ratings yet
- Settings and Formats For Online Tests (End-Sem, Jan-May, 2021)Document7 pagesSettings and Formats For Online Tests (End-Sem, Jan-May, 2021)tom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Radial Flow in Confined Aquifer - SteadyDocument3 pagesRadial Flow in Confined Aquifer - Steadytom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Steady Flow in Confined Aquifer of Variable ThicknessDocument3 pagesSteady Flow in Confined Aquifer of Variable Thicknesstom meetei100% (1)
- Updated Settings, Formats, and Instructions For Online TestsDocument10 pagesUpdated Settings, Formats, and Instructions For Online Teststom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Restrictions On Movement Dated 13 5 21Document3 pagesRestrictions On Movement Dated 13 5 21tom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Radial Flow For Unconfined AquiferDocument4 pagesRadial Flow For Unconfined Aquifertom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Flow Between in Confined Aquifer - Two Water Bodies in Confined AquiferDocument2 pagesGroundwater Flow Between in Confined Aquifer - Two Water Bodies in Confined Aquifertom meeteiNo ratings yet
- 5 Unconfined AquifersDocument10 pages5 Unconfined Aquiferstom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Wedge and Rope FrictionDocument5 pagesWedge and Rope Frictiontom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Degree SYLABUSDocument25 pagesDegree SYLABUStom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Force Defined by Its Magnitude and Two Points On Its Line of ActionDocument3 pagesForce Defined by Its Magnitude and Two Points On Its Line of Actiontom meeteiNo ratings yet
- F T Solution: ProblemsDocument2 pagesF T Solution: Problemstom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Flow in Unconfined Aquifer Without RechargeDocument5 pagesFlow in Unconfined Aquifer Without Rechargetom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Etn S Fo : Wcia)Document3 pagesEtn S Fo : Wcia)tom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Questions For: End-Semester Examination (February-June, 2021) Hydraulics & Water Resources EngineeringDocument1 pageQuestions For: End-Semester Examination (February-June, 2021) Hydraulics & Water Resources Engineeringtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar - 2021Document5 pagesAcademic Calendar - 2021tom meeteiNo ratings yet
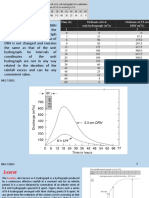
- Base Flow Seperation Numerical Problem ExampleDocument6 pagesBase Flow Seperation Numerical Problem Exampletom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Force Defined by Its Magnitude and Two Points On Its Line of ActionDocument3 pagesForce Defined by Its Magnitude and Two Points On Its Line of Actiontom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Friction 1Document6 pagesFriction 1tom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Midsem QP Ce2201 Jan MayDocument2 pagesMidsem QP Ce2201 Jan Maytom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Mid-Sem JAN MAY 2020 - CE 2201Document2 pagesMid-Sem JAN MAY 2020 - CE 2201tom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Where A Drainage Area in KM and N Is in DaysDocument4 pagesWhere A Drainage Area in KM and N Is in Daystom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Department: Civil Engineering Programme: Certificate in Construction TechnologyDocument7 pagesDepartment: Civil Engineering Programme: Certificate in Construction Technologytom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Base Flow SeperationDocument5 pagesBase Flow Seperationtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- DERIVATION OF T-H UH FROM D-H UH - SUPERPOSITION METHODDocument6 pagesDERIVATION OF T-H UH FROM D-H UH - SUPERPOSITION METHODtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1 Saturated Zone: 390 Engineering Hydrology Land SurfaceDocument4 pages9.2.1 Saturated Zone: 390 Engineering Hydrology Land Surfacetom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Uniform Rainfall Duration, D: HydrographDocument8 pagesUniform Rainfall Duration, D: Hydrographtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Uniform Rainfall Duration, DDocument8 pagesUniform Rainfall Duration, Dtom meeteiNo ratings yet
- Groundwater 2Document2 pagesGroundwater 2tom meeteiNo ratings yet