Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions Practice: Moving Charges and Magnetism
Uploaded by
prakul varshney0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views13 pagesOriginal Title
Questions Practice
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views13 pagesQuestions Practice: Moving Charges and Magnetism
Uploaded by
prakul varshneyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
QUESTIONS PRACTICE
Moving Charges and Magnetism
Magnetic field lines can be entirely confined within the core of a toroid,
but not within a straight solenoid. Why?
Why should the spring/suspension wire in a moving coil galvanometer
have low torsional constant?
A beam of ɑ particles projected along +x-axis, experiences a force due to
a magnetic field along the +y-axis. What is the direction of the magnetic
field?
An ammeter of resistance 0.6 Ω can measure current upto 1.0 A.
Calculate
(i) The shunt resistance required to enable the ammeter to measure
current upto 5.0 A
(ii) The combined resistance of the ammeter and the shunt.
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current
carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
A particle of mass ‘m’ and charge ‘q’ moving with velocity V enters the
region of uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of its
motion. How does its kinetic energy get affected?
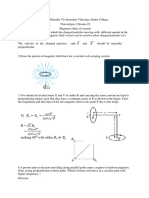
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying
current I and 2I respectively are lying in parallel planes such that they
have a common axis. The direction of current in both the loops is
clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from both the loops. Find
the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point O.
A particle of mass 10-3 kg and charge 5 µC enters into a uniform electric
field of 2 × 105 NC-1, moving with a velocity of 20 ms-1 in a direction
opposite to that of the field. Calculate the distance it would travel before
coming to rest.
A square shaped plane coil of area 100 cm2 of 200 turns carries a steady
current of 5A. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.2 T acting
perpendicular to the plane of the coil. Calculate the torque on the coil
when its plane makes an angle of 60° with the direction of the field. In
which orientation will the coil be in stable equilibrium?
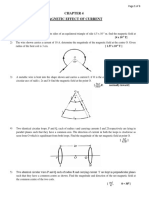
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying
current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a
common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction
of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils
An ammeter of resistance 0.80 Ω can measure current upto 1.0 A.
(i) What must be the value of shunt resistance to enable the ammeter to
measure current upto 5.0A?
(ii) What is the combined resistance of the ammeter and the shunt?
A charged particle whose mass is 19.9 ×10-27 kg and charge is 1.6×10-19C
moves with a speed of 3×105 m/s at right angle to a magnetic field of .75
T. What is the force acting on the charge, centripetal acceleration and
radius of the circle in which charged particle moves.
(a) 3.6×10-14 N,1.81×1012 m/s2, 49.7×10-3 m
(b) 3.0×10-14 N,1.81×1012 m/s2, 49.7×10-3 m
(c) 3.0×10-14 N,1.8×1012 m/s2, 49.7×10-3 mm
(d) None of the above
You might also like
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MovingChargesMagnetismDocument4 pagesMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- Moving Charge & Magnetism-12Document8 pagesMoving Charge & Magnetism-12Mukul RaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSDocument8 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSroyal ghostNo ratings yet
- Magnetism WorksheetDocument3 pagesMagnetism WorksheetRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Document3 pagesChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMKanak TaldaNo ratings yet
- Ninety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesDocument7 pagesNinety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesAryan MurghaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Document36 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Rishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document11 pagesWa0004.ffffffgNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnDocument7 pagesMoving Charges and Magnatharvbaghel4444No ratings yet
- Questions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Document4 pagesQuestions Chap 4 Moving Charges & Magnetism - 77547 - 2023 - 02 - 06 - 22 - 57Ranjith MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Important Quesrtions Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument19 pagesImportant Quesrtions Moving Charges and Magnetismmohitkumarr2411No ratings yet
- VELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMDocument2 pagesVELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMkalyani.kNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Eff of CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Eff of CurrentR K SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 4-MCM-WSDocument8 pagesCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect Full ChapterDocument17 pagesMagnetic Effect Full ChaptervasanthiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document7 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 3Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Test Physics CBSE Class XIIDocument1 pageTest Physics CBSE Class XIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- 03-Moving Charges and Magnetism PyqDocument7 pages03-Moving Charges and Magnetism PyqgudiNo ratings yet
- Assignment On EMIDocument6 pagesAssignment On EMIewrNo ratings yet
- Force Due To Magnetic Field-AssignmentDocument8 pagesForce Due To Magnetic Field-AssignmentS Prasad Shiva PulagamNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Document6 pagesCamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Ashit ModyNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsAriyanayaka SundaramNo ratings yet
- LAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesLAQs - Current Electricity & Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentLanaNo ratings yet
- 6451 Topper 21 129 510 4 138 Moving Charges and Magnetism Up201612091915 1481291127 2904 PDFDocument49 pages6451 Topper 21 129 510 4 138 Moving Charges and Magnetism Up201612091915 1481291127 2904 PDFRoshan Upadhyay0% (1)
- worksheet II ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesworksheet II Electromagnetismboomshakalakab13No ratings yet
- Grade 12 FT Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesGrade 12 FT Sample Paper 1safaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismSanjay MalwiyaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 NEW Worksheet - 1Document3 pagesCH 4 NEW Worksheet - 1ISHITA RajputNo ratings yet
- Physics Term 1Document6 pagesPhysics Term 1Joseph VijuNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Sub BCDocument6 pagesMagnetism Sub BCshivanshNo ratings yet
- REVISION SHEETS GR 12Document13 pagesREVISION SHEETS GR 12itachirao5No ratings yet
- Why Is The Following Situation Impossible? The Magnitude: NM IR X XDocument3 pagesWhy Is The Following Situation Impossible? The Magnitude: NM IR X XCALON TARUNANo ratings yet
- 200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionDocument25 pages200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionZeyad EssamNo ratings yet
- Assignment Magnetic EffectsDocument3 pagesAssignment Magnetic EffectsabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesSubjective Questions: Electromagnetic InductionrgNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Document3 pages12 Physics U3 Assignmnt1Nikita BansalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsDocument8 pagesCBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsAdhish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDocument35 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedabhinashNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Homework #15Document2 pagesPhysics 2 Homework #15Joseph IvanchukNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy. H.H.WDocument4 pagesXii Phy. H.H.WKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current Class XII Physics ProblemsDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current Class XII Physics ProblemsIndraneil SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Class Xii-Physics Worksheet-28.07.23Document3 pagesClass Xii-Physics Worksheet-28.07.23S.Sanjay SubramanianNo ratings yet
- PHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - MagnetostaticsDocument49 pagesPHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - Magnetostaticsنور وائلNo ratings yet
- TEST 9 CH 4Document3 pagesTEST 9 CH 4kumarvishwaa1No ratings yet
- TP B2 Csye CGws GSPRV 2 A ODocument6 pagesTP B2 Csye CGws GSPRV 2 A OjayanthikakrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Question 961019Document11 pagesQuestion 961019rajaNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- Weekly Test PhysicsDocument2 pagesWeekly Test PhysicsSneha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Aadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- Magnetism 1 Per PageDocument33 pagesMagnetism 1 Per PageabhinabaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Q BankDocument15 pagesMagnetic Q BankAnand Classes50% (2)
- Unit 13 Magnetic Field and ForceDocument2 pagesUnit 13 Magnetic Field and Forceapi-323795755No ratings yet
- On Class 10 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument25 pagesOn Class 10 Chemical Reactions and Equationsprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Chem 10 PDFDocument17 pagesChem 10 PDFDishank AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument15 pagesMoving Charges and Magnetismprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Reasoning 3Document8 pagesReasoning 3Prasad Durga DNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Assignmentprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- M Tech Mechanical III Semester 2016-2017Document8 pagesM Tech Mechanical III Semester 2016-2017prakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument11 pagesAtoms and Moleculesprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingDocument12 pagesMatter in Our Surroundingprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- TestDocument1 pageTestprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Diversity TestDocument1 pageDiversity Testprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- კემპბელი თ16 353 363 დნმ და რეპლიკაციაDocument11 pagesკემპბელი თ16 353 363 დნმ და რეპლიკაციაSosoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 & Chapter 10 SolutionsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 & Chapter 10 SolutionsSaeed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Resources and CapabilitiesDocument6 pagesAnalyzing Resources and CapabilitiesImola FazakasNo ratings yet
- NoNuke Spec SheetDocument1 pageNoNuke Spec SheetEster TerneroNo ratings yet
- Photogrammetry and Remote SensingDocument14 pagesPhotogrammetry and Remote SensingJoseph Dincht83% (6)
- Pitch Angle Control For A Small-Scale Darrieus VAWTDocument11 pagesPitch Angle Control For A Small-Scale Darrieus VAWThuy4ngooNo ratings yet
- RXF-C: Air Conditioning Technical DataDocument18 pagesRXF-C: Air Conditioning Technical DataJuan LezamaNo ratings yet
- NOV Anson - M95 Plug ValvesDocument23 pagesNOV Anson - M95 Plug ValvesRafael Perez100% (1)
- Development of High Temperature Superconducting Transformers PDFDocument6 pagesDevelopment of High Temperature Superconducting Transformers PDFBen McConnellNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Green Building in The Existing Building of The Department of The Environment of DKI Jakarta Province in The Order of Reducing Greenhouse Gas EmissionsDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Green Building in The Existing Building of The Department of The Environment of DKI Jakarta Province in The Order of Reducing Greenhouse Gas EmissionsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nederhoff Kees MSC ThesisDocument188 pagesNederhoff Kees MSC ThesisSiddhant AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Teaching The Internet of Things Iot Using Universally Available Raspberry Pi and Arduino PlatformsDocument11 pagesTeaching The Internet of Things Iot Using Universally Available Raspberry Pi and Arduino PlatformsVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Green BuildingsDocument40 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Green Buildingsniti860No ratings yet
- Applied MechatronicDocument16 pagesApplied MechatronicDuong Van Tu33% (3)
- DAILY LESSON LOG in Grade 7 ScienceDocument2 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG in Grade 7 Sciencejanice alquizar100% (3)
- MCE 244 Course OutlineDocument1 pageMCE 244 Course OutlineKaren DavisNo ratings yet
- 80312A-ENUS Error LogDocument10 pages80312A-ENUS Error LogSafdar HussainNo ratings yet
- Delhi Skill and Entrepreneurship University: Application Form Session 2021-2022Document3 pagesDelhi Skill and Entrepreneurship University: Application Form Session 2021-2022Shyam DubeyNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Step-By-Step TutorialDocument20 pagesBank Reconciliation Step-By-Step TutorialTạ Tuấn DũngNo ratings yet
- Chinese Character Writing Exercise SheetsDocument47 pagesChinese Character Writing Exercise Sheetsapi-3700050100% (1)
- Self Healing ConcreteDocument20 pagesSelf Healing ConcreteshivangNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Morphogenesis in Hyphomycetes New CharDocument27 pagesAnalysis of Morphogenesis in Hyphomycetes New Charestefaniacb1305No ratings yet
- Craig2016.traditions in Communication TheoryDocument10 pagesCraig2016.traditions in Communication TheoryDelia ConstandaNo ratings yet
- Axiatonal Lines Connection IntroductionDocument9 pagesAxiatonal Lines Connection IntroductionDavid Lopes100% (1)
- Week 7 Cycling Materials in The Ecosystem and How Do Human Activities Affect The Ecosystem 1Document6 pagesWeek 7 Cycling Materials in The Ecosystem and How Do Human Activities Affect The Ecosystem 1lourdes SanchezNo ratings yet
- Of For of or Or: The Professional School of Psychology San Francisco, CaliforniaDocument9 pagesOf For of or Or: The Professional School of Psychology San Francisco, CaliforniaSamiMolinaNo ratings yet
- KIA Motors Corporation ProfileDocument3 pagesKIA Motors Corporation ProfileIlham K GustavakuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PPTDocument41 pagesChapter 3 PPTidNo ratings yet
- Argument From IgnoranceDocument2 pagesArgument From Ignorancegio7850No ratings yet
- 2010 IMCO CatalogDocument170 pages2010 IMCO Cataloggeav25653855No ratings yet