Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 4-MCM-WS
Uploaded by
mmkishore067Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 4-MCM-WS
Uploaded by
mmkishore067Copyright:
Available Formats
Page |1
Dr. G.S Kalyanasundaram Memorial School
Patteswaram Road, Chozhan Maligai, Kumbakonam
Class: XII DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
CHAPTER-4-WORK SHEET
1.A proton, a deutron and alpha particle whose kinetic energies are same,
enter perpendicularly a uniform magnetic field. Compare the radii of their
circular paths.
2. A straight wire of mass 200 mg and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is
suspended in mid-air by a uniform horizontal magnetic field B. What is the
magnitude of the magnetic field?
3. The electron in a hydrogen atom is moving with a speed of 2.3X106 m/s in an
0
orbit of radius 0.53 A . Calculate the magnetic moment of revolving electron.
4. Two equal-length wires are bent into two loop shapes. One of the loops is
circular, while the other is square in shape. The same current flows through
them while they are hung in a constant magnetic field. Which loop will be
subject to more torque? Explain.
5. What would a charged particle travelling in the direction of a constant
magnetic field take?
6. A long, straight solenoid carrying current I, on an axis along which an
electron is travelling at velocity v. What will the magnetic field of the
solenoid’s magnetic field be doing to the electron?
7. Would your response alter if the circular coil in (a) were swapped out for a
planar coil that encloses the same space but has a different shape? (All other
information remains the same).
8. Derive an expression for the force acting on a current carrying conductor
placed in a uniform magnetic field Name the rule which gives the direction of
the force. Write the condition for which this force will have (1) maximum (2)
minimum value?
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |2
9. A straight wire carries a current of 10 A .An electron moving at 10 7 m/s is at
a distance 2.0 cm from the wire. Find the force acting on the electron if its
velocity is directed towards the wire.
10. What is radial magnetic field? How it is obtained in moving coil
galvanometer?
11. A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a
current of 0.40 A. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the centre
of the coil?
12. A long straight wire carries a current of 35 A. What is the magnitude of the
field B at a point 20 cm from the wire?
13. Answer the following questions:
(a) A magnetic field that varies in magnitude from point to point but has a
constant direction (east to west) is set up in a chamber. A charged particle
enters the chamber and travels un deflected along a straight path with
constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle?
(b) A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform
magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction,
and comes out of it following a complicated trajectory. Would its final speed
equal the initial speed if it suffered no collisions with the environment?
(c) An electron travelling west to east enters a chamber having a uniform
electrostatic field in north to south direction. Specify the direction in which a
uniform magnetic field should be set up to prevent the electron from
deflecting from its straight line path.
14.A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic
field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A,
what is the (a) total torque on the coil,(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
15. Galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 and the metre shows full scale
deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert the metre into a
voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |3
16. A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 and the metre shows full scale
deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an
ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
17. A steady current flows in the network
shown in the figure. What will be the
magnetic field at the centre of the
network?
18. An - particle and a proton are moving
in the plane of paper in a region where
there is uniform magnetic field B directed normal to the plane of paper. If two
particles have equal linear momenta, what will be the ratio of the radii of their
trajectories in the field?.
19. An electron of kinetic energy 25KeV moves perpendicular to the direction
of a uniform magnetic field of 0.2 milli tesla calculate the time period of
rotation of the electron in the magnetic field?
20. What will be the path of a charged particle moving along the direction of a
uniform magnetic field?
21. State two properties of the material of the wire used for suspension of the
coil in a moving coil galvanometer?
22. What are the units of magnetic permeability?
23. Under what conditions is the force acting on a charge moving through a
uniform magnetic field minimum?
24. A long straight wire carries a current of 35 A. What is the magnitude of the
field B at a point 20 cm from the wire? 9. Write SI unit of magnetic field .
25. Two long parallel straight wires X and Y separated by a distance of 5 cm in
air carry currents of 10 A and 5 A respectively in opposite directions.Calculate
the magnitude and direction of the force on a 20 cm length of the wire Y.
26. An electron is moving along +ve x-axis in the presence of uniform magnetic
field along +ve y-axis. What is the direction of force acting on it?
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |4
27. Define current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer.
Increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage
sensitivity of galvanometer. Justify.
28. If a piece of metal has a charge + 0.1 micro coulomb and is placed inside a
hollow metal sphere of radius 20 cm (without touching it), what is the
potential of the sphere? What will the potential of the sphere become, if a)the
sphere is temporarily earthed and then left insulated, b)the metal
subsequently touched the inside of the sphere?
29. The pole pieces of magnet are cut concave in a galvanometer. Why?
30. What happens if an ammeter is connected in parallel to the circuit? What is
the resistance of an ideal ammeter? Why an ammeter is connected in series in
an electric field?
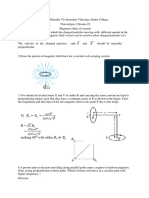
31. What will be the resultant magnetic field intensity
of point O as shown in the figure?
32. The frequency of a cyclotron oscillator is 10 MHz. What should be the
magnetic field required to accelerate a proton (e = 1.6 x 10-19C, m =1.67 x 10-
27
kg)
33. A particle having 100 times charge of an electron is revolving in a circle of
radius 0-8 metre in each second. Calculate the intensity of magnetic field.
34. Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents I
are placed vertically (with respect to the plane of the paper) with their
geometrical axis perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the
magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point O.
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |5
35. Two identical circular loops, P and Q each of radius r and carrying currents I
and 2I respectively are lying in parallel planes such that they have a common
axis. Their centres are distance 2 r apart. The direction of current in both the
loops is clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from both the loops.
Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point O.
36.Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current I
are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as
shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field
at the common centre of the two coils.
37. A wire of uniform cross-section is bent into s circular loop of radius R.
Consider two points A and B on the loop, such that
<AOB=θ as shown. If now a battery is connected
between A and B, show that the magnetic field at the
centre of the loop will be zero irrespective of angle .
38. A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle moving with equal velocities,
enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper as shown.
Trace their paths in the field and justify your statement.
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |6
39. A charged particle q moving in a straight line is accelerated by a potential
difference V. It enters a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its path.
Deduce in terms of V an expression for the radius of the circular path in which
it travels.
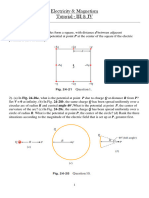
40. Following figure shows the path of an electron that passes through two
regions, containing uniform magnetic fields of magnitudes and . Its path in
each region is a half circle .i) Which field is stronger ii) What are the directions
of two fields? iii) Is the time period by the electron in the B1 region greater
than less than or the same as the time spent in B 2 region?
41. An electron travels in a circular path of radius 20 cm in a magnetic field 2 ×
10 -3T. (i) Calculate the speed of the electron (ii) What is the potential
difference through which the electron must be accelerated to acquire this
speed? Charge of electron = 1 ⋅ 6 × 10-19 C. Mass of electron = 9 × 10-31 kg
42. Each of the eight conductors in the figure carries 2A of current into or out
of the page. Two paths are indicated for the line integral . What is
the value of the integral for (a) path 1 and (b) path 2?
43. Two particles A and B of masses m and 2m have charges q and 2q,
respectively. They are moving with velocities v1 and v2, respectively, in the same
direction, enters the same magnetic field, B acting normally to their direction of
motion. If the two forces FA and F B acting on them are in the ratio of 1:2, find the
ratio of their velocities.
44. An α-particle and a proton moving with the same speed enter the same
magnetic field region at right angles to the direction of the field. Show the
trajectories followed by the two particles in the region of the magnetic field.
Find the ratio of the radii of the circular paths which the two particles may
describe.
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |7
45.Why is it necessary to introduce a cylindrical soft iron core inside the coil of
a galvanometer?
ii) State Biot-Savart's law. A current I flows in a conductor
placed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Indicate the
direction of the magnetic field due to a small element dl at
a point situated at a distance r from the element as shown
in figure O .
46.The wire shown in figure carries a current of 10 A. Determine the
magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre O. Given radius of the bent coil
is 3 cm.
47.A closed circuit is in the form of a regular hexagon of side r. If the circuit
carries current I. What is the magnetic field induction at the centre of the
hexagon?
48.Three wires each of length 2.0 m are bent into
different rectangular loops and then suspended in a
magnetic field. If the current in each of them be the
same ,which loop shall be acted upon by largest
torque? If any of the wires be bent into circular
loop,then?
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
Page |8
49.A rectangular current carrying loop PQRS
is kept in a uniform magnetic field as shown
in figure.
a)What is the direction of magnetic moment
of the current loop?
b)When is the torque acting on the loop i)maximum ii)Zero?
50.Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field
remains constant.
51.Why is phosphor bronze alloy preferred for the suspension wire of a
moving coil galvanometer?
52.The current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is 10 div/mA and
voltage sensitivity is 20 div/V. Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
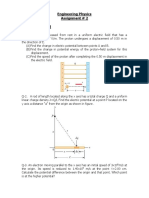
53.A current I is flowing in a conductor shaped as
shown n figure. The radius of the curved part is r
and length of straight portion is very large. Find
the magnetic field induction at the centre O.
54.A square loop of side a carrying a current I 2 is kept at
a distance x from an infinitely long straight wire carrying
a current I 1 as shown in figure. Obtain the expression for
the resultant force acting on the loop.
55. Find an expression for the magnetic field induction at
the centre of a coil bent in the form of a square of side 2 a , carrying current I.
***********************************************
DR.GSK MEMORIAL SCHOOL CHAPTER-4 DEPT OF PHYSICS
You might also like
- Ninety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesDocument7 pagesNinety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesAryan MurghaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)Document3 pagesChapter - 04 (Magnetic Effects of Currents)ghuNo ratings yet
- VELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMDocument2 pagesVELS VIDYASHRAM PHYSICS WORKSHEET ON MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISMkalyani.kNo ratings yet
- MovingChargesMagnetismDocument4 pagesMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviNo ratings yet
- Magnetism WorksheetDocument3 pagesMagnetism WorksheetRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Magnetic EffectsDocument3 pagesAssignment Magnetic EffectsabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Document36 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism: Previous Year Board Exam Questions (2007-2016)Rishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2022-08-16 at 10.04.10 PMKanak TaldaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsAriyanayaka SundaramNo ratings yet
- Assignment Electricity and Mag.Document3 pagesAssignment Electricity and Mag.Hafiz IkramaNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Document6 pagesCamScanner 07-01-2022 23.10Ashit ModyNo ratings yet
- STPM U6 21 1Document2 pagesSTPM U6 21 1Tutor_KLNo ratings yet
- worksheet II ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesworksheet II Electromagnetismboomshakalakab13No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Magnetic Effects of Electric Current and MagnetismSanjay MalwiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter-4 Ncert Practice QuestionsRAHIM MDNo ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument8 pagesSodapdfsdfbvshbdfNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Eff of CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Eff of CurrentR K SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wa0004.Document11 pagesWa0004.ffffffgNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Questions 1.: Question BankDocument4 pages1 Mark Questions 1.: Question Bankharipriya3011No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetis1m Sneh CH - 4 and CH - 5 - SnehDocument7 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current and Magnetis1m Sneh CH - 4 and CH - 5 - SnehJarjar BinksNo ratings yet
- Ihw 4Document7 pagesIhw 4LogoNo ratings yet
- Assignment On EMIDocument6 pagesAssignment On EMIewrNo ratings yet
- Moving Charge & Magnetism-12Document8 pagesMoving Charge & Magnetism-12Mukul RaiNo ratings yet
- 3 Magnetic Effect of Current & MagnetismDocument4 pages3 Magnetic Effect of Current & MagnetismNathanianNo ratings yet
- Question 961019Document11 pagesQuestion 961019rajaNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Test Physics CBSE Class XIIDocument1 pageTest Physics CBSE Class XIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document19 pagesCH 6terasaini77No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSDocument8 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current PROBLEMSroyal ghostNo ratings yet
- Part Xxvii - Magnetic Fields & Forces-Set 2Document8 pagesPart Xxvii - Magnetic Fields & Forces-Set 2apostolos efstathiouNo ratings yet
- Magnetics DPPDocument14 pagesMagnetics DPPwattariq47No ratings yet
- Magnetic Q BankDocument15 pagesMagnetic Q BankAnand Classes50% (2)
- Magnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Document6 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current 2020-21Rgpadma NathanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document7 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 3Abhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsDocument8 pagesCBSE Board Problems Magnetic FieldsAdhish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 FT Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesGrade 12 FT Sample Paper 1safaaNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Magnetism Tutorial III & IVDocument7 pagesElectricity & Magnetism Tutorial III & IVsachini weesingheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Moving Charges and FieldDocument19 pagesChapter 4 Moving Charges and FieldSANDRONo ratings yet
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Document6 pagesEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentHarsh JuyalNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asgnmt CH - 04Document5 pagesAissce Asgnmt CH - 04Arunima SinghNo ratings yet
- TEST 9 CH 4Document3 pagesTEST 9 CH 4kumarvishwaa1No ratings yet
- Magnetism Subjective & Obj.Document10 pagesMagnetism Subjective & Obj.Aviram YadavNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionDocument6 pagesClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonNo ratings yet
- REVISION SHEETS GR 12Document13 pagesREVISION SHEETS GR 12itachirao5No ratings yet
- Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument2 pagesMoving Charges and MagnetismAslam FaruqiNo ratings yet
- 200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionDocument25 pages200512-Application of Motion of Charged Particles-SS SolutionZeyad EssamNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Revision Questions FINALDocument5 pagesMagnetism Revision Questions FINALARSHAD JAMIL100% (2)
- Electromagnetism: Magnetic Fields, Forces, and InductionDocument19 pagesElectromagnetism: Magnetic Fields, Forces, and InductionFirdaus BhathenaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Magnetic Fields and ForcesDocument11 pagesMCQ Magnetic Fields and ForcesMaha TharwatNo ratings yet
- 6451 Topper 21 129 510 4 138 Moving Charges and Magnetism Up201612091915 1481291127 2904 PDFDocument49 pages6451 Topper 21 129 510 4 138 Moving Charges and Magnetism Up201612091915 1481291127 2904 PDFRoshan Upadhyay0% (1)
- Magnetism Guided NotesDocument14 pagesMagnetism Guided Notesdericksonj32No ratings yet
- Important Quesrtions Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument19 pagesImportant Quesrtions Moving Charges and Magnetismmohitkumarr2411No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect Full ChapterDocument17 pagesMagnetic Effect Full ChaptervasanthiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Work Class: Xii Subject: Physics (Magnetism and Matter)Document7 pagesAssignment Work Class: Xii Subject: Physics (Magnetism and Matter)NishantNo ratings yet
- EP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesEP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFanon_429934438No ratings yet
- Assignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldDocument5 pagesAssignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldBilal KhalidNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsFrom EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsNo ratings yet
- The MCQDocument8 pagesThe MCQAboahmed Ali100% (1)
- Science SSB PDFDocument5 pagesScience SSB PDFDivye SakhujaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Physical Chemistry II Quantum Theory and SpectroscoptyDocument41 pagesLecture Notes For Physical Chemistry II Quantum Theory and Spectroscopty3334333No ratings yet
- Thesis Vishvesh Tadsare Modified 15oct2018 PDFDocument133 pagesThesis Vishvesh Tadsare Modified 15oct2018 PDFMohammadNo ratings yet
- Electron DiffractionDocument4 pagesElectron Diffractionpriyanka .SNo ratings yet
- 10th Physics Pre-BoardExam 2024-2Document3 pages10th Physics Pre-BoardExam 2024-2mathswithquratNo ratings yet
- Siemens Digitron DatasheetDocument33 pagesSiemens Digitron DatasheetAdan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Optics by Ajoy Ghatak Chepter 7Document16 pagesOptics by Ajoy Ghatak Chepter 7Sumit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Coulombs Law and ChargesDocument47 pagesCoulombs Law and ChargesBea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PHYS 342 13Document6 pagesSyllabus PHYS 342 13heehee2010No ratings yet
- Evolution of Microelectronics: (From Discrete Devices To Modern Integrated Circuits - A Brief Review)Document50 pagesEvolution of Microelectronics: (From Discrete Devices To Modern Integrated Circuits - A Brief Review)ARUOS SouraNo ratings yet
- Element 110 in Vedic Nuclear Physics: by John Frederick SweeneyDocument9 pagesElement 110 in Vedic Nuclear Physics: by John Frederick SweeneyKrivi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistryDocument2 pagesXi Chemistry, Comprehensive ChemistrySANGRAM5200% (1)
- How Migratory Birds Find Their WayDocument3 pagesHow Migratory Birds Find Their WayPRATIKSHA ThakurNo ratings yet
- Wave-Particle Duality and Quantum PhysicsDocument14 pagesWave-Particle Duality and Quantum PhysicsRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Radiation ProtectionDocument259 pagesAn Introduction To Radiation ProtectionNabaaAlazawy89% (9)
- Educ 563 UnitDocument10 pagesEduc 563 Unitapi-297909206No ratings yet
- AYJR Math Questions and AnswersDocument68 pagesAYJR Math Questions and AnswersAditya Kinjawadekar100% (2)
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 2ruel rinconadaNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Nature of ElectricityDocument5 pages1.2. Nature of ElectricityKATE ARBIE LACDO-ONo ratings yet
- Quantum Dots Red TideDocument10 pagesQuantum Dots Red TideWidya MeiriskaNo ratings yet
- Mass Action Law:: in N-Type SemiconductorDocument10 pagesMass Action Law:: in N-Type Semiconductordheeraj rajNo ratings yet
- Biology-Dynamics of Life - 0078741890 PDFDocument524 pagesBiology-Dynamics of Life - 0078741890 PDFZhafira Drianta100% (3)
- Thermal Radiation Heat TransferDocument372 pagesThermal Radiation Heat Transferdarkknight77100% (1)
- Principles of Analytical Electron Microscopy (1986, Springer US)Document458 pagesPrinciples of Analytical Electron Microscopy (1986, Springer US)RafaelNo ratings yet
- Chm524 3 Quantum Chemistry 2022 StudentDocument43 pagesChm524 3 Quantum Chemistry 2022 Studentasyraf azlan99No ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Section 3Document15 pagesChapter 4, Section 3Abdullah AlthaniNo ratings yet
- SP025 Modul Chapter 1Document33 pagesSP025 Modul Chapter 1naderaqistina23No ratings yet
- Sabrina Alkayfee Lesson Plan Edu-2000tDocument12 pagesSabrina Alkayfee Lesson Plan Edu-2000tapi-466588787No ratings yet
- As A Level GCE Physics B Mark Scheme January 2007Document50 pagesAs A Level GCE Physics B Mark Scheme January 2007Simon_Wong_691No ratings yet