Professional Documents
Culture Documents
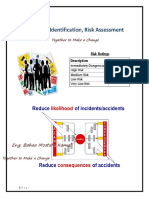
Hazards Identification and Risk Assessment: For Continual Improvement in Safety and Towards Zero Disaster Risk Management
Uploaded by
Pranoti JoshiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazards Identification and Risk Assessment: For Continual Improvement in Safety and Towards Zero Disaster Risk Management
Uploaded by
Pranoti JoshiCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazards Identification and Risk
Assessment
For continual improvement in
safety and towards zero Disaster
Risk Management
OH&S Policy
Management
Review Continual
Improvement
Checking & Planning
Corrective Action
Implementation
& Operation
OH&S Policy
Clearly states overall OH&S objectives
Authorised by top management
Appropriate to nature & scale of OH&S risks
Documented, implemented, and maintained
Communicated to all employees
Available to interested parties
Reviewed periodically
OH&S Policy Commitments
Improve health & safety performance*
Continual improvement
“at least” comply with current applicable
OH&S legislation and other requirements
*Performance: measurable results of the OH&S
management system, related to the organization’s
control of health and safety risks, based on its OH&S
policy and objectives.
OH&S Planning
Hazard identification, risk
assessment, and risk control
Legal and other requirements
Objectives
OH&S management program(s)
Hazard Identification, Risk
Assessment & Risk Control
Conceptually similar to environmental
aspects and impacts –target of
management program(s)
Much more detailed than 14001 approach
Assessment must address:
routine and non-routine activities
all personnel, including contractors and
visitors
facilities at the workplace, whether provided
by the organization or by others
Hazard Identification, Risk
Assessment & Risk Control
Methodology must be proactive
in advance of process/equipment changes
allow engineering of hazard controls during
design
implementation of controls as change
occurs
Success requires strong Management of
Change (MOC) procedure
Hazard Identification, Risk
Assessment & Risk Control
Process overview
identification of hazards
evaluation of risks under current controls
evaluation of the tolerability of residual risk
identification of needed additional controls
People are involved
significant risks must be controlled
individual behaviour is a significant factor
Hazard Identification, Risk
Assessment & Risk Control
Process overview
identification of hazards
evaluation of risks under current controls
evaluation of the tolerability of residual risk
identification of needed additional controls
People are involved
significant risks must be controlled
individual behaviour is a significant factor
OH&S Planning
Film
Implementation & Operation
Structure and responsibilities
Training awareness and competence
Consultation and communication
Documentation
Document and data control
Operational control
Emergency preparedness and response
Structure & Responsibilities
Documented roles, responsibilities,
authorities, and accountability
Management appointee
responsible for implementation
Resources
Managers must demonstrate
commitment to continual
improvement
Training, Awareness &
Competence
Ensure employee awareness and
competence
Take into account differing levels of:
Responsibility
Ability
Literacy
Risk
Much of required training driven by
regulation
Consultation & Communication
More internally focused than ISO 14001
Employee involvement and consultation
in development/review of policies and
procedures
about changes that affect workplace safety
or health
ensuring representation in OH&S matters
Buy-in, ownership, motivation
Insights of shop floor perspective
Documentation & Data
Documentation of core elements
aids employee awareness
shows how the various system relate
extremely valuable during certification
process
Document and data control procedures
critical documents are available
obsolete documents and data are removed
Operational Control
Identify operations and activities where
risk requires further control
Plan these to ensure that
documented procedures are developed
operating criteria specify key steps and
requirements
procedures addressing risks related to
contractor goods and services
establish design procedures to
reduce/eliminate source of risks
Emergency Preparedness &
Response
Emergency response procedures to
address
identifying potential for incidents and
emergencies
preventing and mitigating resultant
illnesses and injuries
responding to incidents and
emergencies when they occur.
Checking & Corrective Action
Performance measurement and
monitoring
Accidents, incidents, non-
conformances and corrective and
preventive action
Records and records management
OH&S management system audit
Performance Measurement &
Monitoring
Monitoring the achievement of
objectives
Quantitative and qualitative measures
Proactive and reactive methods
Records to facilitate corrective and
preventive actions
Calibration of monitoring equipment
Quantitative & Qualitative
Direct Quantitative Measures
number of lost work days following an
injury
decibel levels of noise in a work area
Indirect Qualitative Measures
review of inspection logs
observation of a task
interviews
Proactive & Reactive Measures
Proactive monitoring of compliance
routine basis, independent of any event
monitoring may be required by regulations
daily equipment checks
periodic review of hot-work permits
Reactive monitoring of accidents or
incidents
in response to an event or trigger
accident investigation
monitoring in response to a complaint
Accident, Incidents, Non-conformances &
Corrective and Preventive Action
Handle, investigate, mitigate
Accidents
Incidents
non-conformances
Corrective and preventive actions
Review action plans through risk
assessment process
Accident, Incidents & Non-
conformances
Handle = immediate action
Notification
emergency response
recordkeeping to facilitate investigation
Investigation process
team and procedures
root cause analysis
People are involved
human elements
Corrective and Preventive Action
Correct immediate problem
Mitigate consequences
Eliminate or control root cause
Prevent recurrence
Review action plans through risk
assessment process
Communicate results and monitor
Case study
Records & Record Management
Identification, maintenance, and
disposition
Records must be:
Legible
Identifiable
traceable to the activities involved
easily retrievable
protected from damage, deterioration, or loss
held for specified and documented retention
times
OH&S Management System Audit
Determine if OH&S-MS:
conforms with planned arrangements
is properly implemented and maintained
is effective in meeting policy and objectives
Results provided to top management
Audit program and schedule reflect risks
and previous audit results
Description and
definition of system
iption and definition of
Safety Analysis
system
Hazard Identification
Probabilistic Safety
Analysis
On-site and Off -
System Modification to
site Emergency
incorporate suggested
Accident
risk control measures
Quantitative Risk
management
Planning
assessment
Modeling/investigation
Risk
dent
Modeling/investigation
Frequency estimations
Risk Quantification
Risk Documentation &
Follow up plan
Management Review
OHSAS 18001 -
Occupational health and
safety management system
Continual improvement : Pl refer the
papers circulated and open for
discussion
Thanks
You might also like
- Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment GuidelineDocument81 pagesHazard Identification & Risk Assessment Guidelinebahaa mostafa100% (5)
- 3) 23114 - Safety, Health and Environmental LegislationDocument15 pages3) 23114 - Safety, Health and Environmental Legislationnilesh100% (5)
- 3) 23114 - Safety, Health and Environmental LegislationDocument15 pages3) 23114 - Safety, Health and Environmental Legislationnilesh100% (5)
- CSSLP 2016 NotesDocument26 pagesCSSLP 2016 Notesparul154No ratings yet
- Hazards and Effects Management ProcessDocument12 pagesHazards and Effects Management ProcessrwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Safety and Accident Loss Statistics: Prof. Shishir SinhaDocument43 pagesSafety and Accident Loss Statistics: Prof. Shishir SinhaganeshNo ratings yet
- HSE Strategic ProcessDocument15 pagesHSE Strategic ProcessardhianhkNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Bicycle FrameDocument28 pagesDesign and Analysis of Bicycle Framejamunaa83100% (2)
- Human Factores ErgonomicDocument664 pagesHuman Factores ErgonomicMarco AbreuNo ratings yet
- HIRAC Training (English)Document31 pagesHIRAC Training (English)IGede Sumantra100% (5)
- Risk AnalysisDocument125 pagesRisk AnalysisDennise ShughniNo ratings yet
- Oh S Management SystemDocument25 pagesOh S Management Systempaulina15vNo ratings yet
- Food Training Hygiene TrainingDocument45 pagesFood Training Hygiene TrainingLynne Corpuz BenignoNo ratings yet
- Cost Reduction Through Supply Chain ManagementDocument4 pagesCost Reduction Through Supply Chain ManagementAustin AudiNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Jawad HSE EngineerDocument3 pagesMuhammad Jawad HSE EngineerJawad abbasiNo ratings yet
- Environment, Health, Safety and Sustainability Application SolutionDocument4 pagesEnvironment, Health, Safety and Sustainability Application SolutionCompliance QuestNo ratings yet
- HSE Interview Q&ADocument20 pagesHSE Interview Q&ANaveed AkramNo ratings yet
- Fire Drills Safety HandoutDocument2 pagesFire Drills Safety HandoutRahulPrakash100% (1)
- 1) 23112 - Envionmental Management PDFDocument220 pages1) 23112 - Envionmental Management PDFnilesh100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Evaluation of Risk Management Strategies Annotated NotesDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Evaluation of Risk Management Strategies Annotated NotesRoshan PednekarNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Performance Indicators - Pspi: Risk Engineering Position Paper - 04Document16 pagesProcess Safety Performance Indicators - Pspi: Risk Engineering Position Paper - 04EduardoNo ratings yet
- Safety Analysis 1693858999Document176 pagesSafety Analysis 1693858999Nedhal YusufNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Selection ChartDocument1 pageFire Extinguisher Selection ChartPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Hilti Corrosion-Handbook EN PDFDocument48 pagesHilti Corrosion-Handbook EN PDFElenildo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Safety Training: Risk Management ProcessDocument42 pagesSafety Training: Risk Management ProcessLailatul Mufida100% (1)
- Budget of Work EAPP Quarter 2Document3 pagesBudget of Work EAPP Quarter 2Abegail Gulla100% (1)
- Ensuring Health and Safety Standard in The WorkplaceDocument19 pagesEnsuring Health and Safety Standard in The Workplacedodozee100% (1)
- Quick Guide Plus To... Chartered Engineer: Short Guidebook For ApplicationsDocument3 pagesQuick Guide Plus To... Chartered Engineer: Short Guidebook For ApplicationsnarkooNo ratings yet
- Fire Drill Training 2017Document14 pagesFire Drill Training 2017Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- TÜV Functional Safety Program: WWW - Prosalus.co - UkDocument267 pagesTÜV Functional Safety Program: WWW - Prosalus.co - Ukmurali krishna100% (1)
- Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control (HIRARC)Document29 pagesHazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control (HIRARC)Marites BalmasNo ratings yet
- Risk Management 1Document41 pagesRisk Management 1Amit Agarwal100% (2)
- Process Safety ManagementDocument26 pagesProcess Safety ManagementJune DominicNo ratings yet
- Quality, Health, Safety AND Environment Management SystemsDocument50 pagesQuality, Health, Safety AND Environment Management SystemsJay JaniNo ratings yet
- Risk ControlDocument19 pagesRisk ControlVincent Anthony MilitanteNo ratings yet
- Occupational Exposure Monitoring ProgramDocument23 pagesOccupational Exposure Monitoring ProgramKimi Zyky Lopez ReañoNo ratings yet
- APPLIED SAFETY HW Due Tomorrow 12-14-2010Document15 pagesAPPLIED SAFETY HW Due Tomorrow 12-14-2010Robert Ivan HerreraNo ratings yet
- Bip2050 Chapter06Document12 pagesBip2050 Chapter06Cristian TrincadoNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Applicant PreviousDocument4 pagesSection 3 Applicant PreviousAkhilNo ratings yet
- Safety Management System Structure: What Is A SMS?Document8 pagesSafety Management System Structure: What Is A SMS?Sayed AbbasNo ratings yet
- 04 Hazard Identification & AssessmentDocument12 pages04 Hazard Identification & AssessmentdsnrmrbdrdNo ratings yet
- HSE in DrillingDocument50 pagesHSE in DrillingBitsindouNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Learning Material 20240306184108Document33 pagesWeek 3 Learning Material 20240306184108Erikka Mykaela AguilaNo ratings yet
- Organizing For Safety and Health Evaluating Health and Safety ProgramsDocument10 pagesOrganizing For Safety and Health Evaluating Health and Safety ProgramsSitti Rahma Amilbahar AdgesNo ratings yet
- BSBWHS605 Assessment 2Document32 pagesBSBWHS605 Assessment 2GybNo ratings yet
- Igc1 5Document14 pagesIgc1 5Amir SohailNo ratings yet
- HSE Management System PresentationDocument16 pagesHSE Management System PresentationAshraf AboeleninNo ratings yet
- 02 SystematicApproachDocument25 pages02 SystematicApproachnuratikah5964No ratings yet
- CO2: Explain The Measurement and Monitoring TechniquesDocument41 pagesCO2: Explain The Measurement and Monitoring TechniquesSreejith S NairNo ratings yet
- HSE Audits & InspectionsDocument38 pagesHSE Audits & InspectionsZain Ali KidwaiNo ratings yet
- SevesoDocument15 pagesSevesoGustavo Agudelo100% (1)
- Nabling Rocesses: Governance Practice Inputs Outputs EDM03.01 Evaluate Risk Management. From Description Description ToDocument2 pagesNabling Rocesses: Governance Practice Inputs Outputs EDM03.01 Evaluate Risk Management. From Description Description ToMNTOUISE0% (1)
- PS leadingindicatorREv1Document2 pagesPS leadingindicatorREv1ali zaenal abidinNo ratings yet
- Ise 101 F4Document32 pagesIse 101 F4PERATCHI SELVANNo ratings yet
- Safety Management - Why Bother?: Legal RequirementsDocument37 pagesSafety Management - Why Bother?: Legal RequirementsRizwan Muhammad HussainNo ratings yet
- By Heriberto "Eddie" GarciaDocument11 pagesBy Heriberto "Eddie" GarciaanniseazaliaNo ratings yet
- CHP 10Document35 pagesCHP 10yadanarmyintmo.yaryarNo ratings yet
- Risk Cost Assess.00Document19 pagesRisk Cost Assess.00johnny_cashedNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Chap 7 Principles of Risk Assessment (1) RevisedDocument37 pagesModule 2 - Chap 7 Principles of Risk Assessment (1) Revisedngemanonjabulo02No ratings yet
- OSHA and You As A SupervisorDocument28 pagesOSHA and You As A Supervisorfgdgrte gdfsgdNo ratings yet
- R4R Brochure BowtieDocument1 pageR4R Brochure BowtieJonasNo ratings yet
- Hse Consultancy ServicesDocument6 pagesHse Consultancy ServicesEsamKhalilAlQadiNo ratings yet
- Planstsafe: Hse Incident ManagementDocument20 pagesPlanstsafe: Hse Incident ManagementESSMSS FirstOneNo ratings yet
- 008 PSMDocument21 pages008 PSMniels.cauwenberghNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 OSH Management SystemDocument25 pagesChap 1 OSH Management Systemkimberly_87No ratings yet
- Safety OverviewDocument25 pagesSafety OverviewelmohNo ratings yet
- Audits & Assessments: What Are The Differences and How Do We Learn From The Results?Document21 pagesAudits & Assessments: What Are The Differences and How Do We Learn From The Results?Richie RismyNo ratings yet
- Module Chapter 4Document20 pagesModule Chapter 4srushti thoratNo ratings yet
- W11 - Performance IndicatorDocument72 pagesW11 - Performance IndicatorGrace ChowNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis: MONA EMAD 202000169Document6 pagesHazard Analysis: MONA EMAD 202000169monae00169No ratings yet
- Ohsas 18001Document77 pagesOhsas 18001VijayakumarVageesanNo ratings yet
- Nobabgonjr Agontuk by Shirshendu MukhopadhyayDocument41 pagesNobabgonjr Agontuk by Shirshendu MukhopadhyayPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Nirbachito Bhooter Golpo by Humayun AhmedDocument74 pagesNirbachito Bhooter Golpo by Humayun AhmedPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Blast Burn InjuriesDocument1 pageBlast Burn InjuriesPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Avoiding SuicideDocument1 pageAvoiding SuicidePranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Direct Recruitment For Various Position in Civil Cadre. Ref Advt No 10-2019 - Revised - 29.11.2019Document10 pagesDirect Recruitment For Various Position in Civil Cadre. Ref Advt No 10-2019 - Revised - 29.11.2019Rohan RewatkarNo ratings yet
- Business Templates Info-Graphics Graph Templates Time Plan Templates Flow Diagrams Different CategoriesDocument28 pagesBusiness Templates Info-Graphics Graph Templates Time Plan Templates Flow Diagrams Different CategoriesPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Suffocation Gas GeyserDocument1 pageSuffocation Gas GeyserPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Directions On Revised CEPIDocument22 pagesDirections On Revised CEPIPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- TBDN-HSPRA-JSA-Confined Space PDFDocument1 pageTBDN-HSPRA-JSA-Confined Space PDFPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Claitec PAS Pedestrian Alert System - EN PDFDocument10 pagesClaitec PAS Pedestrian Alert System - EN PDFPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Min Wage-1Document6 pagesMin Wage-1Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 HazardIDDocument52 pagesMod 3 HazardIDbadar13No ratings yet
- 3rd SEA Mumbai Chapter WebinarDocument1 page3rd SEA Mumbai Chapter WebinarPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- HIRA Hazard Identification Guide FromDocument3 pagesHIRA Hazard Identification Guide FromPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- HD Front Line 17 July 2020 - 030170045426Document86 pagesHD Front Line 17 July 2020 - 030170045426Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- HazardsDocument18 pagesHazardsPranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Extra Dosed Bridge Over River Bramhaputra, Guwahati (Assam)Document1 pageExtra Dosed Bridge Over River Bramhaputra, Guwahati (Assam)Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ehs - Department Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment (Hira)Document6 pagesEhs - Department Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment (Hira)Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Guide To Address Stigma Associated With: COVID-19Document4 pagesGuide To Address Stigma Associated With: COVID-19Pranoti JoshiNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Hera PGDMMDocument117 pagesTerm Paper Hera PGDMMMd. Arifur Rahman HeraNo ratings yet
- What Is A SWOT AnalysisDocument6 pagesWhat Is A SWOT AnalysisaisyahNo ratings yet
- Analyze The Challenges and Problems in Air Cargo Operations, Chennai, Tamil NaduDocument5 pagesAnalyze The Challenges and Problems in Air Cargo Operations, Chennai, Tamil Naduarulrajpec2001gmailcomNo ratings yet
- MARK 302-A-Fall 2023-Course OutlineDocument6 pagesMARK 302-A-Fall 2023-Course Outlinedawsonkieran19No ratings yet
- Course PlanDocument4 pagesCourse PlanKarthik GsNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Geometric Brownian Motion Parameters For Oil PriceDocument9 pagesEstimation of Geometric Brownian Motion Parameters For Oil PriceDaniel LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Independent Evaluation of FDA's First Cycle Review Performance - Retrospective Analysis Final ReportDocument37 pagesIndependent Evaluation of FDA's First Cycle Review Performance - Retrospective Analysis Final Reportrgodeshwer1No ratings yet
- Literature Reviews As Independent Studies: Guidelines For Academic PracticeDocument19 pagesLiterature Reviews As Independent Studies: Guidelines For Academic Practiceferry nurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- The Ways of Grade 10 Students in Overcoming Laziness in Studying To Get Good GradesDocument50 pagesThe Ways of Grade 10 Students in Overcoming Laziness in Studying To Get Good GradesBryane Jayke FernandezNo ratings yet
- SIP Quality Assessment (QA) Tool: School Effectiveness Division Bureau of Human Resource and Organizational DevelopmentDocument19 pagesSIP Quality Assessment (QA) Tool: School Effectiveness Division Bureau of Human Resource and Organizational DevelopmentJelyn OkekeNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Agri - Tourism Programs in Quezon Province Basis For Sustainable Action PlanDocument10 pagesImplementation of Agri - Tourism Programs in Quezon Province Basis For Sustainable Action PlanIOER International Multidisciplinary Research Journal ( IIMRJ)No ratings yet
- Humanitarian Informal Feedback Project: Za'atari Refugee Camp, Jordan. Evaluation Report 2015/16Document18 pagesHumanitarian Informal Feedback Project: Za'atari Refugee Camp, Jordan. Evaluation Report 2015/16OxfamNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Construction Safety Management in Sri LankaDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Construction Safety Management in Sri LankaKumara WilegodaNo ratings yet
- Fashion Business Research Report On SreetwearDocument15 pagesFashion Business Research Report On SreetwearNandini SahNo ratings yet
- 1 FDPDocument45 pages1 FDPImdad HaqueNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Submission:: Syed Kamrul Islam (SKI)Document24 pagesResearch Proposal Submission:: Syed Kamrul Islam (SKI)Tahsin Kabir NakibNo ratings yet
- Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs AnDocument12 pagesProblems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs AnvaishalichakravarthiNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Acid-Base Tit RationsDocument2 pagesPotentiometric Acid-Base Tit RationsMark del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Screen Time Among School-Aged Children of Aged 6-14: A Systematic ReviewDocument19 pagesScreen Time Among School-Aged Children of Aged 6-14: A Systematic ReviewKeith MacalamNo ratings yet
- Rural Crafts and Trades Collections Today. Part One - The ReportDocument90 pagesRural Crafts and Trades Collections Today. Part One - The ReportalinhanchesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analysis of VarianceDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Analysis of VarianceTONYA WOODWARDNo ratings yet
- Course Manual 13-14Document120 pagesCourse Manual 13-14Brady XuNo ratings yet
- The Statisticians Role in Pharmaceutical DevelopmentDocument27 pagesThe Statisticians Role in Pharmaceutical DevelopmentSparsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Labour WelfareDocument58 pagesLabour WelfareFathimath Sayyida100% (2)
- Arihant JainDocument9 pagesArihant Jainarihant jainNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Construction Project Overhead ExpensesDocument13 pagesFactors Affecting Construction Project Overhead ExpensesbuddikalrNo ratings yet