Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 - Construction of Foundation
Uploaded by
Jetty Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views17 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views17 pages7 - Construction of Foundation
Uploaded by
Jetty CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Construction of Foundation
Engr. Lito I. Mauro
Most commonly used foundations for buildings
1. Strip foundation under walls (wall footings)
2. Spread or pad footing foundation under columns
3. Raft foundation
4. Pile footing
5. Pier foundation (bridges)
After excavation and leveling the foundation, sandfill
at 15 – 30cm if the foundation soil is not sandy.
Where it is necessary to fill the foundation to a higher
level from the excavation, the filling is done by a
hard core consisting of sand and gravel, known as
hard core.
Evolution of strip foundation
With the advent of reinforced concrete cement in
modern construction, reinforced concrete footings
are mostly used in strip and pad footings.
Such foundations do not require much thickening of
the brickwork at the base, but can be carried
straight from the RCC strip.
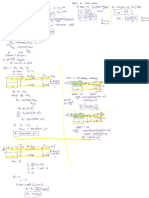
Determination of width of foundation
The width of a strip footing will depend on the load to
be carried by the wall and the safe bearing capacity of
the soil.
Load on unit length of wall
Safe bearing capacity
but should not be less than 1m the minimum width
required for excavation
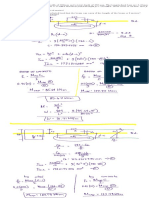
Placing levelling course of concrete in foundation
2 levelling courses provided in the foundation
1. Sand levelling course
2. Concrete levelling course
Sand levelling course should not be less than 100mm to
level up the foundation.
Concrete levelling course should be of lean cement
concrete 1 : 3 : 6 or 1 : 4 : 8 of large size aggregates
50mm.
Setting out for brickwork of a load-bearing
wall
After the base concrete foundation has set,
transfer the lines from the profile board to
the bottom of the trench on the concrete
surface board.
Foundation of partition walls
Foundations of external and internal load-
bearing walls should always be placed at
sufficient depths so a not to be affected
by climatic changes.
4 types of partition walls
Type 1 walls – These are half-brick walls (11m) taken to
ceiling heights only.
The foundation should consist one-brick walls (23cm).
They are constructed below the floor level and taken to
30cm below the original ground level.
A nominal concrete foundation of width 30cm and depth
15cm is provided beneath it.
A sandfilling of 15cm is also provided under the concrete.
Type 2 walls – These are half-brick walls taken
only up to 1.73m and are used for storage
shelves.
The wall can be made to rest directly on a
concrete foundation 30cm wide and 20cm
thick provided just below the base concrete for
the floor.
Type 3 walls – Partition walls in framed
structures can be built on connecting beams
made just below the floor concrete level and
connected to other beams such as grade
beams supported on columns.
Type 4 walls – Minor partition walls of low height
can be directly built on top of the floor if a good
depth of sandfilling over the original ground has
been provided below the floor beneath the wall.
A lightly reinforced shallow beam resting on sandfill
at the level of the floor an be provided to support
the wall.
Foundations of framed buildings
Framed buildings are built with columns and
beams forming the framework.
The columns are built on reinforced concrete
footings.
Foundations for staircases
Foundations for staircases need not be very deep
unless the soil is clayey.
In good soil conditions, the foundations are laid about
40cm below the original ground level.
If the sight is to be filled up for a large height, special
care should be taken so that the soil below the
foundation of staircases is well compacted while
filling is made
Plinth beams
The projecting part of the wall immediately above the
ground up to the ground floor is known as plinth.
It gives an appearance of additional stability to the
building and also the clearance from the ground level.
An RCC beam usually provided in the main walls above
the ground level and just below the ground floor level
is called a plinth beam.
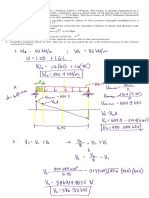
Eccentrically-loaded foundations
In construction of compound walls, their foundations
have to be built in one’s own property .
Eccentric footings can be adopted for these walls only
if the soil is sandy.
As the pressure on the foundation at the boundary side
is higher, there will be greater settlement at the
boundary.
You might also like
- 7 - Construction of FoundationDocument17 pages7 - Construction of FoundationJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- The Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcFrom EverandThe Modern Bricklayer - A Practical Work on Bricklaying in all its Branches - Volume III: With Special Selections on Tiling and Slating, Specifications Estimating, EtcRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Types of Foundation and Methods of Construction of FoundationDocument7 pagesTypes of Foundation and Methods of Construction of FoundationshakeelNo ratings yet
- Note On FoundationsDocument5 pagesNote On FoundationsArchit PatelNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundations-1Document55 pagesShallow Foundations-1Nisshant Singh SaudNo ratings yet
- Raft FoundationDocument3 pagesRaft FoundationDylan Ramasamy0% (2)
- Shallow FoundationDocument36 pagesShallow FoundationJhonny Wanky100% (1)
- Wall FootingDocument8 pagesWall FootingDrew FerrerNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls and Basement OnstructionDocument18 pagesRetaining Walls and Basement OnstructionreemadeponNo ratings yet
- STAGES of ConstructionDocument34 pagesSTAGES of Constructionbhaskar_065No ratings yet
- When Mat/Raft Foundation Is RecommendedDocument4 pagesWhen Mat/Raft Foundation Is RecommendedPrathamesh NaikNo ratings yet
- A.P. Satashia Civil Dept., Ssasit SuratDocument17 pagesA.P. Satashia Civil Dept., Ssasit SuratParth AnajwalaNo ratings yet
- CBRI - Waffle Unit & JoistDocument11 pagesCBRI - Waffle Unit & JoistAnkita Ghodke100% (2)
- Foundations: Strip FoundationDocument2 pagesFoundations: Strip FoundationMohd Karafi Md SallehNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design and Detailing of Non Engineered ConstructionDocument16 pagesSeismic Design and Detailing of Non Engineered ConstructionPavithra SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Raft Foundation (Shallow Foundation) Raft or Mat FoundationsDocument7 pagesRaft Foundation (Shallow Foundation) Raft or Mat FoundationsLiewKianHong100% (1)
- April 2005 BLDGCONST3Document106 pagesApril 2005 BLDGCONST3jjNo ratings yet
- Strip FootingDocument12 pagesStrip FootingChiew Yen TeoNo ratings yet
- STAGES of ConstructionDocument34 pagesSTAGES of ConstructionMahmoud ShakerNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteDocument26 pagesEarthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteHana SiddNo ratings yet
- CH-7 Presentation of Building ConstructionDocument68 pagesCH-7 Presentation of Building ConstructionUjas PandyaNo ratings yet
- BT3 Heavy RCPrestressetcDocument106 pagesBT3 Heavy RCPrestressetcHeather HallNo ratings yet
- FoundationsDocument53 pagesFoundationsBini Francis100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document40 pagesLecture 7Chibunda ChibundaNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument22 pagesBuilding ConstructionRAGU IRINNo ratings yet
- Concrete Foundations GuideDocument6 pagesConcrete Foundations GuideSuryasis DasguptaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Earthwork and Anti-Termite TreatmentDocument17 pages6 - Earthwork and Anti-Termite TreatmentJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Earthwork and Anti-termite Foundation TreatmentDocument17 pagesEarthwork and Anti-termite Foundation TreatmentJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- RCC Foundation and FootingDocument35 pagesRCC Foundation and Footingarchi_shwetaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 FoundationsDocument6 pagesUnit 4 FoundationsHoàng NamNo ratings yet
- Construction of Footings and Flooring SystemsDocument24 pagesConstruction of Footings and Flooring SystemsAlbert LiuNo ratings yet
- Secant Pile Wall Construction MethodsDocument54 pagesSecant Pile Wall Construction Methodsariyarathne100% (4)
- UnderpinningDocument66 pagesUnderpinningvetrivelanpec100% (1)
- Foundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of ADocument12 pagesFoundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of Ahabtamu abateNo ratings yet
- Basement Construction Methods Explained in 40 CharactersDocument51 pagesBasement Construction Methods Explained in 40 CharactersMUHAMMAD IMAN ASYRAF AHMAD NIZANo ratings yet
- Building Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021Document55 pagesBuilding Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021hyperloop707 designNo ratings yet
- Secant Piles: What Are Secant Pile Walls?Document3 pagesSecant Piles: What Are Secant Pile Walls?ulhas_nakashe100% (2)
- FloorsDocument9 pagesFloorsDharma Teja GhantasalaNo ratings yet
- Section Drawing Autocad PresentationDocument17 pagesSection Drawing Autocad PresentationSami UllahNo ratings yet
- Specification of 'Bricks WallsDocument6 pagesSpecification of 'Bricks WallsSohel Mridha100% (1)
- Foundation Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesFoundation Seminar ReportYash Boharupi0% (1)
- Strip, Pad & Raft Foundations ExplainedDocument8 pagesStrip, Pad & Raft Foundations ExplainedkannanNo ratings yet
- ARBT05 PrelimResearch1Document22 pagesARBT05 PrelimResearch1keithNo ratings yet
- B III SEM 2. Foundations and BasementsDocument26 pagesB III SEM 2. Foundations and BasementsNishma GuragaiNo ratings yet
- Jenis Jenis AsasDocument56 pagesJenis Jenis AsasShyboyzz JusopizNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Report On FoundationDocument19 pagesCivil Engineering Report On FoundationBD Biswajeet Ds67% (3)
- Substructure DesignDocument65 pagesSubstructure Designmmae64No ratings yet
- Building Construction & RepairDocument13 pagesBuilding Construction & RepairYasin ShahNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation DesignDocument17 pagesPile Foundation Designsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Pile FoundationDocument17 pagesAssignment: Pile Foundationsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering FoundationsDocument8 pagesGeotechnical Engineering FoundationsXiuming ChenNo ratings yet
- Building Construction EngineeringDocument27 pagesBuilding Construction EngineeringUsama KardarNo ratings yet
- AS2870 Footing SystemsDocument7 pagesAS2870 Footing SystemsEver Piñon-Simonsson83% (6)
- Construction of A 3 Bedroom BungalowDocument13 pagesConstruction of A 3 Bedroom BungalowElujekwute Benjamin100% (1)
- Reinforced BESSERTM Block Retaining and Basement Wall GuideDocument16 pagesReinforced BESSERTM Block Retaining and Basement Wall GuideA NT LeilyNo ratings yet
- Flooring Types and UsesDocument4 pagesFlooring Types and UsesPratik GhimireNo ratings yet
- Top Down Construction MethodDocument2 pagesTop Down Construction MethodJoe A. CagasNo ratings yet
- Stairs: Engr. Lito I MauroDocument34 pagesStairs: Engr. Lito I MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsDocument32 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsGerald PrimaveraNo ratings yet
- 17 Reinforced ConcreteDocument46 pages17 Reinforced ConcreteJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 17 Reinforced ConcreteDocument46 pages17 Reinforced ConcreteJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab: Engr. Lito I. MauroDocument29 pagesConcrete Slab: Engr. Lito I. MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 15-Formwork and ScaffoldingDocument21 pages15-Formwork and ScaffoldingJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab: Engr. Lito I. MauroDocument29 pagesConcrete Slab: Engr. Lito I. MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Stairs: Engr. Lito I MauroDocument34 pagesStairs: Engr. Lito I MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 6 - Earthwork and Anti-Termite TreatmentDocument17 pages6 - Earthwork and Anti-Termite TreatmentJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Site Preparation and Setting Out of WorksDocument12 pagesSite Preparation and Setting Out of WorksJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 4 - Components of A BuildingDocument6 pages4 - Components of A BuildingJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 8 - Brick MasonryDocument18 pages8 - Brick MasonryJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsDocument32 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsGerald PrimaveraNo ratings yet
- 15-Formwork and ScaffoldingDocument21 pages15-Formwork and ScaffoldingJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Site Preparation and Setting Out of WorksDocument12 pagesSite Preparation and Setting Out of WorksJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 4 - Components of A BuildingDocument6 pages4 - Components of A BuildingJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Earthwork and Anti-termite Foundation TreatmentDocument17 pagesEarthwork and Anti-termite Foundation TreatmentJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Project Development Framework: Engr. Lito I. MauroDocument15 pagesProject Development Framework: Engr. Lito I. MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- 8 - Brick MasonryDocument18 pages8 - Brick MasonryJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Construction Project Management IntroductionDocument52 pagesConstruction Project Management IntroductionJetty Cruz100% (3)
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityXyrezs AniNo ratings yet
- Activity: Identify The Effectuation Principle UsedDocument1 pageActivity: Identify The Effectuation Principle UsedJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 2 Shear: Monday, March 1, 2021 9:08 AMDocument1 pageExample 2 Shear: Monday, March 1, 2021 9:08 AMJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 3 DesignDocument1 pageExample 3 DesignJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 1 WSDDocument1 pageExample 1 WSDJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Planning: Engr. Lito I. MauroDocument32 pagesPlanning: Engr. Lito I. MauroJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 1 Shear: Monday, March 1, 2021 8:49 AMDocument1 pageExample 1 Shear: Monday, March 1, 2021 8:49 AMJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- Example 2: Monday, February 22, 2021 7:16 AMDocument1 pageExample 2: Monday, February 22, 2021 7:16 AMJetty CruzNo ratings yet
- SAES-Q-010 Cement Based, Non-Shrink Grout PDFDocument4 pagesSAES-Q-010 Cement Based, Non-Shrink Grout PDFWaqar Ahmed100% (1)
- Is 802Document16 pagesIs 802Sourav DeyNo ratings yet
- Lucas-Cav P/ N. OMAP P/n. Application - Verwendung - Application - ApplicazioneDocument12 pagesLucas-Cav P/ N. OMAP P/n. Application - Verwendung - Application - ApplicazioneDaniele AnsaloniNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation - Corrected (1) .PPTX RaviDocument15 pagesFinal Presentation - Corrected (1) .PPTX RavisudamNo ratings yet
- Sor JKR 2017 PDFDocument49 pagesSor JKR 2017 PDFRozita Abdullah Sani0% (1)
- Chapter ThreeDocument38 pagesChapter ThreeAbi DemNo ratings yet
- A789 PDFDocument4 pagesA789 PDFmahmoud hanafiNo ratings yet
- Parker RHDDocument46 pagesParker RHDDuygu GerçekNo ratings yet
- For Sample Cards and Testing To EBDocument3 pagesFor Sample Cards and Testing To EBjaymarNo ratings yet
- Non-Ferrous MetalDocument21 pagesNon-Ferrous MetalKArthik AustinNo ratings yet
- Assignment Answer WPS HK40Document4 pagesAssignment Answer WPS HK40RahulNo ratings yet
- Auto ClaveDocument16 pagesAuto ClaveAhmed QomaruddinNo ratings yet
- TR-CA-MS-003 - B Concrete FoundationDocument31 pagesTR-CA-MS-003 - B Concrete Foundationsamer8saifNo ratings yet
- Binder Box CulvDocument9 pagesBinder Box CulvHardy KamalNo ratings yet
- Ps Primer: DescriptionDocument2 pagesPs Primer: DescriptionEngr KamalNo ratings yet
- Timber Boards Used in Construction IndustryDocument2 pagesTimber Boards Used in Construction IndustryKumarasiri GalwattaNo ratings yet
- An Study On SFRC PDFDocument48 pagesAn Study On SFRC PDFVìctòry VèéráNo ratings yet
- Detail 2006 10Document28 pagesDetail 2006 10filipgavrilNo ratings yet
- Gs 09 PaintingDocument19 pagesGs 09 PaintingAshish PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Building With Earth A Guide To Flexible-Form Earthbag ConstructionDocument91 pagesBuilding With Earth A Guide To Flexible-Form Earthbag Constructionjhnmayor83% (6)
- Details of Measurement (Preliminaries)Document30 pagesDetails of Measurement (Preliminaries)Engr SwapanNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Chajja SlabDocument4 pagesDesign of Cantilever Chajja SlabMaheshNo ratings yet
- Test Certificate b8mDocument2 pagesTest Certificate b8msingaravelan narayanasamy50% (2)
- Trifold Brochure-NewDocument2 pagesTrifold Brochure-NewSaravana VelNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Grouting BrochureDocument9 pagesFosroc Grouting BrochurePratim SenguptaNo ratings yet
- pRICE LISTDocument3 pagespRICE LISTJohn ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica - Abrigo Retractil S430Document2 pagesFicha Tecnica - Abrigo Retractil S430Mauricio Aranda MillaNo ratings yet
- Steam and Condensate Piping Design BasicsDocument21 pagesSteam and Condensate Piping Design BasicsVIVEKZI0No ratings yet
- Mil e 5400TDocument71 pagesMil e 5400TNikola GrgićNo ratings yet
- Class M6C1Document13 pagesClass M6C1SalimNo ratings yet