Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon Cycle
Uploaded by
Yana Tv0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views27 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views27 pagesCarbon Cycle
Uploaded by
Yana TvCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Group 9
Members: Javed Mustafer
Leshana Talmakund
Class: Grade 10 Arts
Subject: Agricultural Science
Topic: The Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle
Teacher: Ms. Lindie
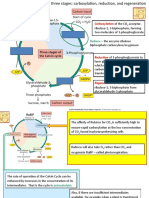
DEFINATION OF THE CARBON CYCLE
The carbon cycle is defined as the process in
which carbon atoms continually travel from the
atmosphere to the Earth and back to the
atmosphere. It also shows how carbon and
carbon compounds are linked to natural
processes and products.
Processes of the Carbon Cycle
There are three processes of the carbon cycle.
These are:
● Photosynthesis
● Respiration
● Decomposition
In the process of photosynthesis, plants use
carbon dioxide from the atmosphere which is
used to manufacture simple sugar. The simple
sugar is then built up in the plant to produce
carbohydrates, lipids and proteins which is then
consumed by humans and animals.
Carbon compounds release energy
which living organisms need to survive
through respiration. Carbon dioxide is a
waste product of respiration and is
released into the atmosphere by
humans. Plants use this waste product to
manufacture their own food.
In decomposition, micro organisms
digest the waste products from animal
urine, faeces and crop residue. These
products provide energy and carbon
dioxide is released into the air from their
respiration.
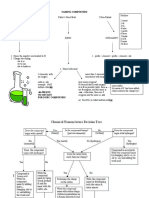
DEFINITION OF THE NITROGEN CYCLE
Nitrogen from the air is converted into soluble
ions that plant roots absorb. It forms apart of the
nitrogen compounds in plants and is then passed
from one organism to the next. It is then returned
to the atmosphere as nitrogen gas. This process
is known as the Nitrogen Cycle.
Nitrogen is said to be essential for
I
producing plants and animals proteins.
Approximately 79% of the Earth's
atmosphere is made up of Nitrogen gas.
Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle
There are four processes of the nitrogen
cycle. These include:
● Nitrogen Fixation
● Nitrogen Ammonification
● Nitrogen Nitrification
● Nitrogen Denitrification
NITROGEN
FIXATION
About 79% of the atmosphere is nitrogen
gas. However, nitrogen is too unreactive
to be used directly by plants to make
proteins. It must be converted into soluble
ions, such as nitrates, by nitrogen fixing
bacteria in the root nodules. Lightning can
also convert nitrogen gas to nitrates.
NITROGEN
AMMONIFICATION
Ammonification is the process of
decaying. The decomposers break
down the proteins in dead
organisms and animal waste.
Ammonium ions are released
through this process which
nitrifying bacteria can convert into
nitrates for plants to absorb.
NITROGEN
NITRIFICATION
Nitrification is a two step process carried
out by nitrifying bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria
is the organic matter from the remains of
plants, animals, urine and feaces.
Ammonium ions are converted to nitrites
and then to nitrates which plants roots
take in to make proteins.
NITROGEN
DENITRIFICATION
Denitrification is the process by
which nitrates are reduced to
nitrogen gas by denitrifying
bacteria. Denitrifying bacteria
obtain their energy through this
process.
Image showing the
Nitrogen Cycle
References
M.Perrett-Pearson, R. Ramharacksingh. 2020.
Agricultural Science for CSEC Examinations
NOAA. 2021. National Ocean Service
2020. The British Broadcasting Corporation
You might also like
- Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesProcess of PhotosynthesisJennifer Dizon100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosyntesisDocument32 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosyntesisTifahNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes PDFDocument12 pagesEcology Notes PDFvenkat_nsn100% (2)
- Mechanism of Loss of Water by PlantsDocument24 pagesMechanism of Loss of Water by PlantsarenaierNo ratings yet
- Ecological Succession ActivityDocument3 pagesEcological Succession Activityapi-236697820100% (1)
- Nitrogen Cycle: Ecological Planning - Assignment - 1Document13 pagesNitrogen Cycle: Ecological Planning - Assignment - 1Akshay KorlekarNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle and Sulphur CycleDocument16 pagesShort Notes On Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle and Sulphur Cyclesivaaero41No ratings yet
- Managing Natural Resources WiselyDocument17 pagesManaging Natural Resources Wiselyvikashvvn100% (1)
- Causes of Soil Erosion: 1. Deforestation For AgricultureDocument3 pagesCauses of Soil Erosion: 1. Deforestation For AgricultureSpice MoralesNo ratings yet
- The Oxygen CycleDocument9 pagesThe Oxygen CycleAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. PhotosynthesisDocument53 pagesChapter 6. Photosynthesisankurbiology100% (6)
- Abiotic and Biotic FactorsDocument3 pagesAbiotic and Biotic FactorsEmily Torrace Dunbar100% (1)
- EcosystemDocument48 pagesEcosystemYana PericoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: Multidisciplinary Nature and EcosystemsDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Science: Multidisciplinary Nature and EcosystemsInstagramNo ratings yet
- SymbiosisDocument10 pagesSymbiosisCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Nutrients CycleDocument35 pagesNutrients Cyclesureshk0201No ratings yet
- ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS (Environmental Science)Document43 pagesECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS (Environmental Science)Kris John SilvanoNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction LabDocument2 pagesDNA Extraction LabNur'Izzah Juarah100% (1)
- Non Conventional Farming SystemsDocument22 pagesNon Conventional Farming Systemsapi-262572717100% (1)
- Interactions in An EcosystemDocument31 pagesInteractions in An Ecosystemapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Ecology Guide to Biomes and EcosystemsDocument41 pagesEcology Guide to Biomes and EcosystemsMarixanne Niña Roldan Manzano100% (1)
- Inventions Weird and Awesome InventionsDocument48 pagesInventions Weird and Awesome InventionsKat MirandaNo ratings yet
- g7 EcosystemDocument13 pagesg7 EcosystemGenie SorianoNo ratings yet
- Biotic and Abiotic Components of An EcosystemDocument24 pagesBiotic and Abiotic Components of An Ecosystemcathlyn ranarioNo ratings yet
- Soil ProfileDocument22 pagesSoil ProfileRunjun BoraNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Visit Our Website for Agri Study Material & Mock TestsDocument115 pagesVisit Our Website for Agri Study Material & Mock TestsUmais nabiNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationships ExplainedDocument28 pagesSymbiotic Relationships ExplainedNomer PacilanNo ratings yet
- Applying Population Ecology: The Human Population and Its ImpactDocument58 pagesApplying Population Ecology: The Human Population and Its ImpactAPES2000No ratings yet
- Ecosystem PresentationDocument32 pagesEcosystem PresentationJanna Gomez100% (1)
- Economic Importance of Fungi SpirogyraDocument4 pagesEconomic Importance of Fungi Spirogyram.ameer0% (1)
- Nitrogen Cycle: Conversion of N2 to Multiple FormsDocument10 pagesNitrogen Cycle: Conversion of N2 to Multiple FormskilaxxdmaxNo ratings yet
- Community Ecology NotesDocument9 pagesCommunity Ecology Notesapi-233187566No ratings yet
- c4 InterdependenceDocument52 pagesc4 InterdependenceultrakaweNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle by Isabella GobelDocument16 pagesCarbon Cycle by Isabella Gobelapi-311703865100% (2)
- Symbiotic Relationships in EcosystemsDocument14 pagesSymbiotic Relationships in EcosystemsJane PaguiaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument14 pagesCalvin CycleWahyu ArifNo ratings yet
- Soil Texture and Soil StructureDocument24 pagesSoil Texture and Soil StructureRaquel Bona Viñas100% (4)
- Natural ResourcesDocument4 pagesNatural ResourcesShalini C G100% (1)
- Ecology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument69 pagesEcology Multiple Choice QuestionsJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Syllabus 2017 - 2018Document8 pagesEnvironmental Science Syllabus 2017 - 2018api-368018407No ratings yet
- LeavesDocument16 pagesLeavesjasta114No ratings yet
- Lec 3, 4 Ecology, EcosystemDocument16 pagesLec 3, 4 Ecology, Ecosysteminortoganic inortoganicNo ratings yet
- Ecological Relationships 1Document12 pagesEcological Relationships 1api-512405061No ratings yet
- Behavioral EcologyDocument16 pagesBehavioral EcologyrvshnNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument43 pagesFlowering Plantskingbanakon100% (1)
- Weathering and Soil Formation: The Breakdown of RocksDocument46 pagesWeathering and Soil Formation: The Breakdown of Rocksfaizankhan23100% (1)
- Biogeochemical Cycles ExplainedDocument22 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles ExplainedBrinda Eo LassNo ratings yet
- SalinityDocument5 pagesSalinityhemant8988100% (1)
- Ecosystem Structure and Types EcosystemDocument27 pagesEcosystem Structure and Types EcosystemMOVIES star100% (1)
- Aquatic EcosystemsDocument16 pagesAquatic Ecosystemsapi-323141584No ratings yet
- Soil MicroorganismsDocument8 pagesSoil Microorganismsaqarab HusnainNo ratings yet
- Community EcologyDocument60 pagesCommunity EcologyBom ChanNo ratings yet
- Lady Ann E. Murillo III- BEEd Principles of Ecology Vocabulary ListDocument3 pagesLady Ann E. Murillo III- BEEd Principles of Ecology Vocabulary ListLady Ann Enanoria MurilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Chemical Basis of LifeDocument81 pagesLesson 3. Chemical Basis of LifeMB Loterte100% (3)
- Lecture 8 - Soil FertilityDocument47 pagesLecture 8 - Soil FertilityGieann AcostaNo ratings yet
- Oceanography 5 - Properties of WaterDocument13 pagesOceanography 5 - Properties of WatersnamprogNo ratings yet
- Contract of EmploymentDocument2 pagesContract of Employmentßhăñĕ ßîñğhNo ratings yet
- Emancipation in Other Caribbean TerritoriesDocument4 pagesEmancipation in Other Caribbean TerritoriesYana TvNo ratings yet
- Anti-Slavery MovementsDocument3 pagesAnti-Slavery MovementsYana TvNo ratings yet
- British Emancipation Act 1833: Steps and ImpactDocument4 pagesBritish Emancipation Act 1833: Steps and ImpactYana Tv100% (1)
- Forms of ResistanceDocument4 pagesForms of ResistanceYana TvNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Curriculum GuideDocument59 pagesGrade 5 Curriculum GuideJazminie OsborneNo ratings yet
- Contract of EmploymentDocument2 pagesContract of Employmentßhăñĕ ßîñğhNo ratings yet
- Arguments For And Against SlaveryDocument4 pagesArguments For And Against SlaveryYana TvNo ratings yet
- Newsletters: NameplateDocument3 pagesNewsletters: NameplateYana TvNo ratings yet
- THE BENEFITS ARE AWESOME Natalia Science ProjectDocument2 pagesTHE BENEFITS ARE AWESOME Natalia Science ProjectYana TvNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument27 pagesCarbon CycleYana TvNo ratings yet
- Conference Agenda - tf00002077 - WacDocument1 pageConference Agenda - tf00002077 - WacSashaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Grade 10 Assignment InstructionsDocument1 pageIntegrated Science Grade 10 Assignment InstructionsYana TvNo ratings yet
- PDF Edpm-2013-SbaDocument19 pagesPDF Edpm-2013-SbaMandy ThomasNo ratings yet
- 10 Facts ofDocument4 pages10 Facts ofYana TvNo ratings yet
- RootDocument2 pagesRootYana TvNo ratings yet
- Fresh Water FishDocument1 pageFresh Water FishYana TvNo ratings yet
- Poems - 2018 - 2023Document22 pagesPoems - 2018 - 2023Yana TvNo ratings yet
- Assistance Presiding OfficerDocument1 pageAssistance Presiding OfficerYana TvNo ratings yet
- Committee Documents or Meeting DocumentsDocument1 pageCommittee Documents or Meeting DocumentsYana TvNo ratings yet
- Add Math SbaDocument17 pagesAdd Math SbaYana TvNo ratings yet
- Growth of Microorganisms Andrea, PPT WorkDocument12 pagesGrowth of Microorganisms Andrea, PPT WorkYana TvNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Curriculum Guide - Language PDFDocument82 pagesGrade 5 Curriculum Guide - Language PDFJazminie OsborneNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide Mathematics Grade 5 2008Document56 pagesCurriculum Guide Mathematics Grade 5 2008Jazminie OsborneNo ratings yet
- 10 Facts ofDocument4 pages10 Facts ofYana TvNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Curriculum GuideDocument59 pagesGrade 5 Curriculum GuideJazminie OsborneNo ratings yet
- DateDocument2 pagesDateYana TvNo ratings yet
- DateDocument2 pagesDateYana TvNo ratings yet
- Prereg Pharmacist Drug Calculations Roy Sinclair Booklet 2Document144 pagesPrereg Pharmacist Drug Calculations Roy Sinclair Booklet 2Maha tabiNo ratings yet
- Egemaster-Non Sparking Tools Safety PDFDocument5 pagesEgemaster-Non Sparking Tools Safety PDFZulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- Notes - Thermodynamics of Polymer Solution and Solubility ParameterDocument6 pagesNotes - Thermodynamics of Polymer Solution and Solubility Parameter79Jay ShethNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons Are The Group of Organic Compounds Containing Only Carbon and HydrogensDocument30 pagesHydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons Are The Group of Organic Compounds Containing Only Carbon and HydrogensKreis MDRPU CHIKMAGALORENo ratings yet
- US20030075077A1Document12 pagesUS20030075077A1Kyaw Kyaw LinnNo ratings yet
- FT-5 - JEE (Advanced) Paper-1 - CODE-A - 1558164094Document30 pagesFT-5 - JEE (Advanced) Paper-1 - CODE-A - 1558164094Suleiman NoumanjNo ratings yet
- CHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular GeometryDocument91 pagesCHM 171 Theme 3 Bonding and Molecular Geometrycatman123123No ratings yet
- Snibe Day 0302 Agenda (International Conference On Immunoassay) 0209Document3 pagesSnibe Day 0302 Agenda (International Conference On Immunoassay) 0209Laboratorium RSPONNo ratings yet
- Polymer SolubilityDocument13 pagesPolymer SolubilityDr. Stan Wardel BA, MA, MChem, MBA, DPhil, DSc.No ratings yet
- Manual For SP1Document19 pagesManual For SP1Mai Huong Bui ThiNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument2 pagesFlow ChartJames PerriamNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Electron ConfigurationsDocument1 page2.3 Electron ConfigurationsEoghan KuiperNo ratings yet
- Heat of ReactionDocument10 pagesHeat of ReactionAlok ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Siwes Report - 2021Document43 pagesSiwes Report - 2021Stephen Hardeykunle OladapoNo ratings yet
- Spoljne Resetke - TPI 03 PZ - ENDocument6 pagesSpoljne Resetke - TPI 03 PZ - ENKundzoNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics & PharmacokineticsDocument10 pagesBiopharmaceutics & PharmacokineticsEstelle Janica FusterNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Electrochemistry: Dr. Lipeeka Rout PHD, NitrDocument76 pagesUnit 1: Electrochemistry: Dr. Lipeeka Rout PHD, Nitrtenguria samriddh0% (1)
- LGR 7000XLi Owners Manual - 2015Document63 pagesLGR 7000XLi Owners Manual - 2015hqwaterNo ratings yet
- 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry PDFDocument12 pages1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry PDFDr. Mamta SinghNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 FractionationDocument49 pagesLect 4 FractionationKashif hussainNo ratings yet
- Module 5 General Biology 1Document23 pagesModule 5 General Biology 1Glenn Capcap Jr.No ratings yet
- A Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and PunarnarishtaDocument5 pagesA Comparative Pharmaceutico-Analytical Study of Punarnasava and Punarnarishtaalnrmamckoppa19No ratings yet
- P525/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Page 1Document8 pagesP525/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Page 1ArthurNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Genetron 407C Technical SpecsDocument18 pagesHoneywell Genetron 407C Technical Specsvinoth kumarNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Solubility Enhancement By: 1. Alteration in PH of The Solvent System 2. Comlexation TechniquesDocument38 pagesSeminar On Solubility Enhancement By: 1. Alteration in PH of The Solvent System 2. Comlexation Techniquesumamaheswararao4No ratings yet
- ASME BPV - 08 Section II SFA 5.9 PDFDocument24 pagesASME BPV - 08 Section II SFA 5.9 PDFCarlos PovedaNo ratings yet
- 05 Separation (3004) PDFDocument45 pages05 Separation (3004) PDFHenry OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Detection of Adulteration in Milk A ReviewDocument21 pagesDetection of Adulteration in Milk A ReviewLabconquim SAS LaboratorioNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectDocument5 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: SciencedirectHaroon Ur RashidNo ratings yet
- The CLEAPSS Recipe Book Introduction ToDocument128 pagesThe CLEAPSS Recipe Book Introduction ToJsckson Jaden NtuliNo ratings yet