Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophy of Aortic Stenosis
Uploaded by
Benedict James Bermas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
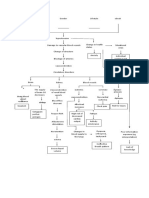
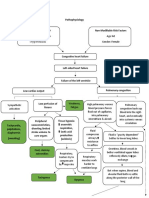
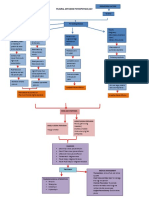
6 views1 pageA 72-year-old patient is experiencing aortic stenosis caused by the wear and tear of the aortic valve over many years resulting in fibrosis and calcification. This stenosis impedes blood flow through the aortic valve, forcing the left ventricle to contract harder to pump blood through. Over time, the increased pressure and workload on the left ventricle causes it to hypertrophy and leads to decreased cardiac output and pulmonary congestion, presenting as dyspnea, fainting, and crackles upon exertion or inspiration.
Original Description:
Original Title
pathophy of aortic stenosis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA 72-year-old patient is experiencing aortic stenosis caused by the wear and tear of the aortic valve over many years resulting in fibrosis and calcification. This stenosis impedes blood flow through the aortic valve, forcing the left ventricle to contract harder to pump blood through. Over time, the increased pressure and workload on the left ventricle causes it to hypertrophy and leads to decreased cardiac output and pulmonary congestion, presenting as dyspnea, fainting, and crackles upon exertion or inspiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePathophy of Aortic Stenosis
Uploaded by
Benedict James BermasA 72-year-old patient is experiencing aortic stenosis caused by the wear and tear of the aortic valve over many years resulting in fibrosis and calcification. This stenosis impedes blood flow through the aortic valve, forcing the left ventricle to contract harder to pump blood through. Over time, the increased pressure and workload on the left ventricle causes it to hypertrophy and leads to decreased cardiac output and pulmonary congestion, presenting as dyspnea, fainting, and crackles upon exertion or inspiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Predisposing Factors:
Age of 72
Wear and tear of valve over many years
disrupts valve and endothelium and
underlying matrix
Fibrosis and calcification of aortic valve
Pathophysiology Irregular flow through valve during systolic
contraction is audible on auscultation
Risk Factors
Mechanism Impedes blood flow through the aortic valve
Heart has decreased cardiac output Decreased perfusion of
Signs and Symptoms when doing activities brain
LV contracts harder to pump blood across the
stenotic valve
Faintness on exertion
dyspnea
Left atrium dilates and hypertrophies form as
a result of pressure overload Forceful contraction of LV overtime will cause
LV myocardial hypertrophy
Cardiac output becomes more reliant on
atrial filling of LV Stiff and hypertrophied LV with LV pressure will
both make the LV harder to fill (diastolic
dysfunction)
Bibasilar inspiratory
Atrial fibrillation develops causing severe crackles
decrease in cardiac output
Pressure overload in the LV causing The passing through of fluids
pulmonary congestion through alveolar walls into air sacs
Dyspnea
You might also like
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseAfif Al BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument2 pagesAortic RegurgitationJustine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Cardio PathDocument6 pagesCardio PathPranay ManiarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CHF Secondary To RHDDocument89 pagesPathophysiology of CHF Secondary To RHDMira MariantiNo ratings yet
- PJBDocument13 pagesPJBAmaliahHarumiKarimNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYgrumpy_mealNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyJanica MarinasNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) : Causes DiagnosisSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- All PathoDocument2 pagesAll PathoroseasNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis-Pathophysiology - Updated 2Document2 pagesCholecystitis-Pathophysiology - Updated 2Kylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- PathwayDocument1 pagePathwayLin DaNo ratings yet
- DELIVS Cardio Module 5 No. 2Document3 pagesDELIVS Cardio Module 5 No. 2Jaiton PagayonanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 1Document3 pagesConcept Map 1Rubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Valvular DiseasesDocument8 pagesValvular DiseasesBeryl Ben MergalNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Diseases Part 2 - Dr. BartolomeDocument9 pagesValvular Heart Diseases Part 2 - Dr. BartolomeMedisina101No ratings yet
- ECHAVEZ, Hazel Marie Section 2-H Patho B CPC #1: MyopericarditisDocument1 pageECHAVEZ, Hazel Marie Section 2-H Patho B CPC #1: MyopericarditisHazel Marie EchavezNo ratings yet
- Pathway ALODocument2 pagesPathway ALOIlhamYuandokoNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Diseases 3rd Yr BMTDocument38 pagesPericardial Diseases 3rd Yr BMT211941103014100% (1)
- Pathway ALO Revisi FixDocument2 pagesPathway ALO Revisi FixAyu Meiliana SetyamanNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument8 pagesHeart FailureApple Mae AlmoniaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- Activity #3: Pathophysiology and Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesActivity #3: Pathophysiology and Nursing Care PlanMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- CARDIO - Valvular Disease of The HeartDocument4 pagesCARDIO - Valvular Disease of The HeartMoon KillerNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesCor Pulmonale PATHOPHYSIOLOGYChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- PATHWAYDocument1 pagePATHWAYFitria NorkhalidaNo ratings yet
- Cvspa05 Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument8 pagesCvspa05 Valvular Heart DiseaseRobert So JrNo ratings yet
- Aortic Stenosis and Aortic RegugitationDocument3 pagesAortic Stenosis and Aortic RegugitationAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-LCHFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology-LCHFNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Physiology & Classification of Varicose Veins: Ravul Jindal, Bhanupriya Wadhawan, Piyush ChaudharyDocument4 pagesAnatomy, Physiology & Classification of Varicose Veins: Ravul Jindal, Bhanupriya Wadhawan, Piyush ChaudharyhyeNo ratings yet
- Disorder/Condition/Disease Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestations Assessment and Diagnostic StudiesDocument9 pagesDisorder/Condition/Disease Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestations Assessment and Diagnostic StudiesKasey C. PintoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Document8 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Michelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument73 pagesValvular Heart Diseaseindia2puppy100% (4)
- Aortic RegurgitationDocument2 pagesAortic RegurgitationMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- CVS Embryology Questions and Study Guide - Quizlet Flashcards by Hugo - OxfordDocument5 pagesCVS Embryology Questions and Study Guide - Quizlet Flashcards by Hugo - OxfordAzizNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesValvular Heart Disease: Etiology PathophysiologyensiNo ratings yet
- Pleurl Effusion Pathophysiology DiagramDocument2 pagesPleurl Effusion Pathophysiology DiagramAkiraMamo67% (3)
- Aortic StenosisDocument8 pagesAortic Stenosisdr.moni.co.ukNo ratings yet
- Aortic Stenosis BY ISRARDocument50 pagesAortic Stenosis BY ISRARAkramNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided and Right-Sided Heart Failure: Group 1Document11 pagesLeft-Sided and Right-Sided Heart Failure: Group 1Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument7 pagesHeart FailureLovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework of CVDDocument1 pageConceptual Framework of CVDJethro Bacayo ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle (Page Print 1-2)Document2 pagesCardiac Cycle (Page Print 1-2)hihariv794No ratings yet
- Narrative Pathophysiology of Varicose VeinsDocument2 pagesNarrative Pathophysiology of Varicose VeinsKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle AtfDocument2 pagesCardiac Cycle Atfdemirkan.oytunkasimNo ratings yet
- Asinas Shairabsn3aDocument28 pagesAsinas Shairabsn3aJoshua ApolonioNo ratings yet
- 19, Fetal Circulation& Heamo.. Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument59 pages19, Fetal Circulation& Heamo.. Congenital Heart Diseasesumayya hameedNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: Cardiac Conduction System DisordersDocument2 pagesHealth Assessment: Cardiac Conduction System DisordersLeigh ProsyneNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Pleural EffusionventimiglionNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Diseases and ConditionsDocument2 pagesCardiovascular System Diseases and Conditionsjava developerNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCardiac PhysiologyJoezer Gumangan VeranoNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in CirculationDocument12 pagesDisturbances in CirculationJoei OcampoNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Lec Prelim NotesDocument35 pagesNCM 114 Lec Prelim Notesmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesPathophysiologyeunams_1195% (20)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome PathophysiologyJocelle Joy OrellanedaNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Varicose Veins: How To Reduce Or Cure Varicose VeinsFrom EverandVaricose Veins: How To Reduce Or Cure Varicose VeinsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Benedict James Roldan BermasDocument4 pagesBenedict James Roldan BermasBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Focus Data, Action, and ResponseDocument2 pagesDate/Time Focus Data, Action, and ResponseBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For DutyDocument4 pagesReviewer For DutyBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Focus Data, Action, and ResponseDocument3 pagesDate/Time Focus Data, Action, and ResponseBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Benedict James R. Bermas Grand Towers Condominium RM 2309 Tower II Malate, ManilaDocument1 pageBenedict James R. Bermas Grand Towers Condominium RM 2309 Tower II Malate, ManilaBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- PEPC - Assiting With Crutches, Cane, WalkerDocument3 pagesPEPC - Assiting With Crutches, Cane, WalkerBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Answer RationalizationDocument2 pagesAnswer RationalizationBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- NonDisclosure 2021 - BERMASDocument1 pageNonDisclosure 2021 - BERMASBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Research GuideDocument2 pagesResearch GuideBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Core-Values - BERMAS, Benedict James R.Document1 pageCore-Values - BERMAS, Benedict James R.Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Psychriatric Nursing Learning Exp.Document82 pagesPsychriatric Nursing Learning Exp.Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Action Plan - Inadequate IncomeDocument2 pagesAction Plan - Inadequate IncomeBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- BERMAS Critical-ThinkingDocument4 pagesBERMAS Critical-ThinkingBenedict James Bermas0% (1)
- Inadequate Income As Health Resources ProblemDocument2 pagesInadequate Income As Health Resources ProblemBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Group 1-Exam RationaleDocument5 pagesGroup 1-Exam RationaleBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Bermas PSYCHE Exam1Document5 pagesBermas PSYCHE Exam1Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- BERMAS - Johari'sWindowActivityDocument1 pageBERMAS - Johari'sWindowActivityBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Psychiatric Nursing Clinical Case PresentationDocument124 pagesSchizophrenia: Psychiatric Nursing Clinical Case PresentationBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- BERMAS, Benedict James R-OutputDocument6 pagesBERMAS, Benedict James R-OutputBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Psyche TestDocument3 pagesPsyche TestBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Research Title Statement of The ProblemDocument2 pagesResearch Title Statement of The ProblemBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Document28 pagesObstetric Nursing: Note-Taking Guide 2021)Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- The Rite of Baptism Is Divided Into Four (4) Parts: Reception of The Child Celebration of God's Word Celebration of The Sacrament Conclusion of The RiteDocument11 pagesThe Rite of Baptism Is Divided Into Four (4) Parts: Reception of The Child Celebration of God's Word Celebration of The Sacrament Conclusion of The RiteBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Slide Test For Anti - Streptolysin O (Latex Agglutination Test)Document2 pagesSlide Test For Anti - Streptolysin O (Latex Agglutination Test)Dinesh SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Ordinance On Contact TracingDocument9 pagesOrdinance On Contact Tracingkayo roi dielNo ratings yet
- MumpsDocument1 pageMumpsFikri PutroNo ratings yet
- McMurray (2015) ESC Modes of Death in HFDocument8 pagesMcMurray (2015) ESC Modes of Death in HFerza jeiel garcesNo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutrition For NursingDocument34 pagesEnteral Nutrition For NursingMoonNo ratings yet
- What Is The Best Way To Treat Tinea Cruris?: Clinical InquiriesDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Best Way To Treat Tinea Cruris?: Clinical InquiriesKenny JapNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planssairej06100% (3)
- Hand Book of Veterinary Internal MedicineDocument88 pagesHand Book of Veterinary Internal MedicineDanielle Fisher91% (11)
- Kasus 3 KardiovaskularDocument3 pagesKasus 3 KardiovaskularHelmin DhNo ratings yet
- Maternity - Postnatal Care in The First Week - CG - 2015Document41 pagesMaternity - Postnatal Care in The First Week - CG - 2015Monica SurduNo ratings yet
- A Paradigm Shift in The Management of AsthmaDocument3 pagesA Paradigm Shift in The Management of AsthmaRuqayya AdamuNo ratings yet
- High Resolution CT of The Lungs: Technique, Indications and FindingsDocument9 pagesHigh Resolution CT of The Lungs: Technique, Indications and FindingsHari Baskar SNo ratings yet
- Online Med Ed NotesDocument12 pagesOnline Med Ed NotessonNo ratings yet
- Analisis Hubungan Lama Menderita Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Kualitas Hidup Penderita Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesAnalisis Hubungan Lama Menderita Diabetes Mellitus Dengan Kualitas Hidup Penderita Diabetes Mellitusandi asliaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia ADULTDocument6 pagesPneumonia ADULTSebastian TjuwatjaNo ratings yet
- The Progression of Pathology in Parkinson's DiseaseDocument8 pagesThe Progression of Pathology in Parkinson's DiseasejNo ratings yet
- Original Research Article: Vitan Patel, Minal Shastri, Nisha Gaur, Prutha Jinwala, Abhishek Y. KadamDocument5 pagesOriginal Research Article: Vitan Patel, Minal Shastri, Nisha Gaur, Prutha Jinwala, Abhishek Y. KadamTam LyNo ratings yet
- Losing WeightDocument3 pagesLosing WeightSimp 02No ratings yet
- Herbs and Uses 2Document13 pagesHerbs and Uses 2donjuanmadNo ratings yet
- Erik Van Woensel Classical Homeopathy Evidence Based Medicine Vol. 2Document23 pagesErik Van Woensel Classical Homeopathy Evidence Based Medicine Vol. 2Sohail LatifNo ratings yet
- Occupational Lung Disease. Diagnosis and Communication - Fact or Fiction?Document1 pageOccupational Lung Disease. Diagnosis and Communication - Fact or Fiction?Zali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transverse Myelitis and Vaccines - A Multi-AnalysisDocument8 pagesTransverse Myelitis and Vaccines - A Multi-AnalysisKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- 2008-CE337 - The Intraoral and Extraoral ExamDocument33 pages2008-CE337 - The Intraoral and Extraoral Examyongky100% (1)
- Surgery of The Adrenal GlandsDocument24 pagesSurgery of The Adrenal GlandsRafal SmolinskiNo ratings yet
- Breast, Imaging, Reporting and Data System (BI RADS) - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument3 pagesBreast, Imaging, Reporting and Data System (BI RADS) - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFnn hijo de alguienNo ratings yet
- SURGERY MedicalDocument15 pagesSURGERY MedicalSNo ratings yet
- Adult Health Nursing Mcqs Uint Wise BY BILAL SAEEDDocument16 pagesAdult Health Nursing Mcqs Uint Wise BY BILAL SAEEDAkml Khan100% (2)
- Anemiile HemoliticeDocument4 pagesAnemiile HemoliticeIoana GalNo ratings yet
- 1st Long Test in HealthDocument1 page1st Long Test in HealthRovilyn Dizon71% (7)
- Meningitis Beyond Neonatal AgeDocument57 pagesMeningitis Beyond Neonatal AgeTilahun Kegne100% (2)