Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Losses in Pipe Flow
Uploaded by
HenryRidler0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views5 pagesThe document discusses two types of energy losses that can occur in pipe flow: major losses due to friction, and minor losses due to factors like bends, fittings, obstructions, or changes in pipe diameter. It provides details on minor losses caused by sudden expansion and sudden contraction, explaining that they result from turbulence and changes in flow velocity. Formulas are given for calculating the head loss due to sudden expansion and sudden contraction based on the velocities before and after the change in diameter.
Original Description:
Original Title
Losses in pipe flow
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses two types of energy losses that can occur in pipe flow: major losses due to friction, and minor losses due to factors like bends, fittings, obstructions, or changes in pipe diameter. It provides details on minor losses caused by sudden expansion and sudden contraction, explaining that they result from turbulence and changes in flow velocity. Formulas are given for calculating the head loss due to sudden expansion and sudden contraction based on the velocities before and after the change in diameter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views5 pagesLosses in Pipe Flow
Uploaded by
HenryRidlerThe document discusses two types of energy losses that can occur in pipe flow: major losses due to friction, and minor losses due to factors like bends, fittings, obstructions, or changes in pipe diameter. It provides details on minor losses caused by sudden expansion and sudden contraction, explaining that they result from turbulence and changes in flow velocity. Formulas are given for calculating the head loss due to sudden expansion and sudden contraction based on the velocities before and after the change in diameter.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Two major energy losses in pipe flow
Major Losses Minor Losses
• (due to friction) • Sudden expansion
• Sudden contraction
• Bend in pipe
• Pipe fitting
• An obstruction in pipe
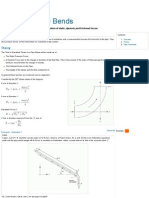
Minor Energy head loss: Sudden Expansion
• As fluid flows from a smaller pipe into a larger pipe through sudden enlargement,
its velocity abruptly decreases; causing turbulence that generates an energy loss.
• Sudden enlargement in the diameter of pipe results in the formation of eddies in
the flow at the corners of the enlarged pipe
• The amount of turbulence, and therefore the amount of energy, is dependent on the
ratio of the sizes of the two pipes.
Formula for calculating head loss: Sudden
Expansion
• he =
he = head loss due to sudden expansion
v1 = velocity before expansion
v2 = velocity after expansion
g = acceleration due to gravity
Minor Energy head loss: Sudden Contraction
• The loss is related to the velocity in the smaller pipe
• In reality, the head loss does not take place due to the sudden contraction but due
to the sudden enlargement, which takes place just after vena-contracta
• The section at which the flow is the narrowest is called vena-contracta
• At vena-contracta the velocity is maximum.
Formula for calculating head loss: Sudden
Contraction
• hc = 0.5
hc = head loss due to sudden
contraction
v2 = velocity after contraction
g = acceleration due to gravity
You might also like
- Unsteady FlowDocument31 pagesUnsteady FlowMuhammad Usman JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Oil Circuit BreakerDocument29 pagesOil Circuit Breakerfalu_29No ratings yet
- Surge Analysis: Mostafa Ajjawi, Jr. Engineer 16230 Mr. Barry Howe, Head of Piping StressDocument17 pagesSurge Analysis: Mostafa Ajjawi, Jr. Engineer 16230 Mr. Barry Howe, Head of Piping StressprashantNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer PDFDocument30 pagesWater Hammer PDFbhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Turbulent Flow in Circular PipesDocument29 pagesChapter 8 Turbulent Flow in Circular PipesSiti Nurshahira100% (1)
- Unit-3-Flow Through Pipes FMDocument75 pagesUnit-3-Flow Through Pipes FMPrãfûl Wådhãî100% (2)
- Minor Losses in PipesDocument9 pagesMinor Losses in PipesRam Krishna Singh60% (5)
- Water HammerDocument52 pagesWater HammerNidas SameeraNo ratings yet
- LESSON#9 SURGE PREVENTION IN THE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR - Jeff LeeDocument42 pagesLESSON#9 SURGE PREVENTION IN THE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR - Jeff LeeNimmakayala Manikanta100% (1)
- Flow Through Circular PipesDocument105 pagesFlow Through Circular PipesArchangel VenantNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument18 pagesWater Hammersaishankarl100% (1)
- Losses in Piping SystemDocument5 pagesLosses in Piping SystemHemashwaryNo ratings yet
- Surges in PipelinesDocument26 pagesSurges in PipelinesRaghuveer Rao Pallepati100% (1)
- Water HammerDocument30 pagesWater Hammerbhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Ce 314-Water Resource Engineering Lab: Experiment No. 2 - Minor Losses in Pipe FittingsDocument13 pagesCe 314-Water Resource Engineering Lab: Experiment No. 2 - Minor Losses in Pipe FittingsHenryRidlerNo ratings yet
- Losses in Flow Through PipesDocument19 pagesLosses in Flow Through PipessayaliraikarNo ratings yet
- Uni Flow Through PipesDocument39 pagesUni Flow Through PipesPranil KarangaleNo ratings yet
- Losses in FlowDocument30 pagesLosses in Flowkapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Valve & Pieline Cavitation (By Erhard Valve Co.)Document16 pagesValve & Pieline Cavitation (By Erhard Valve Co.)reza rashidian malekiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 4Document33 pagesHydraulics 4Avaricious AndrewNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer: A Mysterious Phenomena That Breaks Pipes and Damage Valves .Document30 pagesWater Hammer: A Mysterious Phenomena That Breaks Pipes and Damage Valves .Eder Callejas PerezNo ratings yet
- Minor Losses in Pipes: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageMinor Losses in Pipes: Department of Mechanical Engineeringsunil kumar sahNo ratings yet
- Pipe FittingDocument3 pagesPipe FittingMitesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow: Ce2002D Mechanics of FluidsDocument56 pagesPipe Flow: Ce2002D Mechanics of FluidsRITWIKI PRIYADARSINo ratings yet
- Ch1-Flow of Fluids in Pipes - StudentDocument112 pagesCh1-Flow of Fluids in Pipes - Studentmelki blair kamga nougoueNo ratings yet
- Eat 259 (Chapter 2) Part 2Document67 pagesEat 259 (Chapter 2) Part 2Muhammad Faiz bin Ahmad ShafiNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Pipes (Fluid Mechanics)Document13 pagesEnergy Losses in Pipes (Fluid Mechanics)DrakeNo ratings yet
- Forces On Pipe Bends - Pipes - Fluid Mechanics - Engineering Reference With Worked ExamplesDocument3 pagesForces On Pipe Bends - Pipes - Fluid Mechanics - Engineering Reference With Worked ExamplesMadhusudan MandalNo ratings yet
- Arc Length and Dynamic Correction in CMTDocument4 pagesArc Length and Dynamic Correction in CMTRumman Ul AhsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 KNDocument64 pagesChapter 7 KNmoeen.tariq9252100% (1)
- Losses in Piping SystemDocument5 pagesLosses in Piping SystemKhuram MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Ee6702 - Protection & Switchgear: By, Vinitha JC Asso. Prof. Rmd-EeeDocument80 pagesEe6702 - Protection & Switchgear: By, Vinitha JC Asso. Prof. Rmd-Eeeshahab moinNo ratings yet
- Lica 2 MarksDocument41 pagesLica 2 MarksVadivelu K RNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow: Major and Minor Losses: Puja Upadhyay Florida Center For Advanced Aero - PropulsionDocument35 pagesPipe Flow: Major and Minor Losses: Puja Upadhyay Florida Center For Advanced Aero - PropulsionJohn Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- Arc PhenomenonDocument12 pagesArc PhenomenonMudit BarrhwalNo ratings yet
- L1 Water HammerDocument19 pagesL1 Water HammerOPONo ratings yet
- Pipe FlowDocument12 pagesPipe Flowpapanoggie100% (1)
- Flow Through PipesDocument14 pagesFlow Through Pipesjadhavrushi403No ratings yet
- CH 3 2020Document62 pagesCH 3 2020Emmanuel LazoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 (07-10-2022)Document21 pagesLecture 18 (07-10-2022)Harshaa BattuNo ratings yet
- RVFDocument31 pagesRVFephNo ratings yet
- Sudden Enlargement & ContractionDocument2 pagesSudden Enlargement & ContractionFatin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Lecture7 - Flow in PipesDocument127 pagesChapter 5 - Lecture7 - Flow in PipesChris AdaminovicNo ratings yet
- Circuit BreakerDocument80 pagesCircuit Breaker2K20 CEEE 27 RAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow - Upadhyay 2017Document35 pagesPipe Flow - Upadhyay 2017John Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers: V.RajkumarDocument41 pagesCircuit Breakers: V.RajkumarRajKumarNo ratings yet
- Module IvDocument53 pagesModule Iv12015010 AMAL PAULSONNo ratings yet
- Piping Design - Unit 1Document74 pagesPiping Design - Unit 1valorantclips7.ioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - C - Reverse Breakdown and Zener Diodes - Revised - 1Document16 pagesChapter 1 - C - Reverse Breakdown and Zener Diodes - Revised - 1Hoàng ZioNo ratings yet
- Garden Watering 1 Garden Watering 2: Pressure Difference Pipe Diameter Flow 128 Pipe Length ViscosityDocument4 pagesGarden Watering 1 Garden Watering 2: Pressure Difference Pipe Diameter Flow 128 Pipe Length Viscositypathfind007No ratings yet
- 11 Introduction To Circuit BreakersDocument42 pages11 Introduction To Circuit BreakersShovon RoyNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Bends Lab Report Download Full VersionDocument2 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends Lab Report Download Full VersionOBO EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Flow Through PipesDocument34 pagesFlow Through PipesBrian SamendeNo ratings yet
- Condensate Induced Water HammeringDocument26 pagesCondensate Induced Water Hammeringparag14No ratings yet
- CH 2001 Fluid Mechanics Video Lectures: Module 31: Transportation of FluidsDocument35 pagesCH 2001 Fluid Mechanics Video Lectures: Module 31: Transportation of FluidsSai KumarNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer SeparationDocument20 pagesBoundary Layer SeparationGohar KhokharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4chamDocument33 pagesChapter 4chamhoangvubui4632No ratings yet