Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8 Products, Services, Brand Building Customer Value
Uploaded by
Vy Nguyen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views51 pagesThe document discusses key topics in chapter 8 including defining products, services and experiences. It outlines the major classifications of consumer and industrial products and services. It also discusses the individual product and service decisions companies must make regarding attributes, packaging, branding and labeling. Lastly, it covers services marketing and branding strategy, specifically how to build strong brands.
Original Description:
mkt
Original Title
Chapter 8 Products, Services, Brand Building customer value(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key topics in chapter 8 including defining products, services and experiences. It outlines the major classifications of consumer and industrial products and services. It also discusses the individual product and service decisions companies must make regarding attributes, packaging, branding and labeling. Lastly, it covers services marketing and branding strategy, specifically how to build strong brands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views51 pagesChapter 8 Products, Services, Brand Building Customer Value
Uploaded by
Vy NguyenThe document discusses key topics in chapter 8 including defining products, services and experiences. It outlines the major classifications of consumer and industrial products and services. It also discusses the individual product and service decisions companies must make regarding attributes, packaging, branding and labeling. Lastly, it covers services marketing and branding strategy, specifically how to build strong brands.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 51
Chapter 8
Products, Services, and Brand: Building Customer Value
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Learning Outcomes
• Define product and the major classifications of products and services
• Describe the decisions companies make regarding their individidual
products and services
• Identify four characteristics that affect the marketing of services and
the additional marketing considerations that services require
• Discuss branding strategy
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Content:
I. Product, Service and Experiences
Consumer Products & Industrial Products
II. Product and Services Decision
III. Services Marketing
IV. Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
1. Definition:
• Product is anything that can be offered in a market for attention,
acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need or want
• Service is a product that consists of activities, benefits or satisfaction
that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of
anything
• Experiences represent what buying the product or service will do for the
customer
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
2. Level of Products & Services
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Figure 1: Levels of Product and Services
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
Consumer
products
Industrial
products
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
A. Consumer products are products and services bought by final
consumers for personal consumption
• Classified by how consumers buy them
a. Convenience products
b. Shopping products
c. Specialty products
d. Unsought products
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
a. Convenience products
• Consumer products and services that the customer usually buys
frequently, immediately, and with a minimum comparison and buying
effort
• Usually low price and located in many areas
• E.g: Newspapers, Candy, Fast Food
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
b. Shopping Products
• Consumer products and services that the customer compares carefully on
suitability, quality, price, and style
• Distribute products through fewer outlets but provide deeper sales
support to help customers in their comparison efforts.
• E.g: Furniture, Cars, Appliances, Hotel, Airline Services.
Are clothes considered as shopping products?
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
c. Specialty Product
• Consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand
identification for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a
special purchase effort
• Buyers do not compare specialty products, but reach dealers carrying the
wanted products
• E.g: Medical services, Designer clothes, Medical Services & High-end electronics
(Audio, Video, Laptop)
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
d. Unsought product
• Consumer products that the consumer does not know about or knows
about but does not normally think of buying
• E.g: Life insurance, funeral services, blood donations & cosmetic surgery
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Discussion Question
• What is a product that could be convenience, shopping, and specialty?
ANSWER:
Depending on the purchasing situation => how consumers buy them?
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
B. Industrial Products:
• Products purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a
business
• Classified by the purpose for which the product is purchased
Materials and parts
Capital
Raw materials
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
3. Product & Service Classification:
B. Industrial Products:
• Capital: items are industrial products that aid in the buyer’s production
or operations
• Materials and parts: include raw materials and manufactured materials
and parts usually sold directly to industrial users
• Supplies and services: include operating supplies, repair and
maintenance items, and business services
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
4. Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas
a. Organization Marketing:
• Consist of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes
and behavior of target consumers toward an organization
• Both profit and non-profit organizations
=> Sponsor public relations or corporate image marketing campaigns for
marketing purposes
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
4. Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas
b. Person Marketing:
• Consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes
and behavior of target consumers toward particular people
• People ranging from presidents, entertainers, and sports figures to
professionals such as doctors, lawyers, and architects use person
marketing to build their “reputations”
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
4. Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas
b. Person Marketing:
• Consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes
and behavior of target consumers toward particular people
• People ranging from presidents, entertainers, and sports figures to
professionals such as doctors, lawyers, and architects use person
marketing to build their “reputations”
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
I. Products, Services, & Experiences
4. Organizations, Persons, Places, Ideas
c. Place Marketing:
• Consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes
and behavior of target consumers toward particular places.
• Cities, states, regions, and even entire nations compete to attract
tourists, new residents, conventions, and company offices and factories.
d. Social marketing:
• The use of commercial marketing concepts and tools in programs
designed to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being
and that of society.
• Cover wide range of issues in society.
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
Figure 2: Individual Product & Service Decisions
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
1. Product or service attributes
• Communicate and deliver the benefits
a. Quality
b. Features
c. Style and Design
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
1. Product or service attributes
a. Quality:
• Product Quality Level is the level of quality that supports the product’s
positioning
=> Reflect the Performance Quality
• Product Conformance Quality is the product’s freedom from defects
and consistency in delivering a targeted level of performance
=> Reflect the Consistency in delivering the expected quality
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
1. Product or service attributes
b. Features:
• Are a competitive tool for differentiating a product from competitors’
products
• Are assessed based on the value to the customer versus the cost to the
company
• E.g: Adidas Boost
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hrXaFhkTsWo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H9nlNnjRx9w
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Discussion Question
If the product is well-qualified, do manufacturer require to add more
features to it? How can they identify new features?
ANSWER:
• It should periodically survey buyers who have used the product and ask
these questions:
- How do you like the product?
- Which specific features of the product do you like most?
- Which features could we add to improve the product?
=> The answers to these questions provide the company with a rich list of
feature ideas.
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
1. Product or service attributes
c. Style and Design
• Style describes the appearance of the product
• Design contributes to a product’s usefulness as well as to its looks
Between style and design, which is more important?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tUIeUi-zYro
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NAaW6GSVaCE
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
2. Branding
• Brand is the name, term, sign, or design—or a combination of these—that
identifies the maker or seller of a product or service.
• Enhancing quality & consistency (segmentation, positioning,
communication product features) => brand’s meaning > physical attributes
• Help consumers to identify brand name. Support sellers in legal protection
for unique product features
• How to come up with a brand name? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4CaB_dSMHcU
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
3. Packaging
• Packaging involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a
product
• Past: function to protect the product
=> Now: becoming sale tasks
=> Create consumer recognition of a brand
=> Boosting Sales
• E.g:
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Packaging has its own purposes
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
4. Labelling
• Labels identify the product or brand, describe attributes, and provide
promotion.
• Supporting brand’s positioning and adding personality to the brand.
• “What are on the label?”
• Misleading labelling: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JXDo-73uaAI&t=94s
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Logo on label
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
5. Product Support Services
• Support services are an important part of the customer’s overall brand
experience.
• Using a sophisticated mix of phone, e-mail, Internet, and interactive voice
and data technologies to provide support services.
• Help companies to:
+ Assess the value of current services to obtain ideas for new ones.
+ Assess the costs of providing these services.
+ Develop a package of services to satisfy customers and provide profit to the
company
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6J5NFj1xuUw
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
5. Product Support Services
a. Product Line Decisions:
• Product line is a group of products that are closely related because they
function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are
marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price
ranges.
=> Adding items to product line => Increasing profit
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
5. Product Support Services
b. Product Line Length:
• The number of items in the product line
• Line filling: adding more items within the present line
Pros: extra profits, satisfying dealers, utilize capacity
Cons: cannibalization & confusion
• Line stretching: occur when the line is beyond its current range
Stretching upward & downward
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
II. Product and Service Decisions
5. Product Support Services
c. Product Mix Decisions:
• Product mix width is the number of different product lines the company
carries.
• Product mix length is the total number of items the company carries
within its product lines.
• Product mix depth is the number of versions offered of each product in
the line.
• Consistency is how closely the various product lines are in end use,
production requirements, or distribution channels.
• E.g: Sony
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
1. Types of Service Industries:
• Government: offer services through courts, employment services,
hospitals, military services, police and fire departments, the postal
service, and schools
• Private not-for-profit organizations: offer services through museums,
charities, churches, colleges, foundations, and hospitals
• Business services: offer services—airlines, banks, hotels, insurance
companies, consulting firms, medical and legal practices,
entertainment and telecommunications companies, real-estate firms,
retailers, and others
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
2. The Nature and Characteristics of a Service:
Figure 3: The Nature & Characteristics of a Service
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
3. Marketing Strategies for Service Firms:
• In addition to traditional marketing strategies, service firms often
require additional strategies; 4P+3P
a. Service-profit chain
b. Internal marketing
c. Interactive marketing
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
3. Marketing Strategies for Service Firms
a. Service-profit chain:
• links service firm profits with frontline-employee and customer
satisfaction
• Internal service quality
• Satisfied and productive service employees:
• Greater service value:
• Satisfied and loyal customers:
• Healthy service profits and growth: superior service firm performance
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
3. Marketing Strategies for Service Firms
b. Internal Marketing:
• Internal marketing means that the service firm must orient and
motivate its customer contact employees and supporting service
people to work as a team to provide customer satisfaction
• Internal marketing must precede external marketing
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
III. Services Marketing
3. Marketing Strategies for Service Firms
c. Interactive Marketing:
• Interactive marketing means that service quality depends heavily on the
quality of the buyer-seller interaction during the service encounter
• Service differentiation, Service quality & Service productivity
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Managing Service Differentiation
• Managing service differentiation creates a competitive advantage
from the offer, delivery, and image of the service.
• Offer can include distinctive features.
• Delivery can include more able and reliable customer contact people,
environment, or process.
• Image can include symbols and branding.
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Managing Service Quality
• Managing service quality provides a competitive advantage by
delivering consistently higher quality than its competitors
• Service quality always varies depending on interactions between
employees and customers
• E.g: Bamboo vs Vietjet (Proactive customer communication team)
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Managing Service Productivity
• Managing service productivity refers to manage the cost side of marketing
strategies for service firms
• Through employee recruiting, hiring, and training strategies
• Service quantity and quality strategies
• E.g: Check in kiosks vs Online checking vs Personal Counter Service
=> Improving Service quality -> Improving productivity
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
1. Brand Equity
• The differential effect that knowing the brand name has on customer
response to the product or its marketing.
• Dimensions of brand equity in consumer perception:
+ Differentiation (what makes the brand stand out),
+ Relevance (how consumers feel it meets their needs),
+ Knowledge (how much consumers know about the brand), and
+ Esteem (how highly consumers regard and respect the brand)
=> Competitive Advantages: brand awareness, loyalty, more leverage &
customer equity
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
Figure 4: Major Brand Strategy Decisions
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
2. Building Strong Brands
a. Brand Positioning:
• Position the brands clearly in target customers’ minds
• Positioning brands at 3 levels:
+ Product attributes: from product features (easy to copy by competitors)
+ Product benefits: customer service and support
+ Product beliefs and values: strong emotional connection with the brand.
=> Promise to deliver a specific set of features, benefits, services, and
experiences consistently to buyers -> “Lovemark”
E.g:
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
2. Building Strong Brands
b. Brand Name Selection:
• Providing “Desirable qualities”
o Suggest benefits and qualities
o Easy to pronounce, recognize, and remember
o Distinctive
o Extendable
o Translatable for the global economy
o Capable of registration and legal protection
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
2. Building Strong Brands
c. Brand Sponsorship:
• Manufacturer’s brand (National brand) vs Private brand (Store Brand)
- How these brands compete?
• Licensed brand: take years and spend millions to create their own brand
names
• Co-brand: occurs when two established brand names of different companies
are used on the same product
Pros: Taking strength from 2 brands, expanding category on both sides
Cons: Required legal contracts and licenses
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sl6Pebtcpz4
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
IV. Brand Strategy: Building Strong Brands
2. Building Strong Brands
c. Brand Development
Figure 5: Brand Development Strategies
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Recap
Product, Service and Experiences
Consumer Products & Industrial Products
Product and Services Decision
Services Marketing
Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
Next Week
Chapter 10: Pricing – Understanding & Capturing Customer Value
Principles of Marketing _ Lai Vinh Phuc, MBA
You might also like
- Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer Value: Session 7Document30 pagesProducts, Services, and Brands: Building Customer Value: Session 7ABDUL MUNAM KHANNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 2.2 Product ConceptsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 2.2 Product ConceptsSneha SofatNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - Product, Branding & PackagingDocument22 pagesMarketing Management - Product, Branding & PackagingJon JonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Products Services and BrandsDocument76 pagesChapter 8 - Products Services and BrandsSyeda RizviNo ratings yet
- Products, Services and Brands: Building Customer Value: Unit 5 Chapter 8 Kotler and Armstrong (2018)Document55 pagesProducts, Services and Brands: Building Customer Value: Unit 5 Chapter 8 Kotler and Armstrong (2018)Elias Macher CarpenaNo ratings yet
- BST - CHP 11Document11 pagesBST - CHP 11JOrdanNo ratings yet
- Air SHS Abm PM-Q4 Mod10Document21 pagesAir SHS Abm PM-Q4 Mod10Park ChimChimNo ratings yet
- Entrep ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrep ReviewerlablabyieeeNo ratings yet
- IEM Y1Q3 Marketing - Slides - Part 1Document24 pagesIEM Y1Q3 Marketing - Slides - Part 1Lahcen SafraouiNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam in Principles of Marketing ReviewerDocument6 pages1st Periodical Exam in Principles of Marketing ReviewerJaderick BalboaNo ratings yet
- CKY Module 2 EMDocument36 pagesCKY Module 2 EMloida f. rosalinNo ratings yet
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueDocument51 pagesCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueAlina IsrarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: MarketingDocument36 pagesPresentation On: MarketingTejesh ShamiNo ratings yet
- Mktng_-Q4_MOD10Document20 pagesMktng_-Q4_MOD10Jade ivan parrochaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 8 NotesHager MassoudNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document36 pagesSession 5uwxodjiuwuuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Marketing: Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument47 pagesChapter One: Marketing: Creating and Capturing Customer Valueharbi66622No ratings yet
- What Is MarketingDocument12 pagesWhat Is MarketingLeila JanelleNo ratings yet
- Chaper 8&9Document83 pagesChaper 8&9duyennhk21No ratings yet
- Operations On The Marketing MixDocument117 pagesOperations On The Marketing MixEdward AyineNo ratings yet
- EDS321 Prod Dev ClassDocument15 pagesEDS321 Prod Dev ClassWisdom ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Products, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueDocument27 pagesProducts, Services, and Brands: Building Customer ValueSANAD MEHYARNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: Session 1: Introduction About MarketingDocument197 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: Session 1: Introduction About MarketingHải Lê100% (1)
- Market and EnvironmentDocument59 pagesMarket and EnvironmentCathy DoodzNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument31 pagesMarketingTrecy PaccialNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Class 12 Study Material Chapter 11Document24 pagesBusiness Studies Class 12 Study Material Chapter 11BUrhanNo ratings yet
- BRANDINGDocument11 pagesBRANDINGKrithika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module I For TeamsDocument26 pagesModule I For TeamsAlex BarlaNo ratings yet
- VI SEM B.B.M Subject BRAND MANAGEMENTDocument42 pagesVI SEM B.B.M Subject BRAND MANAGEMENTAbhishek DANo ratings yet
- Marketing Concept and FunctionsDocument28 pagesMarketing Concept and FunctionsSuchi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Product, Services, and BrandingDocument8 pagesChapter 7-Product, Services, and BrandingCrystalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 30052022 034634pmDocument49 pagesChapter 8 30052022 034634pmaimal AkakhailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundamentals of MarketingDocument67 pagesChapter 1 Fundamentals of MarketingEYOB AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Product Strategy and Managing ServicesDocument26 pagesProduct Strategy and Managing ServicesBibbidi BobbidiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Tech-VocDocument170 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Tech-Vocjuvan05No ratings yet
- Workshop 3 - Customer ServiceDocument9 pagesWorkshop 3 - Customer ServiceaskjdkjasdNo ratings yet
- B2B Unit 3Document72 pagesB2B Unit 3HR ADMINNo ratings yet
- Activity Performance Worksheet In: Computer Systems ServicingDocument8 pagesActivity Performance Worksheet In: Computer Systems ServicingSACATA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- Features of Marketing 1. Needs and WantsDocument11 pagesFeatures of Marketing 1. Needs and Wantslakshy bansalNo ratings yet
- Deepening Principles of MarketingDocument83 pagesDeepening Principles of MarketingResmin Joy Dayag0% (1)
- BM 4 Chapter 8 LessonDocument43 pagesBM 4 Chapter 8 LessonMarjNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing-Week 1-2Document8 pagesPrinciples of Marketing-Week 1-2Trisha EnilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Customer - Driven Marketing StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 7 Customer - Driven Marketing StrategyVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.2Document61 pagesChapter 7.2Trang Nguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Assignment Norashikin Binti Azahari Edsm 30-7-2023Document35 pagesAssignment Norashikin Binti Azahari Edsm 30-7-2023haiza aliyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Mod MCV 112Document297 pages6 Mod MCV 112chetti akahayNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 261Document33 pagesCh.8 261asmasajjadNo ratings yet
- Module-Principles of MarketingDocument174 pagesModule-Principles of MarketingMrBigbozz21100% (2)
- Pom Qtr2 Module1 StudentsDocument7 pagesPom Qtr2 Module1 Studentsmryjoy05No ratings yet
- How to Create an Effective Value Proposition and Unique Selling PropositionDocument2 pagesHow to Create an Effective Value Proposition and Unique Selling PropositionMarie Kaye-Anne De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Marketing ChannelsDocument36 pagesChapter 12 Marketing ChannelsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- MM Unit 3Document68 pagesMM Unit 3Raju NagarNo ratings yet
- Tourism and Hospitality Marketing: Chapter 1: Overview of MarketingDocument17 pagesTourism and Hospitality Marketing: Chapter 1: Overview of MarketingNorharnaniNo ratings yet
- Sssss - in .In .In .In .In: MarketingDocument46 pagesSssss - in .In .In .In .In: MarketingSamina HaiderNo ratings yet
- CBSE Guide Marketing Management Class 12 Notes Business StudiesDocument20 pagesCBSE Guide Marketing Management Class 12 Notes Business StudiesGangadhar Mamadapur0% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Week 4 Marketing+MixDocument46 pagesEntrepreneurship Week 4 Marketing+MixCassandra AguiluchoNo ratings yet
- Pinciples of MarketingDocument42 pagesPinciples of Marketingsirjagz0611No ratings yet
- Building Customer Value Through Products, Services and BrandsDocument13 pagesBuilding Customer Value Through Products, Services and BrandsAtifAshrafKianiNo ratings yet
- Marketing AssignmentDocument12 pagesMarketing AssignmentRiponPrasadNo ratings yet
- Evaporation ProblemsDocument4 pagesEvaporation ProblemsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- U2 Lec5 Screening - MixingDocument98 pagesU2 Lec5 Screening - MixingVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture on Size Reduction in Food ProcessingDocument69 pagesLecture on Size Reduction in Food ProcessingVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Fermentation of Honey in Mead ProductionDocument11 pagesFactors Influencing The Fermentation of Honey in Mead ProductionVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions 2020 2021 HK2 AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Questions 2020 2021 HK2 AnalysisVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mixing: Homogenization EmulsificationDocument13 pagesFluid Mixing: Homogenization EmulsificationVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Processes: Unveiling The Evolution of Madeira Wine Key Metabolites: A Three-Year Follow-Up StudyDocument12 pagesProcesses: Unveiling The Evolution of Madeira Wine Key Metabolites: A Three-Year Follow-Up StudyVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Guidance Allergen Food PDFDocument85 pagesGuidance Allergen Food PDFAllan BatistaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - External Factors & Internal FactorsDocument31 pagesLecture 7 - External Factors & Internal FactorsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mead Production: Selection and Characterization Assays of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae StrainsDocument7 pagesMead Production: Selection and Characterization Assays of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae StrainsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids Vary in ShapeDocument30 pagesFatty Acids Vary in ShapeVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Handout 2021 22Document78 pagesChapter1 Handout 2021 22Vy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Right Understanding About The Roles of Food LipidsDocument40 pagesRight Understanding About The Roles of Food LipidsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Yeast Micronutrient Requirements 2017Document4 pagesYeast Micronutrient Requirements 2017Vy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Review A Review of Clean-Label Approaches To Chilli Paste ProcessingDocument11 pagesReview A Review of Clean-Label Approaches To Chilli Paste ProcessingVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Marketing ChannelsDocument36 pagesChapter 12 Marketing ChannelsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - On Site Assignment 6 (Cloud 2) - Nutrition and Functional FoodsDocument27 pagesGroup 1 - On Site Assignment 6 (Cloud 2) - Nutrition and Functional FoodsVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bank of America SwotDocument3 pagesBank of America SwotIftikhar JatoiNo ratings yet
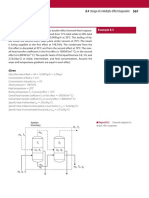
- 8.4 Design of A Multiple-Eff Ect Evaporator: GivenDocument3 pages8.4 Design of A Multiple-Eff Ect Evaporator: GivenVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapet 10 Pricing - Understanding and Capture Customer ValueDocument31 pagesChapet 10 Pricing - Understanding and Capture Customer ValueVy Nguyen100% (1)
- Assignment of Lecture 2Document1 pageAssignment of Lecture 2Minh Duy100% (1)
- IU-VNU Differentiation ChapterDocument75 pagesIU-VNU Differentiation ChapterVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Food Unit Operation 1 - Laboratory ManualDocument17 pagesFood Unit Operation 1 - Laboratory ManualVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Communicating Customer Value - Integrated Marketing - Communications StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 14 - Communicating Customer Value - Integrated Marketing - Communications StrategyVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- HPP Food ProcessingDocument3 pagesHPP Food ProcessingAldea MihaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Analyzing Marketing EnvironmentDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Analyzing Marketing EnvironmentVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Application and Analysis of The Folin Ciocalteu Method ForDocument13 pagesApplication and Analysis of The Folin Ciocalteu Method ForBrave AhilesNo ratings yet
- ĐkyDocument1 pageĐkyVy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Food Quality Assurance Systems: 3 Credits (3 +0) Ver. No.3Document4 pagesFood Quality Assurance Systems: 3 Credits (3 +0) Ver. No.3Vy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Name: Morgan, Cam, FranDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Name: Morgan, Cam, Franapi-397819018No ratings yet
- Sahasrayogam Text With English Translation 2nd Edition PDFDocument2 pagesSahasrayogam Text With English Translation 2nd Edition PDFLokesh Nagaraj0% (1)
- Buy Google 5 Star ReviewsDocument4 pagesBuy Google 5 Star ReviewsJeffrey LehouxNo ratings yet
- Formulir Astra 1st 2012Document7 pagesFormulir Astra 1st 2012Annisa Rahayu PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Niche Site BloggingDocument163 pagesNiche Site BloggingZonoiko ArafatNo ratings yet
- NFC Digital Protocol Technical SpecificationDocument194 pagesNFC Digital Protocol Technical Specificationtomathivanan100% (1)
- Communicating Corporate Handloom StrategyDocument7 pagesCommunicating Corporate Handloom StrategychayaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile CV - Wakatobi Indonesia - EmailDocument26 pagesCompany Profile CV - Wakatobi Indonesia - EmailMohamad RopikNo ratings yet
- ST Chapter 4 Using Number Bonds To SubtractDocument6 pagesST Chapter 4 Using Number Bonds To Subtractapi-298455456No ratings yet
- Danielson Framework Correlation With IntascDocument2 pagesDanielson Framework Correlation With Intascapi-416734680No ratings yet
- UMTS and LTE-TRSDocument23 pagesUMTS and LTE-TRSJitendraNo ratings yet
- Jacob Stewart ResumeDocument2 pagesJacob Stewart Resumeapi-250063152No ratings yet
- Ancient Hebrew A Student GrammarDocument243 pagesAncient Hebrew A Student GrammarUCLfan100% (5)
- Reading Lesson Plan Form 3Document2 pagesReading Lesson Plan Form 3nuriel100% (1)
- Assignment Questions Module 1&2Document6 pagesAssignment Questions Module 1&2Derreck VolzNo ratings yet
- Friendship With Foreigners - A2+Document4 pagesFriendship With Foreigners - A2+Юліана РевенкоNo ratings yet
- Mbo 222Document16 pagesMbo 222Daniel GebreHiwotNo ratings yet
- 201172-HUAWEI HG655b Home Gateway Quick Start (V100R001 - 01, General, English)Document12 pages201172-HUAWEI HG655b Home Gateway Quick Start (V100R001 - 01, General, English)rgabiNo ratings yet
- Celta Essay 1Document4 pagesCelta Essay 1Roger Gilbert100% (1)
- Video Conferencing I.T. HW.Document6 pagesVideo Conferencing I.T. HW.Kxñg Messíí IVNo ratings yet
- 1.5.7-Packet - Tracer-Network-Representation Respuestas.Document2 pages1.5.7-Packet - Tracer-Network-Representation Respuestas.no se por que piden correoNo ratings yet
- Social Media Use and Preferences of Bahir Dar University StudentsDocument43 pagesSocial Media Use and Preferences of Bahir Dar University Studentsmubarek oumerNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun LPDocument4 pagesPersonal Pronoun LPJames Andrew PaddayumanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Business CorrespondenceDocument27 pagesUnit 1 - Business CorrespondenceTang TeacherNo ratings yet
- Teaching Games For UnderstandingDocument2 pagesTeaching Games For UnderstandingMat KingNo ratings yet
- 1 Page Marketing PlanDocument4 pages1 Page Marketing PlanRosieNo ratings yet
- Network Devices Guide: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers & GatewaysDocument8 pagesNetwork Devices Guide: Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers & GatewaysrevathiNo ratings yet
- Social Media and Its Relationship To Academic PerformanceDocument18 pagesSocial Media and Its Relationship To Academic PerformanceAira Mae Botor100% (1)
- Cisco ESA Admin Guide 14-0Document1,416 pagesCisco ESA Admin Guide 14-0Samir AliyevNo ratings yet
- Forms of Communication: Suchithra NairDocument68 pagesForms of Communication: Suchithra NairMarzuqi SaufiNo ratings yet