Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classroom Presentation Toolkit Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
XRKhaloodi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views16 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Flowering Plants
Uploaded by
XRKhaloodiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Section 3: Flowering Plants
In anthophytes, seeds and fruits can develop from flowers after
fertilization.
K W L
What I Know What I Want to Find Out What I Learned
Essential Questions
• How can the life cycle of a flowering plant be described?
• What is the process of fertilization and seed formation in flowering plants?
• What are the different methods of seed dispersal?
• What is seed germination?
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Vocabulary
Review New
• cytoskeleton • polar nuclei
• endosperm
• seed coat
• germination
• radicle
• hypocotyl
• dormancy
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
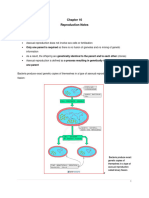
Life Cycle
• Anthophytes, like all plants, exhibit alternation of generations.
• Sporophyte generation is dominant
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Life Cycle
Gametophyte development
• Female gametophyte development:
• A megaspore forms in the pistil, and the nucleus undergoes mitosis,
forming one cell with 8 nuclei.
• The nuclei separate: 3 on each end of the cell, and 2 polar nuclei in the
center.
• One of the nuclei closest to the micropyle becomes the egg; the egg plus
the cell with seven nuclei are the female gametophyte.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Life Cycle
Gametophyte development
• Male gametophyte development:
• In the anther, specialized cells under go meiosis
and produce microspores.
• Each microspore nucleus undergoes mitosis that
forms two nuclei
• A protective cell wall grows around the
microspore, forming the immature male
gametophyte.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Plant Growth
Go to your ConnectEd resources to play Animation: Plant Growth.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Life Cycle
Pollination and fertilization
• When a compatible pollen grain lands
on a stigma, the pollen tube forms.
• The pollen grain produces two sperm,
one of which fuses with the egg
forming the zygote, and the other of
which fuses with the two polar nuclei
forming a triploid (3n) cell.
• This process is called double
fertilization and is unique to
anthophytes.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Double Fertilization
Go to your ConnectEd resources to play Animation: Double
Fertilization in Flowers.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Results of Reproduction
Seed and fruit development
• The sporophyte zygote undergoes numerous cell divisions to become an embryo.
• The 3n cell becomes the endosperm tissue, which provides nutrients to the
growing embryo.
• The endosperm is mostly absorbed into the cotyledons of eudicots, but in
monocots it accounts for a large volume of the seed.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Results of Reproduction
Seed and fruit development
• As the endosperm matures, the outside layers of the ovule harden and form a
protective tissue called the seed coat.
• The ovary of a plant can contain one or many ovules.
• As the ovule develops into a seed, changes occur in the ovary that cause it to
develop into a fruit.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Types of Fruit
Go to your ConnectEd resources to play Interactive Table: Types of
Fruit.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Results of Reproduction
Seed dispersal
• Fruits help disperse the seeds away from their parent plant, reducing competition
and increasing their chance of survival.
• Some seeds pass unharmed through the digestive tracts of animals before being
deposited.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Results of Reproduction
Seed germination
• When the embryo in a seed starts to grow, the process is called germination.
• The first part of the embryo to appear outside the seed is the radicle.
• The hypocotyl is the first part of the seed to appear above ground.
• Seeds produced at the end of the growing season may enter dormancy, a state of
little to no growth, to increase survival in harsh conditions.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Seed Germination in Flowering Plants
Go to your ConnectEd resources to play Animation: Seed Germination
in Flowering Plants.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
Review
Essential Questions
• How can the life cycle of a flowering plant be described?
• What is the process of fertilization and seed formation in flowering plants?
• What are the different methods of seed dispersal?
• What is seed germination?
Vocabulary
• polar nuclei • germination • hypocotyl
• endosperm • radicle • dormancy
• seed coat
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Flowering Plants
You might also like
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Introduction To Plant ReproductionDocument24 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Introduction To Plant ReproductionXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction: From Asexual Cloning to Seed GerminationDocument33 pagesPlant Reproduction: From Asexual Cloning to Seed GerminationJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument50 pagesPlant Reproductiongoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesReproduction in PlantsMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction StudentDocument64 pagesPlant Reproduction StudentmrkoutsantanouNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination in PlantsDocument49 pagesSeed Germination in PlantsbridgetnicolelimNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument36 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- II. Seed-GerminationDocument49 pagesII. Seed-GerminationAndrew GatesNo ratings yet
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Reproduction in PlantsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Pollinators Vital for Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesPollinators Vital for Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBHUPENDER KUMARNo ratings yet
- M.3 Plant Propagation 3-2020 Seed Development-DefDocument44 pagesM.3 Plant Propagation 3-2020 Seed Development-DefMUSTOFANo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization in PlantsDocument24 pagesDouble Fertilization in PlantsAshmit Srinjoy DuttaNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction 2015Document46 pagesPlant Reproduction 2015Jodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Rep in PlantsDocument23 pagesRep in PlantsMira Mohamed NabilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BiologySheggyNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For SurvivalDocument56 pages6.3 Pollination and Fertilisation, 6.4 Development of Seeds and Fruits and 6.5 Importance of Seeds For Survivalwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants FertilizastionDocument29 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants FertilizastionJurez N. EvansNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Document7 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants: "Imperfect or Incomplete Flowers"Jann LarNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsZainurain Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- To Reviewgen BioDocument19 pagesTo Reviewgen Bioguia.mareeseNo ratings yet
- 2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-Padma Madam FinalDocument40 pages2.sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-Padma Madam FinalNamrata NaikNo ratings yet
- Q2 - ReproductionDocument79 pagesQ2 - ReproductionInkie VenturinaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual Reproduction (1)Document36 pagesReproduction of Living Organisms Asexual and Sexual Reproduction (1)stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Plant Lifecycles and ReproductionDocument25 pagesPlant Lifecycles and ReproductionAngel Cipriano LiliaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument25 pagesReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- 02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSDocument35 pages02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSRitik Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerDocument7 pagesChapter-2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants FlowerbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesReproduction in PlantsphemelomashumbaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Botany - Lesson - 1 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument122 pagesBio-Botany - Lesson - 1 - Reproduction in PlantsDEEBA .GNo ratings yet
- Plant DevelopmentDocument115 pagesPlant DevelopmentarumalammaNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4Document9 pagesFlowering Plants Powerpoint Class 3 and 4api-308489491No ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Reproductive SystemsDocument35 pagesChapter 4. Reproductive Systemsalemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- Plant Science: Plant Growth & Development: Seed GerminationDocument51 pagesPlant Science: Plant Growth & Development: Seed GerminationSoumya Ranjan SwainNo ratings yet
- Pollen Tube Growth and Double FertilizationDocument9 pagesPollen Tube Growth and Double FertilizationEllNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plants NotesDocument17 pagesReproduction in Lower and Higher Plants NotesNisha vankhadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document25 pagesChapter 18 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Suffa AcademyNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination: D. KettleDocument18 pagesSeed Germination: D. KettleBossy Thing'sNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination: D. KettleDocument18 pagesSeed Germination: D. KettleBossy Thing'sNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Document22 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Kestina MillerNo ratings yet
- University Search: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesUniversity Search: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsNathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Reproduction in PlantsDocument44 pagesLecture-Reproduction in PlantsMotiourNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDrDibendu Kumar BejNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument125 pagesPlant and Animal ReproductionDavis ShamolmolNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PLANTDocument48 pagesReproduction PLANTmonamoikoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowring PlantsDocument22 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowring PlantsShazia Khatoon100% (1)
- 16 - ReproductionDocument6 pages16 - ReproductionlolshedoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotesDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotespranjaylakshitaNo ratings yet
- 5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341Document28 pages5ad43b99e4b0fa8be1f4fe4f 5e9a092ba8446510cc99fb5a 1615282586341seaid zahidNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal Reproduction GuideDocument120 pagesPlant & Animal Reproduction GuideElizaga ElizagaNo ratings yet
- 16 Reproduction Notes Igcse BiologyDocument29 pages16 Reproduction Notes Igcse Biologyasmatullahmohammed2No ratings yet
- Methods of ReproductionDocument56 pagesMethods of ReproductionJhigo Villar Franco PascualNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsDocument35 pagesPlant Reproduction: Biology For MajorsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument47 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantslastoutriderNo ratings yet
- Organismal Biology: Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument46 pagesOrganismal Biology: Reproduction and DevelopmentJa FloresNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ReproductionDocument77 pagesIGCSE ReproductionTonkaaw KatayouwongchareonNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument58 pagesAngiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: Powerpoint Lectures Forchapter38No ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument18 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDianna josephNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- 07le 06 Pa Thankyoupolicstop STDocument7 pages07le 06 Pa Thankyoupolicstop STXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Reproduction in PlantsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Complex Inheritance and Human HeredityDocument6 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Complex Inheritance and Human HeredityXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Basic Patterns of Human InheritanceDocument16 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Basic Patterns of Human InheritanceXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Presentation Toolkit Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory SystemsDocument6 pagesClassroom Presentation Toolkit Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory SystemsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Preview: Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear ReactionsDocument73 pagesPreview: Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear ReactionsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Key Concepts of Atoms, Subatomic Particles, and Electron ConfigurationDocument29 pagesAtomic Structure - Key Concepts of Atoms, Subatomic Particles, and Electron ConfigurationXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Holt Language Handbook Answer KeyDocument58 pagesHolt Language Handbook Answer KeyXRKhaloodi100% (6)
- Unstable Nuclei Can Break Apart Spontaneously, Changing The Identity of AtomsDocument20 pagesUnstable Nuclei Can Break Apart Spontaneously, Changing The Identity of AtomsXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Clauses: Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics Language Skills PracticeDocument20 pagesClauses: Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics Language Skills PracticeXRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- I Will Use The Following Equipment: (Circle These) : Spoon Bowl ScoopDocument4 pagesI Will Use The Following Equipment: (Circle These) : Spoon Bowl Scoopkatchrak87No ratings yet
- Olive Oil Production ProcessDocument1 pageOlive Oil Production Processliao robinNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Semester 1 2015: Melbourne High School ScienceDocument26 pagesYear 9 Semester 1 2015: Melbourne High School ScienceAndy Lu0% (1)
- Katalog Stahlplus EngDocument254 pagesKatalog Stahlplus EngNilesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Volume 21 10 Oct2010Document68 pagesVolume 21 10 Oct2010Mara Rosana Carvalho MoraisNo ratings yet
- Natural dewormers eliminate parasitesDocument10 pagesNatural dewormers eliminate parasitesMelvin John EnanoNo ratings yet
- Leaf Nutrient Status of Pomegranate (Punica Himachal PradeshDocument4 pagesLeaf Nutrient Status of Pomegranate (Punica Himachal Pradeshalanlima92No ratings yet
- Stone Age StewDocument2 pagesStone Age StewRaluca IlesNo ratings yet
- Rounded Tip PetalsDocument1 pageRounded Tip PetalsNoella100% (2)
- Ahupuaa Week 1 Packet 2016 Copy CompressedDocument12 pagesAhupuaa Week 1 Packet 2016 Copy Compressedapi-260262236No ratings yet
- Salicina en SauceDocument2 pagesSalicina en SauceSol GrumtNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of Dragon FruitDocument6 pagesProduction Technology of Dragon FruitAbhinash MoirangthemNo ratings yet
- Finnish consumers discover tropical fruitsDocument21 pagesFinnish consumers discover tropical fruitsIndou TaichiNo ratings yet
- FM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets: List of FiguresDocument25 pagesFM Global Property Loss Prevention Data Sheets: List of FiguresTienda JoselenaNo ratings yet
- NitrogenDocument19 pagesNitrogenKayıtsız ŞartsızNo ratings yet
- Gross Revenue For A Four Acre Model Household Enteprise Mix: Bananas/Coffee/Dairy/CitrusDocument1 pageGross Revenue For A Four Acre Model Household Enteprise Mix: Bananas/Coffee/Dairy/CitrusHope BalindaNo ratings yet
- Model Answer CH - 1, 2, 3, & 4 From Science Voyage-2Document10 pagesModel Answer CH - 1, 2, 3, & 4 From Science Voyage-2Ahian Altair100% (1)
- GM - Chapter 3 SaladsDocument36 pagesGM - Chapter 3 SaladsPuteri AirinNo ratings yet
- 2014 Lista de Pret Si Formular Seminte Flori COMPLETDocument136 pages2014 Lista de Pret Si Formular Seminte Flori COMPLETStruc Andrei100% (1)
- Horse Drawn Wagon Flower Pot Stand PlanDocument59 pagesHorse Drawn Wagon Flower Pot Stand PlanbrasilgabrielcostaNo ratings yet
- Carpas ReproduzaoDocument38 pagesCarpas ReproduzaoGiorgio FernandesNo ratings yet
- Modicare Customer Price List - April 2021Document5 pagesModicare Customer Price List - April 2021narendarNo ratings yet
- Tulsi (Ocimum Sanctum), Excellent Source of PhytochemicalsDocument7 pagesTulsi (Ocimum Sanctum), Excellent Source of PhytochemicalsIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Entomopathogenic Fungi and Insect BehaviourDocument14 pagesEntomopathogenic Fungi and Insect BehaviourAlejandro MailesNo ratings yet
- Food StylingDocument10 pagesFood StylingpandeybharatNo ratings yet
- Weekly menu for hostel messDocument2 pagesWeekly menu for hostel messVinay SheelNo ratings yet
- Herbal CosmeticsDocument40 pagesHerbal CosmeticsBiren Shah100% (1)
- Palm Oil ProcessingDocument22 pagesPalm Oil ProcessingNurul Amelia Mustaffa75% (4)
- 1st Quarter Exam Science 9Document4 pages1st Quarter Exam Science 9Christian Mark Almagro Ayala100% (3)
- Scope of LandscapeDocument1 pageScope of LandscapeAbhisheK100% (1)