Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 2nd Grading
Uploaded by
DIANE BORROMEO,0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views23 pagesOriginal Title
math-2nd-grading
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views23 pagesMath 2nd Grading
Uploaded by
DIANE BORROMEO,Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
2nd Quarter Week 1
Approximates the measures of
quantities particularly length,
weight/mass, volume, time, angle and
temperature and rate.
• Measurements should be as accurate and precise
as possible. Accuracy pertains to the closeness of
the measurements to the true value while precision
refers to the degree to which successive
measurements agree with each other
• However, no matter how accurate the act of
measurement is considered an approximate value.
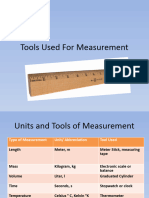
Measuring Length
Length is a measure of how long an object
is or the distance between two points. It is
used for identifying the size of an object or
distance from one point to another. The
length of an object is its extended
dimension, that is, its longest side.
Measuring Length
• Use the Millimeters to measure the small objects
like the thickness of a book, a paper clip or
microchips.
• Use the Centimeter to measure bigger ones like
length of a fork, a pencil or a book.
• Use the Meters to measure longer lengths like
flagpole or a piece of land.
• Use the Kilometers - To measure distance between
towns
Measuring Mass
When you want to know how heavy an object is, you
are quantifying a physical attribute of that object
called mass. We buy things in cans, jars, and sachets.
Written in these containers are the net weight of the
contents. Mass is the amount of matter an object
contains.
Measuring Mass
• Milligrams – terms used in measuring very light
objects such as solid medicine quantity
• Grams - terms used in measuring objects like gold
ring, a cup of sugar, and a small pack of peanuts
• Kilograms - heavier measures like the weight of a
person and a sack of rice
Measuring Capacity
• The volume of a container is the number of a cubic
units of space it encloses. The units of capacity are
used to describe how much container will hold. In
the laboratories, the most common device used for
measuring volume of liquid is the graduated
cylinder.
• Most graduated cylinders are calibrated to the
nearest millimeters. Medicine syrups and soft drink
capacities are express in millimeters, while gasoline
and water tanks are given in liters.
Measuring Temperature
• The measure of the hotness and coldness of an object is
called temperature. Gabriel Fahrenheit created the
Fahrenheit scale in the early years of 18th century. He
set the freezing point of water at 32 degrees and the
boiling point at 212 degrees. In the latter part of the
18th century, Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer,
devised the Celsius scale. He determined the freezing
point as 0 degrees and boiling point as 100 degrees.
There is a limit to how cold something can be. The Kelvin
scale is designed to go to zero at this minimum
temperature. Thermometer are used to measure
temperature.
Measuring Time
• Time is one of the fundamental quantities of the
physical world. It is a period during which an action
or event occurs. Some of the instruments used in
measuring time are the common wristwatch,
pendulum clock, atomic clock, cesium clock, and
quartz crystal clock. These are collectively called
chronometers. These instruments are used to
measure fractions of a day. For longer periods of
time, the calendar is used.
Measuring Angle
• Angles are formed when two rays that are not on
the same line meet or intersect at a common
endpoint. A protractor is used for measuring
angles. The common endpoint is called the vertex
and the rays are called the side s of an angle from
the latin word angulus which means corner.
RATE
You might also like
- Measurement Class 8Document24 pagesMeasurement Class 8mad_sudrocksNo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8From EverandStress-Free Science: A Visual Guide to Acing Science in Grades 4-8No ratings yet
- c2 MeasurementsDocument37 pagesc2 Measurementsapi-240791824No ratings yet
- Math Measuring InstrumentsDocument28 pagesMath Measuring InstrumentsJM Akki BerdenNo ratings yet
- MarkellaDocument23 pagesMarkellamimoakal24No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDocument30 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments AssignmentDocument10 pagesMeasuring Instruments AssignmentJasonKoylassNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Chemistry MeasurementsDocument3 pagesHandout 2 Chemistry MeasurementsZëky NhächëngöNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Units WorksheetDocument3 pagesMeasurement and Units WorksheetYoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2api-298420434No ratings yet
- Process of Comparing A Specific Quantity of Matter With An Agreed StandardDocument26 pagesProcess of Comparing A Specific Quantity of Matter With An Agreed StandardMariss Nudalo SisonNo ratings yet
- Numerical Literacy Waj 3105Document13 pagesNumerical Literacy Waj 3105soyab_1No ratings yet
- Revision Notes PDFDocument7 pagesRevision Notes PDFrafeekherNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDocument29 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- ChemDocument39 pagesChemJhunner BuanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Sec 1 Measurement-PowerpointDocument23 pagesCH 2 Sec 1 Measurement-Powerpointapi-294483847100% (2)
- Examen Final - Idioma TecnicoDocument30 pagesExamen Final - Idioma Tecnicosamuel rojasNo ratings yet
- Final-Math-7-2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesFinal-Math-7-2nd QuarterDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- KobyDocument1 pageKobyJeanette Bonifacio CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Science Notes IGCSE Grade 7Document57 pagesScience Notes IGCSE Grade 7callista.d.fNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - MeasurementDocument28 pagesWeek 1 - MeasurementdianeNo ratings yet
- Arihant - Science - Bio - Heat 7Document24 pagesArihant - Science - Bio - Heat 7Keshav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Measurement-Grade 7Document26 pagesMeasurement-Grade 7a.gayle1998No ratings yet
- Lab 1 MeasurementDocument24 pagesLab 1 MeasurementRichard SerquinaNo ratings yet
- Measurements: General PhysicsDocument19 pagesMeasurements: General PhysicsRodel VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Measurement: The Language of ScienceDocument12 pagesMeasurement: The Language of ScienceJoel CaminoNo ratings yet
- Homework ChemDocument8 pagesHomework ChemCzarina Joy ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Ancient MeasurementDocument5 pagesAncient MeasurementCollene BorantesNo ratings yet
- Measurements: General PhysicsDocument19 pagesMeasurements: General Physicschrist MascoNo ratings yet
- Measurements NotesDocument19 pagesMeasurements NotesMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Measurements: General PhysicsDocument19 pagesMeasurements: General PhysicsRodel VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Their UnitsDocument20 pagesPhysical Quantities and Their Unitsjerico raquizaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1: 1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeDocument57 pagesScience Form 1: 1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeNITIASSWARENo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument30 pagesHeat and TemperatureBhuvaneswari BalaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About Science in This Big Fat BookDocument10 pagesEverything You Need To Know About Science in This Big Fat BookRosalin HuynhNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENTDocument1 pageMEASUREMENTL NarineNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Document13 pagesQ2 Mathematics 7 AS - Week 1Emerald Jane FielNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control and VentilationDocument46 pagesTemperature Control and VentilationjanaeNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding The Use of Measuring Tools. I) Measure LengthDocument4 pages1.4 Understanding The Use of Measuring Tools. I) Measure LengthHarry PanggaiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeDocument57 pages1.1 Understanding That Science Is Part of Everyday LifeGunalan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Measurements: General PhysicsDocument19 pagesMeasurements: General Physicsmaram asharfNo ratings yet
- Arc. NnojeDocument11 pagesArc. NnojeUGOCHI REJOICENo ratings yet
- REVIEWER in MathDocument40 pagesREVIEWER in MathPark Hyuna janeNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Tools Used For MeasurementDocument11 pagesDokumen - Tips Tools Used For Measurementmckhb2dw5nNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 11Document16 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 11megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Basic Measurement: Background HistoryDocument12 pagesBasic Measurement: Background HistoryalphadvirusNo ratings yet
- Basics of Sensors TransducersDocument32 pagesBasics of Sensors TransducersNandha KashwaranNo ratings yet
- Aug 12, 2015 History of MeasurementDocument2 pagesAug 12, 2015 History of MeasurementGlen Kristopher SenoNo ratings yet
- Matter and Measurement: Chapter 1BDocument6 pagesMatter and Measurement: Chapter 1BMarine LecomteNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument17 pagesMeasurementsrodel zafraNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint SS1 PhysicsDocument16 pagesPowerpoint SS1 PhysicsMARYQUEEN AMARACHUKWUNo ratings yet
- Thermometers Homework: Name: Omer Gorkem Das Class: 9/E Number: 1560Document8 pagesThermometers Homework: Name: Omer Gorkem Das Class: 9/E Number: 1560Yiğit Taylan DasNo ratings yet
- Concise Physics - Middle School For Class 9 (Examination 2019-2020) (S.S. Shome, R.P. Goyal)Document129 pagesConcise Physics - Middle School For Class 9 (Examination 2019-2020) (S.S. Shome, R.P. Goyal)Nguyễn Thành DuyNo ratings yet
- Units of Measuring Physical QuantitiesDocument9 pagesUnits of Measuring Physical QuantitiesDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Thermometer Homework 930lDocument5 pagesThermometer Homework 930lapi-404761117No ratings yet
- Measurements in ChemistryDocument66 pagesMeasurements in ChemistryKurt Bryan AnclaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesClass 7 Science Chapter 4 Revision NotesDaksh MeenaNo ratings yet
- All About MeasurementsDocument16 pagesAll About MeasurementsSudeepta Mondal100% (1)
- GoodDocument3 pagesGoodKavyaranjan “Ranju”No ratings yet
- Tle 7 Week 3Document4 pagesTle 7 Week 3DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Math 7 - Q4 - Las 4 RTPDocument4 pagesMath 7 - Q4 - Las 4 RTPDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Tle 7 Week 4Document4 pagesTle 7 Week 4DIANE BORROMEO,100% (1)
- ENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod8Document15 pagesENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod8DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Math 7 - Q4 - Las 3 RTPDocument4 pagesMath 7 - Q4 - Las 3 RTPDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- ENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod6Document22 pagesENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod6DIANE BORROMEO,100% (1)
- Curriculum Implementation Plan of Mathematics - Grade 7 4 QuarterDocument5 pagesCurriculum Implementation Plan of Mathematics - Grade 7 4 QuarterDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Final-Math-7-2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesFinal-Math-7-2nd QuarterDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- English 7: Be Active, Be A Hero Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 4Document27 pagesEnglish 7: Be Active, Be A Hero Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 4DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- English 7 q1 Mod7Document27 pagesEnglish 7 q1 Mod7DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- ENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod5Document25 pagesENGLISH 7 - Q1 - Mod5DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDocument29 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division Office of Balanga CityDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Arts 7 - Q3 - Mod1 - The Unique Identity of The SouthDocument34 pagesArts 7 - Q3 - Mod1 - The Unique Identity of The SouthDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Week 4 Science 2NDDocument3 pagesWeek 4 Science 2NDDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- 2 Quarter - Mathematics Summative Test I. Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. Write The Letter On The Space ProvidedDocument3 pages2 Quarter - Mathematics Summative Test I. Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. Write The Letter On The Space ProvidedDIANE BORROMEO,100% (1)
- MATH 7 - Q2 - Mod2Document18 pagesMATH 7 - Q2 - Mod2DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Arts 7 - Q3 - Mod3 - TheLandofPromiseArtsofMindanao - V1Document28 pagesArts 7 - Q3 - Mod3 - TheLandofPromiseArtsofMindanao - V1DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Arts 7 - Q3 - Module 4 - PreciousTreasuresoftheSouthDocument30 pagesArts 7 - Q3 - Module 4 - PreciousTreasuresoftheSouthDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Arts 7 - Q3 - Mod2 - Vestige of The Past Arts and Crafts of Mindanao ArchitectureDocument33 pagesArts 7 - Q3 - Mod2 - Vestige of The Past Arts and Crafts of Mindanao ArchitectureDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Arts 7 - Q3 - M6 - Carving Out Your Niche Architectures, Sculptures, and Everyday Objects of MindanaoDocument32 pagesArts 7 - Q3 - M6 - Carving Out Your Niche Architectures, Sculptures, and Everyday Objects of MindanaoDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Biomaterials Mechanical Properties PDFDocument308 pagesBiomaterials Mechanical Properties PDFleon155No ratings yet
- Data Sheet For SINAMICS Control Unit CU230P-2 PN: Ambient Conditions Electrical DataDocument1 pageData Sheet For SINAMICS Control Unit CU230P-2 PN: Ambient Conditions Electrical DataWilliam Jefferson RañadaNo ratings yet
- BT GBDocument29 pagesBT GBDerarghNo ratings yet
- Use Polarization Index Test To Determine Condition - Health of Motor InsulationDocument2 pagesUse Polarization Index Test To Determine Condition - Health of Motor InsulationGonzalo VargasNo ratings yet
- 2021 P2 Zone 22 QPDocument108 pages2021 P2 Zone 22 QPKayla DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Servo Hydraulic ValvesDocument6 pagesServo Hydraulic ValvesAli EhabNo ratings yet
- Circular PlatformDocument6 pagesCircular PlatformRamzi GameelNo ratings yet
- Planetary Physics (10 Points) : Theoretical Question 1 - SolutionDocument7 pagesPlanetary Physics (10 Points) : Theoretical Question 1 - SolutionErvan Maulana IlyasNo ratings yet
- User Manual DPS - ENDocument60 pagesUser Manual DPS - ENYiannis Steletaris100% (1)
- ASTM D627 07 - Standard Test Methods For Rubber Property-Heat Generation and Flexing Fatigue in CompressionDocument7 pagesASTM D627 07 - Standard Test Methods For Rubber Property-Heat Generation and Flexing Fatigue in CompressionAndre Rodriguez SpirimNo ratings yet
- MIT803 Assignment 11Document3 pagesMIT803 Assignment 11infoNo ratings yet
- Warner Electric: Bronco II 160 Series DC DrivesDocument24 pagesWarner Electric: Bronco II 160 Series DC DrivesIDIMAFRE SADECVNo ratings yet
- Millenium Permanent PackerDocument3 pagesMillenium Permanent PackerErnest DelacarcovaNo ratings yet
- On An Elliptic Equation of P Kirchhoff Type Via Variational MethodsDocument15 pagesOn An Elliptic Equation of P Kirchhoff Type Via Variational MethodsAdal ZaidNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Transient Numerical ModelDocument28 pagesIsothermal Transient Numerical ModelAditNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Fencing PostsDocument3 pagesPrestressed Concrete Fencing Postsexi johnsonNo ratings yet
- Statics Lab ReportDocument17 pagesStatics Lab ReportThokomelo T. WenaNo ratings yet
- PDA TestDocument11 pagesPDA TestGeorgeshua ZekonNo ratings yet
- Auxiblocker SBDocument1 pageAuxiblocker SBphasithNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailureDocument27 pagesTheories of FailureRaviShankarDuggirala88% (57)
- Linear Functional Analysis: Joan CerdàDocument26 pagesLinear Functional Analysis: Joan CerdàRonan GoisNo ratings yet
- Built-Up Battened Columns Under Lateral Cyclic Loading: Dipti R. Sahoo, Durgesh C. RaiDocument11 pagesBuilt-Up Battened Columns Under Lateral Cyclic Loading: Dipti R. Sahoo, Durgesh C. RaiKhaled Abdel SalamNo ratings yet
- EPM - 07 - 07S - Manual - ENTESDocument4 pagesEPM - 07 - 07S - Manual - ENTESAhmed Mohamed Kamal El-DeenNo ratings yet
- 3.4 4-148077 - Rev00 (Nomenclature Turbine)Document3 pages3.4 4-148077 - Rev00 (Nomenclature Turbine)youghmrassen0% (1)
- Project DescriptionDocument6 pagesProject DescriptionHarsh Garg 24601No ratings yet
- Introducing The: Ranger SystemDocument4 pagesIntroducing The: Ranger SystemSteven Ludeña GavinoNo ratings yet
- Conservation Unit Review 2021 KeyDocument9 pagesConservation Unit Review 2021 Keyoesmfpomsepof100% (1)
- What Is Keyphasor - How Does Keyphasor WorksDocument6 pagesWhat Is Keyphasor - How Does Keyphasor Workskali bangonNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lecture - 1-Introduction-TurbomachineDocument48 pagesVirtual Lecture - 1-Introduction-TurbomachineRukmani Devi100% (2)
- Properties, Benefits and Applications of Ventec Vt47 For PCB IndustryDocument11 pagesProperties, Benefits and Applications of Ventec Vt47 For PCB IndustryjackNo ratings yet