Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Good
Uploaded by
Kavyaranjan “Ranju”0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesOriginal Title
good
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesGood
Uploaded by
Kavyaranjan “Ranju”Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
SUBJECT: SCIENCE
CLASS VII
HEAT - Handout
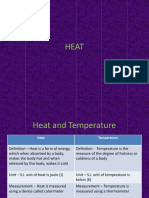
Heat: Heat is a form of energy which makes any object hot or cold. It can be measured in joules or
calories (CGS unit). S.I. unit of heat energy is joules.
The effects of heat on an object are
• Change in temperature of abody
• Change in shape of a body or dimension (thermalexpansion)
• Change of state ofmatter.
• Chemicalchange
Temperature: Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness. S.I. unit of temperature is kelvin. It
can also be measured in degree celsius (℃) and degree fahrenheit (℉).
• Celsius to fahrenheit : (℃ x (9/5)) + 32=℉
• Fahrenheit to celsius : ((℉ - 32) x (5/9)) =℃
• Celsius to kelvin: ℃ + 273 =K.
The device used to measure the temperature is called a thermometer.
They are mainly of two types: Clinical thermometer and Laboratory thermometer.
Clinical thermometer:
• It is made up of a glass tube of uniform thickness.
• The glass tube contains a bulb at one end which is filled withMercury.
• The Mercury level in the thermometer rises up in the thread-like portion of the thermometer
which therefore indicates the temperature of thebody.
• The level of the Mercury can be measured by reading the scale given on thethermometer.
• The temperature range in the thermometer starts from 35o C to 42oC.
• The clinical thermometer has a small sharp curve (kink) present near the bulb. This prevents
theMercury level from falling down on its own in thethermometer.
Precautions to be taken while taking reading in clinical thermometer.
• Wash the thermometer before and after usingit.
• Make sure the temperature of the thermometer is below 35℃ before taking thetemperature.
• Keep the thermometer straight in order to see the Mercury levelprecisely.
• It should always be held with care or it will break. You should not touch the bulb of the
thermometer atall.
Laboratory thermometer:
The laboratory thermometer is used to find out the temperature of the other objects such as water
rather than human body temperature. It can measure the temperature from -10℃ to 110℃.
Precautions to be taken while taking reading in Lab. Thermometer
• You should always follow the same precautions as that of the clinicalthermometer.
• You should always hold the laboratory thermometer in a straight upright position withouttilting
it.
• The bulb of the thermometer should never touch the surface of the container in which the
substance is kept.
• However, the bulb of the thermometer should be completely immersed in the substance so that
it covers the bulb from all the sides.
Maximum Minimum thermometer:
It is a thermometer used to measure the minimum and maximum temperature of the day by
weather forecasters.
Digital thermometer: It is sometimes difficult to handle a Mercury filled thermometer especially
when it breaks and the mercury falls out. However, nowadays digital thermometers are available
to use. This type of thermometer does not contain Mercury. It directly displays the correct
temperature on a display screen.
THE TRANSFER OF HEAT
The flow of heat always takes place from hot object to a coldobject.
There are three modes of transfer of heat.
1. Conduction: The process of flow of heat froma
hot object to a cold object, without the
movement of material as a whole is called
Conduction. Some objects can conduct heat
while others cannot.
Conductors: The objects that can allow heat
to flow through them are called conductors. For Example, metals such as copper and aluminum.
Insulators: The objects that do not allow the flow of heat through them are called insulators. For
Example, Wood and Plastic, jute,sawdust.
2. Convection:The transfer of heat in liquids and
gases, by the movement of the fluid itself is
called Convection. The molecules of the liquid
or gases that are near the source of the heat get
heated first. They become lighter due to the heat
and move upwards. The colder particles being
heavier take the place and this process continues
until the whole liquid or the gas gets heated.
That is why the area above the flame of a candle
always feels hot but the area on the sides of the
candle doesnot.
Sea Breeze
a. The wind blowing from the sea towards the land is called SeaBreeze.
b. During the daytime, the land in the coastal area gets heated due to the sun's radiation.
c. The sea also gets heated, however it takes more time to get heated up than the land.
d. Hence the air above the land gets heated faster than the air above the sea.
e. The hot air from the land rises above as it is lighter and the cool air from the sea being
heavier takes its place. This results in the seabreeze.
Land Breeze
f. The wind blowing from the land towards the sea is called the landbreeze.
g. During the night time, the land in the coastal area cools down faster than the sea. The air
above the sea is hotter than the air above the land.
h. Therefore, the air above the sea rises up and the air from the land being cool flows
towards the sea. This results in the landbreeze.
3. Radiation:The process of transfer of heat in the form of waves without
any material medium is called radiation. For Example, the sun's heat
reaches the Earth’s surface through radiation. Every hot object radiates
some heat into the environment. Hence, many times an object gets heated
just by being near to a hot object.
You might also like
- P6 Man and Impact On Environment NotesDocument13 pagesP6 Man and Impact On Environment NotesJohn John Appleseed50% (2)
- Heat and Temperature Grade 8Document25 pagesHeat and Temperature Grade 8Jc Steve Steven100% (4)
- Food Grade Hydrogen Peroxide - The TruthDocument85 pagesFood Grade Hydrogen Peroxide - The TruthTUartist98% (52)
- NotesDocument146 pagesNotesМарко ШилободNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On HeatDocument4 pagesRevision Notes On HeathannahNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument30 pagesHeat and TemperatureBhuvaneswari BalaNo ratings yet
- Unit of Heat:: ThermometerDocument5 pagesUnit of Heat:: Thermometersmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 HeatDocument2 pagesChapter - 4 HeatDaya SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter4class7th 200622090115 2Document22 pagesChapter4class7th 200622090115 2aryan bhanssaliNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument18 pagesHEATArtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument38 pagesChapter 4 Heatsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4: Unit of HeatDocument16 pagesChapter-4: Unit of HeatRajeevSangamNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument60 pagesHEATxy xyNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control and VentilationDocument46 pagesTemperature Control and VentilationjanaeNo ratings yet
- LO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesLO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- CL-7 CH-4 NotesDocument2 pagesCL-7 CH-4 NotesYograj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Study Material - VII - Heat (Part 1)Document4 pagesStudy Material - VII - Heat (Part 1)Suvam DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Heat: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument2 pagesChapter - 4 Heat: Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDevkinandan PunethaNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control & VentilationDocument30 pagesTemperature Control & VentilationAssasia HydeNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Chapter 4: (Physics) HEATDocument17 pagesClass 7 Science Chapter 4: (Physics) HEATRitesh Gehani100% (1)
- Grade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDocument7 pagesGrade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- Arihant - Science - Bio - Heat 7Document24 pagesArihant - Science - Bio - Heat 7Keshav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Heat UploadDocument94 pagesHeat UploadRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument38 pagesTemperature and Heatmistymint.crewneticNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument125 pagesHeat and TemperatureNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Form FourDocument74 pagesForm FourIdriss DjatsaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Hot and Cold: Taste TouchDocument4 pages4.1 Hot and Cold: Taste TouchGirija KushwahNo ratings yet
- Basics of InfraredDocument58 pagesBasics of InfraredConstantyn_FrederikNo ratings yet
- Heat: - : Types of ThermometersDocument3 pagesHeat: - : Types of ThermometersSweet HomeNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Heat NotesDocument3 pagesClass 7 - Heat NotesAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument163 pagesHeatSrMoonSengChoo100% (1)
- Jsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669Document6 pagesJsunil: Jsunil Tutorial, Samastipur PH: 9835859669ravilullaNo ratings yet
- L2b The AtmosphereDocument34 pagesL2b The AtmosphereZakwan QlateNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Thermo:Heat, Dynamics: Power, MotionDocument43 pagesThermodynamics: Thermo:Heat, Dynamics: Power, MotionAl MahmudNo ratings yet
- Resource 20230426185811 Doc-20230426-Wa0043.Document5 pagesResource 20230426185811 Doc-20230426-Wa0043.ATHARVA SINGH BAGHELNo ratings yet
- Kavita - Int Sci Heat TransferDocument10 pagesKavita - Int Sci Heat Transfer27h4fbvsy8No ratings yet
- Class 7 PPT - Heat and TemperatureDocument45 pagesClass 7 PPT - Heat and TemperatureNAMAN SRIVASTAVA100% (1)
- Ch.5.Heat and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesCh.5.Heat and Its Effectsrishika solankiNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Module 1 2021Document160 pagesPhysics 2 Module 1 2021Yiestene PaloNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- HEAT Class 7Document50 pagesHEAT Class 7Raynaah100% (1)
- Heat & Temprature: by Syeda Shafaq Batool & Rabia TufailDocument20 pagesHeat & Temprature: by Syeda Shafaq Batool & Rabia TufailhelperforeuNo ratings yet
- Heat Aasignment Part 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesHeat Aasignment Part 2 SolutionSagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Heat and TemperatureDocument7 pagesChapter 9 - Heat and TemperatureLesther James CastroNo ratings yet
- Hat and Its EffectsDocument45 pagesHat and Its EffectsFurious GamingNo ratings yet
- Phy Ch5Document7 pagesPhy Ch5vivanhirani11No ratings yet
- Nature of Heat & Temperature 2022Document22 pagesNature of Heat & Temperature 2022Gabriella SteeleNo ratings yet
- Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument56 pagesHeat and ThermodynamicsMd. Sayeed HasanNo ratings yet
- Introductory Thermal Physics Worksheets and SolutionsDocument30 pagesIntroductory Thermal Physics Worksheets and SolutionsLetmiDwiridalNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument53 pagesHeat and Temperaturegeorgy shibuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document43 pagesLecture 3Farhan Mukhtiar YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesClass 7 Science Chapter 4 Revision NotesDaksh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Measurment of Temperature - New1Document12 pagesMeasurment of Temperature - New1Shweta ShelkeNo ratings yet
- Science Class7 Heat RevisionNotesDocument9 pagesScience Class7 Heat RevisionNotesTestEmailForScribd TestEmailForScribdNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesChapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsmesfinNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringDharmendra BelwanshiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument27 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsCasey Louisse GarciaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature by ArchieGBDocument43 pagesHeat and Temperature by ArchieGBArchiemedez BatanganNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimDocument10 pagesFire Protection AND Arson Investigation: Mark Lester E. Caranay, RcrimGemel John CatapNo ratings yet
- Temperature-WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesTemperature-WPS OfficeVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Temp 1Document36 pagesTemp 1Lilian MumoNo ratings yet
- STD 1622 BDocument64 pagesSTD 1622 BDynamicSystemsIncNo ratings yet
- Eating Less Meat Won't Save The PlanetDocument9 pagesEating Less Meat Won't Save The PlanetJoan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Airpollution 111129090637 Phpapp02Document24 pagesAirpollution 111129090637 Phpapp02cjsamarooNo ratings yet
- Topic: Composition of Clean Air Sub-Topic:: NSC: 2 LessonsDocument3 pagesTopic: Composition of Clean Air Sub-Topic:: NSC: 2 LessonsMonique NelsonNo ratings yet
- Plasma Orbital Expansion Electrons Water FrequencyDocument140 pagesPlasma Orbital Expansion Electrons Water FrequencyVincent J. Cataldi100% (1)
- Deodorizer DetailsDocument19 pagesDeodorizer DetailsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.earth Science-WPS OfficeDocument2 pages1.earth Science-WPS OfficeIvy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Earth Astronomical Object Experiment, Ariny Amos (Astronomer)Document1,900 pagesEarth Astronomical Object Experiment, Ariny Amos (Astronomer)Dr. Amos ArinyNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 7 4th WeekDocument7 pagesDLL Science 7 4th WeekMary Angelie GreciaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Climate: 1.latitude 2.altitude 3.distance From The Sea 4.ocean Currents 5.land TopographyDocument54 pagesFactors Affecting Climate: 1.latitude 2.altitude 3.distance From The Sea 4.ocean Currents 5.land TopographyMeljean Kalaw CastilloNo ratings yet
- 4th International Conference On Thermal Equipment, Renewable Energy and Rural Development PDFDocument500 pages4th International Conference On Thermal Equipment, Renewable Energy and Rural Development PDFMittapalli SaikiranNo ratings yet
- 2008 - DESONIE - Climate - Causes and Effects of Climate ChangeDocument217 pages2008 - DESONIE - Climate - Causes and Effects of Climate ChangeGeraldo Antônio100% (1)
- Paket 4Document6 pagesPaket 4Lovis ShalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness & Risk Reduction (4 Quarter Reviewer) : Southwest MonsoonDocument4 pagesDisaster Readiness & Risk Reduction (4 Quarter Reviewer) : Southwest MonsoonFeiweibei SongNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS OF WEATHER CLIMATE Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1Document23 pagesELEMENTS OF WEATHER CLIMATE Quarter 4 Week 3 Day 1Millie LagonillaNo ratings yet
- Forest Problems and Solutions To ReverseDocument2 pagesForest Problems and Solutions To ReverseLienrey MarquitaNo ratings yet
- DumadiDocument29 pagesDumadijesitasilfianaNo ratings yet
- New Challenges To Human Adaptation and Social ChangeDocument11 pagesNew Challenges To Human Adaptation and Social Changejoselitosalmasan221No ratings yet
- Ged Earth Science Test 1bDocument12 pagesGed Earth Science Test 1bapi-301605346No ratings yet
- Pipe Refresher CourseDocument5 pagesPipe Refresher CourseBanilo BanilaNo ratings yet
- BAY of Bengal CyclonesDocument105 pagesBAY of Bengal CyclonesGopesh KashyapNo ratings yet
- Mapeh - Part 4Document13 pagesMapeh - Part 4Lergen B. AguilarNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ TỔNG HỢP SỐ 6, 7Document28 pagesĐỀ TỔNG HỢP SỐ 6, 7Đing Queng VingNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceJoyce Dao-asen100% (1)
- HOME Work Heat Transfer1 50 2Document3 pagesHOME Work Heat Transfer1 50 2Karl Angelo PacolorNo ratings yet
- Furnace AC Example PDFDocument5 pagesFurnace AC Example PDFhanafiNo ratings yet
- Science STage 8 Answers WorkbookDocument15 pagesScience STage 8 Answers WorkbookVanished Man75% (4)