Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leukemia
Uploaded by
Angel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pagesLeukemia is a type of blood cancer that develops in the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It occurs when blood cells acquire genetic mutations that cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably, crowding out healthy blood cells. There are four main types of leukemia - acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and chronic myelogenous leukemia. While the cause is unknown, risk factors include previous cancer treatment, genetic disorders, chemical exposure, and family history. Symptoms can include fatigue, bruising, infections, and bone pain. Treatment options seek to destroy leukemia cells and restore normal blood cell production but currently there is no cure.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLeukemia is a type of blood cancer that develops in the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It occurs when blood cells acquire genetic mutations that cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably, crowding out healthy blood cells. There are four main types of leukemia - acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and chronic myelogenous leukemia. While the cause is unknown, risk factors include previous cancer treatment, genetic disorders, chemical exposure, and family history. Symptoms can include fatigue, bruising, infections, and bone pain. Treatment options seek to destroy leukemia cells and restore normal blood cell production but currently there is no cure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pagesLeukemia
Uploaded by
AngelLeukemia is a type of blood cancer that develops in the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It occurs when blood cells acquire genetic mutations that cause them to grow and divide uncontrollably, crowding out healthy blood cells. There are four main types of leukemia - acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and chronic myelogenous leukemia. While the cause is unknown, risk factors include previous cancer treatment, genetic disorders, chemical exposure, and family history. Symptoms can include fatigue, bruising, infections, and bone pain. Treatment options seek to destroy leukemia cells and restore normal blood cell production but currently there is no cure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
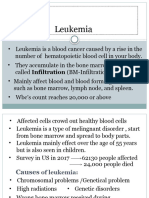
LEUKEMIA
What disorder is leukemia?
• Leukemia is a genetic disease, though in a lot of cases, it’s not genetic.
• It’s a type of blood cancer that develops in lymphoid cells in the bone marrow or
lymphatic system
• It commonly affects the white blood cells making it harder for the body’s immune
system to fight infection
What causes leukemia?
• Scientist don’t know what exactly causes leukemia.
• They believe it develops due to a combination of environmental and genetic
factors
How does it form?
• When some blood cells acquire mutations in their genetic material or DNA.
• The DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, they tell
the cell to grow at a set rate and die at a set time. With leukemia, the mutations
tell the blood cells to continue growing and dividing.
• The blood cell production the goes out of control. The abnormal cells over time
begin to crowd out the healthy blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to less
healthy white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets that cause the signs and
symptoms of leukemia.
Types of leukemia
• ALL- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
• AML- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
• CLL- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
• CML- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
• Acute leukemias are more aggressive.
• Chronic leukemias tend to develop more slowly.
Risk factors
• The following may increase the risk of someone getting leukemia:
• Previous cancer treatment
• Genetic disorders
• Exposure to certain chemicals
• Family history of leukemia
• Smoking
• Human T-cell leukemia virus type I
Symptoms of leukemia
• Loss of appetite
• Unexplained weight loss
• Swollen lymph nodes
• Excessive tiredness and weakness
• Easy bleeding, bruising and nosebleed
• Fever, chills, body aches and other flu-like symptoms
• Repeated infections
• Bone pain or tenderness
• Tiny red spots in skin
When to visit a doctor
• Make an appointment if you have persistent signs or symptoms
• People may overlook symptoms since they may resemble symptoms of the flu or
other common illnesses.
• It can sometimes be discovered during blood tests when testing for other
conditions
Treatment methods
• There is no cure for leukemia but there are ranges of advanced treatments which
are:
• Chemotherapy
• Radiation therapy
• Bone marrow transplants
• Monoclonal antibody therapy
• Clinical trials
• Immunotherapy
You might also like
- Surviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsFrom EverandSurviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsNo ratings yet
- Leukemia MlaDocument3 pagesLeukemia Mlamayliaung4No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument23 pagesLeukemiaMrnj MelorinNo ratings yet
- Leukocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLeukocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Lymphomas and LeukemiasDocument27 pagesLymphomas and LeukemiasgraceNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIADocument20 pagesLEUKEMIAHafsaNo ratings yet
- Leukemia PresentationDocument19 pagesLeukemia Presentationayshu4377No ratings yet
- What Is LeukemiaDocument11 pagesWhat Is LeukemiaNazneen RagasaNo ratings yet
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionDocument6 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Hemogram ADocument62 pagesHemogram AInnister AchampashNo ratings yet
- LEUKAEMIADocument40 pagesLEUKAEMIADoc HamsNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument23 pagesLeukemiaAli Ismail86% (7)
- LeukemiaDocument13 pagesLeukemiaWasan JalalNo ratings yet
- Leukimia Dan ThalasemiaDocument39 pagesLeukimia Dan ThalasemialeilaNo ratings yet
- Leukimia: Ns. Ayu Nanda Lestari, M.KepDocument16 pagesLeukimia: Ns. Ayu Nanda Lestari, M.KepTata BenyNo ratings yet
- Askep LeukemiaDocument25 pagesAskep LeukemiaMyLucky DecodeNo ratings yet
- Blood Diseases ProjectDocument31 pagesBlood Diseases ProjectRomyn MoazNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument34 pagesLeukemiaAnnie Lou AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders - LeukemiaDocument24 pagesBlood Disorders - LeukemiaanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ahmed Fawzi Elshaieb Professor of PathologyDocument163 pagesDr. Ahmed Fawzi Elshaieb Professor of PathologyashrafarafaNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Leukemi ADocument11 pagesGroup 5: Leukemi ARALPH ELVIN MACANLALAYNo ratings yet
- WBC Disorder Chap#4Document41 pagesWBC Disorder Chap#4MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Name: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Document7 pagesName: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Bunmi OluwatosinNo ratings yet
- Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument6 pagesChronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaJhannNo ratings yet
- Symtomps of Illness and DiseaseDocument4 pagesSymtomps of Illness and DiseaseSilvana SabillaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument3 pagesLeukemiacindya13No ratings yet
- What Is LeukemiaDocument13 pagesWhat Is Leukemiazaid505No ratings yet
- Care of Patients With LeukemiaDocument9 pagesCare of Patients With LeukemiaJumar ValdezNo ratings yet
- Leukemia 2018 For GNM 2ndDocument36 pagesLeukemia 2018 For GNM 2ndshapan biswaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument37 pagesLeukemiaVikkineshwaran Siva SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia: Symptoms & Causes Diagnosis & Treatment Doctors & Departments Care at Mayo Clinic PrintDocument3 pagesAcute Myelogenous Leukemia: Symptoms & Causes Diagnosis & Treatment Doctors & Departments Care at Mayo Clinic PrintAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Teks LeukemiaDocument6 pagesTeks LeukemiaDewi FOrtyunaNo ratings yet
- WBC DisordersDocument32 pagesWBC Disordersbpt295% (19)
- Leukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleDocument27 pagesLeukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleKrystal PulmonesNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument4 pagesLeukemiaMuhammad SaYar ShahNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Group 4 - 9 - Einstein Abilene Reglos Danica Cabalmarian Isabel Matampac JP Deveraturda James Guillen PenaflorDocument49 pagesLeukemia: Group 4 - 9 - Einstein Abilene Reglos Danica Cabalmarian Isabel Matampac JP Deveraturda James Guillen PenaflorTheSAmeNonsenseNo ratings yet
- Hematological DisordersDocument19 pagesHematological DisordersEZHIL NNo ratings yet
- Hemafinals 02Document27 pagesHemafinals 02Clarence SantosNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA ProjectDocument17 pagesLEUKEMIA ProjectNayak Alok Ranjan100% (1)
- Leukemia Types of Leukemia: Francisco, Frances Lorraine R. Hematology BSMT / Eac-C Sir Carlo Ace de BelenDocument4 pagesLeukemia Types of Leukemia: Francisco, Frances Lorraine R. Hematology BSMT / Eac-C Sir Carlo Ace de BelenpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Myeloproliferative Diseases: H.A. Mwakyoma, MDDocument32 pagesMyeloproliferative Diseases: H.A. Mwakyoma, MDHadi AdamNo ratings yet
- Leukemia - PPTX 2Document9 pagesLeukemia - PPTX 2Sherly RositaNo ratings yet
- Bio CompleteDocument20 pagesBio Completeeshani0706No ratings yet
- Chronic Leukemia: Carlos Alfredo Cedeño RodríguezDocument24 pagesChronic Leukemia: Carlos Alfredo Cedeño RodríguezCarlos CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Leukemia (Is A Type ofDocument5 pagesLeukemia: Leukemia (Is A Type ofFiru LgsNo ratings yet
- Leukemia ReportDocument5 pagesLeukemia ReportCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Acute Leukemia: Eiyas Al Akiel Group 2Document13 pagesAcute Leukemia: Eiyas Al Akiel Group 2raph faithNo ratings yet
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionDocument3 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Hemopoietic SystemDocument28 pagesHemopoietic Systemyfzzhgv676No ratings yet
- L14 Medicine Leukemia (Word)Document6 pagesL14 Medicine Leukemia (Word)Eslam Ibrahiem IbrahiemNo ratings yet
- Subject: Leukemia Professor: Ia Marashkhia Researcher: Alireza Farhadiyeh (1701940)Document14 pagesSubject: Leukemia Professor: Ia Marashkhia Researcher: Alireza Farhadiyeh (1701940)alirezaNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument16 pagesAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaBeta SharonNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument8 pagesLeukemiaIrmaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument5 pagesLeukemiaviveka_vgo182471100% (1)
- ACUTE LeukemiaDocument28 pagesACUTE LeukemiaParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Kelainan Di Rongga Mulut Karena Gangguan Leukosit (Leukemia)Document60 pagesKelainan Di Rongga Mulut Karena Gangguan Leukosit (Leukemia)Justin Michal DassNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Holman Ricaurte Rey Miguel Angel Bolivar Jose Manuel CordobaDocument7 pagesLeukemia: Holman Ricaurte Rey Miguel Angel Bolivar Jose Manuel CordobaMiGue BolivarNo ratings yet
- WBC DisordersDocument45 pagesWBC DisordersyalahopaNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Disorders: DR Josephine Ojoo MBCHB FRCP CCST (Resp) Dip Hiv Med Senior Lecturer Maseno UniversityDocument70 pagesConnective Tissue Disorders: DR Josephine Ojoo MBCHB FRCP CCST (Resp) Dip Hiv Med Senior Lecturer Maseno UniversityMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet