Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sts Modern Times Report
Uploaded by
Kay Abawag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesSts Modern Times Report
Uploaded by
Kay AbawagCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
HISTORICAL ANTECEDENTS IN
WHICH SOCIAL CONSIDERATIONS
CHANGED THE COURSE OF
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
MODERN TIMES
MODERN TIMES
During the nineteenth century, the world’s
population demands more goods to produce
at a faster rate. People needed efficient means
of transportation to trade more goods to a larger
and farther distance. The needs of machine. The
needs of faster and easier way to communicate.
Because of these kind of neediness various of
industries takes place.
The modern world history, the modern era or the
modern period is the global, linear, historical-
geographical approach to the time frame that comes
post the classical history.
DIVISION OF MODERN
HISTORY
The early modern period, the late modern
period and the contemporary history.
EARLY MODERN PERIOD
The early modern period began approximately at the
beginning of the 16th century. In this period, the major
historical milestones include the Age of Discovery, the
European Renaissance as well as the Protestant
Reformation.
Age of Discovery
Also called the age of exploration began in
the 1400s and continued through the 1600s. It
was a period of time when the European
nations began exploring the world. They
discovered new routes to India, much of the
Far East, and the Americas.
European Renaissance
The Renaissance was a fervent period of European
cultural, artistic, political, and economic “rebirth”
following the Middle Ages.
Generally described as taking place from the 14th
century to the 17th century, the Renaissance promoted
the rediscovery of classical philosophy, literature and
art.
The Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a religious reform
movement that swept through Europe in the 1500s.
It resulted in the creation of a branch of Christianity
called Protestantism, a name used collectively to
refer to the many religious groups that separated
from the Roman Catholic due to differences in
doctrine.
LATE MODERN PERIOD
On the other hand, the late modern period started in
the mid of 18th century.
The American Revolution, The French Revolution,
The Great Divergence, The Industrial Revolution
and The Russian Revolution happened in this period.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION
The American Revolution was an epic political and
military struggle waged between 1765 and 1783
when 13 of Britain's North American colonies
rejected its imperial rule. The protest began in
opposition to taxes levied without colonial
representation by the British monarchy and
Parliament.
FRENCH REVOLUTION
The French revolution was a watershed event in
world history that began in 1789 and ended in the
late 1790s with the ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte.
During this period, French citizens radically altered
their political landscape, uprooting centuries-old
institutions such as the monarchy and the feudal
system.
THE GREAT DIVERGENCE
Historians sometimes refer to the Industrial
Revolution as the “Great Divergence” where
suddenly the energy bonanza of industry catapulted
Europe and North America ahead of most of the rest
of the world for much of the nineteenth century and
the early twentieth century.
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
The Industrial Revolution transformed economies
that had been based on agriculture and handicrafts
into economies based on large-scale industry,
mechanized manufacturing, and the factory
system. New machines, new power sources, and
new ways of organizing work made existing
industries more productive and efficient.
RUSSIAN REVOLUTION
The Russian Revolution took place in 1917, during
the final phase of World War I. It removed Russia
from the war and brought about the transformation of
the Russian Empire into the Union of Soviet Socialist
Republics (USSR), replacing Russia's traditional
monarchy with the world's first Communist state.
CONTEMPORARY HISTORY
The contemporary history includes the span of
historical events starting from 1945. These events are
most relevant to present time and scenario. Many
historians describe the early modern period as the
time frame between 1500 and 1800.
This period mainly follows the late middle ages
period. Further, it is marked by the initial European
Colonies, beginnings of recognizable nation-states as
well as the rise of strong centralized governments.
INVENTIONS DURING
THE MODERN TIMES
PASTEURIZATION
As populations rises, the people were able to develop better
means of production to meet their needs. But food
preservation and food safety became an issue to them.
A French Biologist, microbiologist, and chemist named
Louise Pasture found a way to solve the issue. He invented
the process of heating dairy products to kill the harmful
bacteria that allow the food to spoil faster also called as
pasteurization. Through this process, milk can be stored
and consumed for a longer period.
PASTEURIZATION PROCESS
PETROLEUM REFINERY
Samuel M. Kier was able to invent kerosene by refining
petroleum. Kerosene was later on referred to as the
“illuminating oil” because it was used at first to provide
lighting to homes. after some time, it was applied for
heating purpose. Nowadays, kerosene is still present as still
used by many people for powering automobiles, factories,
and power plants, among others.
TELEPHONE
Alexander Graham Bell was the inventor of
telephone and it was one of the most important
inventions during those times. He thought of
inventing telephone due to the lack and very limited
kind of communication and its very expensive just to
communicate. But nowadays, telephones are one of
our necessities for faster and more stable technology
for us to use for communication.
CALCULATOR
The creation of the modernized calculator pave the
way not only in terms of calculating arithmetic easier
but also to develop more complex processing
machines just like what we are using now.
“Calculating clock” is composed of a multiplying
device, a mechanism for recording intermediate
results, and a 6- digit decimal adding device invented
by Wilhelm Schickard.
You might also like
- Historical Development of TourismDocument3 pagesHistorical Development of TourismAnthony B Pagdanganan0% (1)
- Development of Sociology in The WorldDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Sociology in The WorldJan Alexa Catacutan0% (1)
- CausesDocument4 pagesCausesDurgesh Nandan SrivastavNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument6 pagesSummaryLea Mae AmbaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - History and Theories of GlobalizationDocument40 pagesModule 2 - History and Theories of GlobalizationJeprox MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Revolution and the Industrial RevolutionDocument36 pagesThe Scientific Revolution and the Industrial RevolutiontsangNo ratings yet
- Modernity: Describe and Argue For The Following 1. Dark Ages, Define Characteristics of Dark Ages? AnswerDocument3 pagesModernity: Describe and Argue For The Following 1. Dark Ages, Define Characteristics of Dark Ages? AnswerSidramushtaq IoBMNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution 2ndDocument13 pagesIndustrial Revolution 2ndTOP4UNo ratings yet
- Ch-I - Changing TimeDocument4 pagesCh-I - Changing TimedebdulaldamNo ratings yet
- Emergence of SociologyDocument11 pagesEmergence of SociologyAbhinandan SenNo ratings yet
- (Group 1) World HistoryDocument22 pages(Group 1) World HistoryBarbie Kyle DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Changing The WorldDocument38 pagesChanging The WorldGlaiza AdelleyNo ratings yet
- Local Media5689481733712593790Document9 pagesLocal Media5689481733712593790Lory Grace TorresNo ratings yet
- Sociology's Emergence in Industrial EuropeDocument19 pagesSociology's Emergence in Industrial Europeदिव्य सिंहNo ratings yet
- University of The PunjabDocument18 pagesUniversity of The PunjabShoukat UllahNo ratings yet
- IP University's Industrial Revolution AssignmentDocument18 pagesIP University's Industrial Revolution AssignmentShoukat UllahNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument10 pagesIndexDebapriyo RakshitNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Enlightenment: Key Ideas and FiguresDocument6 pagesIntroduction to the Enlightenment: Key Ideas and FiguresNitishree BhansaliNo ratings yet
- By: Roy Joe Pete L OpenianoDocument34 pagesBy: Roy Joe Pete L Openianojoepete91No ratings yet
- Contemporary-WorldDocument4 pagesContemporary-WorldWattypadie GachANo ratings yet
- The Development of Human Civilization Over Tens of Thousands of YearsDocument1 pageThe Development of Human Civilization Over Tens of Thousands of YearsAnna PrzybyłowskaNo ratings yet
- Development of Industrial SociologyDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Industrial Sociologyamitsharma1882006No ratings yet
- Rizl 111 Unit 2 The Philippines in The 19TH Century As Rizal's ContextDocument10 pagesRizl 111 Unit 2 The Philippines in The 19TH Century As Rizal's ContextLeoterio LacapNo ratings yet
- The Black Death: One of History's Deadliest PandemicsDocument8 pagesThe Black Death: One of History's Deadliest PandemicsSudeep SinghalNo ratings yet
- Mbm-201 Self StudyDocument21 pagesMbm-201 Self StudyAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION and NATIONS NATIONALISMDocument4 pagesTHE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION and NATIONS NATIONALISMvalentina hernandezNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 18th Crisis Old Regime Enlightenment To PRINTDocument5 pagesUNIT 1 18th Crisis Old Regime Enlightenment To PRINTck8h74w8hbNo ratings yet
- Pre Historic PeDocument5 pagesPre Historic PeJianal GambaoNo ratings yet
- OLFU For RIZAL111 The Philippines in The 19th Century As Rizal's Context Age of Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution Study Guide Discussion PaperDocument10 pagesOLFU For RIZAL111 The Philippines in The 19th Century As Rizal's Context Age of Enlightenment and Industrial Revolution Study Guide Discussion PaperJANNA RAZONNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - RizalDocument12 pagesChapter I - RizalLourdes ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Yr9 HISE Exam NotesDocument45 pagesYr9 HISE Exam NotesSinethma KarunatilakeNo ratings yet
- Karachi University Course on the Industrial RevolutionDocument11 pagesKarachi University Course on the Industrial RevolutionSyed Mohsin Mehdi TaqviNo ratings yet
- By: Roy Joe Pete L OpenianoDocument34 pagesBy: Roy Joe Pete L Openianojoepete91No ratings yet
- History of The WorldDocument1 pageHistory of The Worldmahathi bokkasamNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevDocument16 pagesIndustrial RevriomjNo ratings yet
- Modern PeriodDocument10 pagesModern PeriodGilianne Kathryn Layco Gantuangco-CabilingNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World Topic 2Document9 pagesContemporary World Topic 2Arantza Ramirez BarradasNo ratings yet
- The Birth of Now: The Cause and Effect of the Greatest Change in HistoryFrom EverandThe Birth of Now: The Cause and Effect of the Greatest Change in HistoryNo ratings yet
- Western Civilization - TimeMapsDocument1 pageWestern Civilization - TimeMapsmunif hasanNo ratings yet
- 3.medieval Ages Philippine InventionsDocument27 pages3.medieval Ages Philippine Inventionskyla santosNo ratings yet
- Power over Peoples: Technology, Environments, and Western Imperialism, 1400 to the PresentFrom EverandPower over Peoples: Technology, Environments, and Western Imperialism, 1400 to the PresentNo ratings yet
- The Philippines in the 19th Century: Rizal's ContextDocument10 pagesThe Philippines in the 19th Century: Rizal's ContextRoweee DrNo ratings yet
- Strayer CH 17 Strayer Ways of The WorldDocument54 pagesStrayer CH 17 Strayer Ways of The WorldJulia AbreuNo ratings yet
- Changing The WorldDocument5 pagesChanging The Worldleher shahNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument26 pagesEnglish ProjectDarius FloreaNo ratings yet
- History HandoutDocument259 pagesHistory HandoutKiss Csanád100% (1)
- Modernity, Sociology Emergence in Europe Due to Social ChangesDocument5 pagesModernity, Sociology Emergence in Europe Due to Social ChangesakshayNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers about: World HistoryFrom EverandQuestions and Answers about: World HistoryRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Assignment 1 MMW Section A TAYYAB L1S17BBAM0024 Q1: What Is Enlightenment ?Document2 pagesAssignment 1 MMW Section A TAYYAB L1S17BBAM0024 Q1: What Is Enlightenment ?tayyab malikNo ratings yet
- MODERN ERA KEY CHANGESDocument1 pageMODERN ERA KEY CHANGESdailydoseoflawNo ratings yet
- (Old NCERT World History Ch7) Industrial Revolution, Capitalism, Their Effect On Society, Rise of Trade Unions - Socialism Mrunal PDFDocument12 pages(Old NCERT World History Ch7) Industrial Revolution, Capitalism, Their Effect On Society, Rise of Trade Unions - Socialism Mrunal PDFDevesh Jhariya0% (1)
- Modern World TimelineDocument3 pagesModern World Timelineapi-327452561No ratings yet
- Introductio 2Document5 pagesIntroductio 2Chinedu ChikezieNo ratings yet
- Hist8 - 1modern World 2industrial RevolutionDocument5 pagesHist8 - 1modern World 2industrial RevolutionBFF ForeverNo ratings yet
- The Renaissance and Scientific Revolution 1450-1650Document5 pagesThe Renaissance and Scientific Revolution 1450-1650Ezekia Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 129-Allied - I Social Hostroy of England - 1. The RenaissanceDocument6 pages129-Allied - I Social Hostroy of England - 1. The RenaissanceR.VijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- AdeelQureshi - 1701 - 18669 - 2 - L10 Modern PhilosophersDocument19 pagesAdeelQureshi - 1701 - 18669 - 2 - L10 Modern PhilosophersAmmad AktharNo ratings yet
- Modernization TheoryDocument2 pagesModernization TheoryaltheaNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument12 pagesIndustrial Revolutionemowinter33No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Career DevelopmentDocument4 pagesMODULE 3 - Career DevelopmentKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument3 pagesStatsKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Mobile Payments for Local Business EdgeDocument3 pagesLeveraging Mobile Payments for Local Business EdgeKay Abawag100% (1)
- Dadaab Refugee Camps Field ResearchDocument2 pagesDadaab Refugee Camps Field ResearchKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet Engages YouthDocument1 pageActivity Worksheet Engages YouthKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Learning Task (Social Problem Solving)Document1 pageLearning Task (Social Problem Solving)Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- OCLAB Exercise 5Document5 pagesOCLAB Exercise 5Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- CSU Math Assignment on Measures of Central TendencyDocument3 pagesCSU Math Assignment on Measures of Central TendencyKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- PeTa2-3 DataDocument4 pagesPeTa2-3 DataKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- NIBRA Research Priorities 2022-2028Document9 pagesNIBRA Research Priorities 2022-2028Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- The Philippine S&T AgendaDocument3 pagesThe Philippine S&T AgendaKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Finals - Activity 4Document1 pageFinals - Activity 4Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer G4Document25 pagesFertilizer G4Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- G1 Theory of SelfDocument15 pagesG1 Theory of SelfKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- UTS Philosophical PerspectiveDocument4 pagesUTS Philosophical PerspectiveKay AbawagNo ratings yet
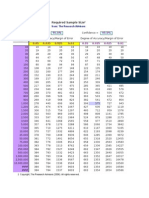
- Required Sample Size: From: The Research AdvisorsDocument3 pagesRequired Sample Size: From: The Research AdvisorsAbhishek Sharma100% (1)
- Essay ContestDocument3 pagesEssay ContestKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument65 pagesResonanceKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Uts Midterms ReviewerDocument29 pagesUts Midterms ReviewerKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument1 pageCONCLUSIONKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- SoclitDocument1 pageSoclitKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- STS ReportDocument10 pagesSTS ReportKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Manuscript TeamCDocument47 pagesManuscript TeamCKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- UTS ReportingDocument1 pageUTS ReportingKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Parties to a Contract CapacityDocument17 pagesParties to a Contract CapacityKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Ethics Chapter on Human ActsDocument26 pagesEthics Chapter on Human ActsKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Act1 AbawagDocument1 pageOrg Chem Act1 AbawagKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Ethics Chapter Explains Socratic Method and Importance of Studying MoralsDocument8 pagesEthics Chapter Explains Socratic Method and Importance of Studying MoralsJasmin SauraNo ratings yet
- Ancient Times ReviewerDocument6 pagesAncient Times ReviewerKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Problems of Peace - Guglielmo Ferrero (1919)Document304 pagesProblems of Peace - Guglielmo Ferrero (1919)WaterwindNo ratings yet
- Is Free News Essential For An Educated SocietyDocument4 pagesIs Free News Essential For An Educated Societyakio haruNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Managerial Accounting 10th EditionDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Managerial Accounting 10th Editionafternoonoutshootukt4100% (44)
- The French Revolution and Napoleon TimelineDocument42 pagesThe French Revolution and Napoleon TimelineJason Mark De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- MARITimes Vol 32 2 R2 PDFDocument28 pagesMARITimes Vol 32 2 R2 PDFBernewsAdminNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Worksheet Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument10 pagesFrench Revolution Worksheet Chapter 1 QuestionsAtique96% (24)
- The Atlantic Revolutions: An Era of RevolutionsDocument3 pagesThe Atlantic Revolutions: An Era of RevolutionsPhoenix 524No ratings yet
- Mrunal HistoryDocument8 pagesMrunal HistoryChinmay JenaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Philosophers On French RevolutionDocument52 pagesImpact of Philosophers On French Revolutionalisyed37100% (2)
- 09 Usp Ch01 Important Questions The French RevolutionDocument12 pages09 Usp Ch01 Important Questions The French RevolutionManish Thakur0% (1)
- Joseph de Maistre's Complex Legacy as a Conservative ThinkerDocument10 pagesJoseph de Maistre's Complex Legacy as a Conservative ThinkerPepe PepitoNo ratings yet
- HomeWork 132949352521835534Document10 pagesHomeWork 132949352521835534Yuvraj AroraNo ratings yet
- Moosaajii Meettaa DaataaDocument132 pagesMoosaajii Meettaa DaataaCHARI BORUNo ratings yet
- French Revolution: Causes and Impact in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesFrench Revolution: Causes and Impact in 40 CharactersharishjoshinainitalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Chemistry An Atoms Focused Approach Second Edition Second Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Chemistry An Atoms Focused Approach Second Edition Second Edition PDF Full Chapterpoliture.caprylicnth9x100% (16)
- French Revolution of 1848 in 38 CharactersDocument13 pagesFrench Revolution of 1848 in 38 CharactersSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Notes PDFDocument5 pagesThe Rise of Nationalism in Europe Notes PDFArtesh Kumar 9bNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Test Bank For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht PDF EbookDocument32 pagesInstant Download Test Bank For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht PDF EbookAngela Rouse100% (13)
- Class Ix Study MaterialDocument74 pagesClass Ix Study MaterialPranav Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Origins of The Revolution: Revolutionary France Ancien Régime 1830 1848Document2 pagesOrigins of The Revolution: Revolutionary France Ancien Régime 1830 1848Prince Pascual Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 9H Iacw1Document172 pages9H Iacw1logiece89No ratings yet
- Mrunal HistoryDocument8 pagesMrunal HistoryChinmay JenaNo ratings yet
- The Congress of Vienna and Its Goal of Restoring OrderDocument4 pagesThe Congress of Vienna and Its Goal of Restoring OrderAkram AkbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Summary & OutlineDocument6 pagesChapter 21 - Summary & OutlinemirbramoNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument43 pagesThe French RevolutionMiron PalaveršićNo ratings yet
- 9 History NcertSolutions Chapter 1 PDFDocument3 pages9 History NcertSolutions Chapter 1 PDFRaj AnandNo ratings yet
- Louis VxiDocument5 pagesLouis VxiTwinkle AgarwalNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Grade 9 - PPT PresentationDocument10 pagesFrench Revolution Grade 9 - PPT Presentationfdkfja dafklaNo ratings yet
- French and Industrial RevolutionDocument4 pagesFrench and Industrial RevolutionAkansha guptaNo ratings yet
- Instant Download American History Connecting With The Past 15th Edition Alan Brinkley Test Bank PDF ScribdDocument32 pagesInstant Download American History Connecting With The Past 15th Edition Alan Brinkley Test Bank PDF ScribdCarrieFloresgxoa100% (15)