100% found this document useful (1 vote)
774 views22 pagesContextualization-Of-learning-materials English and Short Version
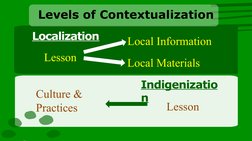
This document provides information about contextualizing learning materials in the Philippines. It defines contextualization as relating the curriculum to the specific setting or area to make competencies relevant and useful to learners. Contextualization has legal bases in the Philippine constitution and the Enhanced Basic Education Act. It discusses different levels of contextualization including localization, which uses local information and materials, and indigenization, which incorporates local culture and practices. The importance of contextualization is that it considers learners' geography, cultural diversity, and individuality. Teachers can contextualize by relating lessons to students' prior knowledge and experiences.
Uploaded by
charles stone panuncilloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
774 views22 pagesContextualization-Of-learning-materials English and Short Version
This document provides information about contextualizing learning materials in the Philippines. It defines contextualization as relating the curriculum to the specific setting or area to make competencies relevant and useful to learners. Contextualization has legal bases in the Philippine constitution and the Enhanced Basic Education Act. It discusses different levels of contextualization including localization, which uses local information and materials, and indigenization, which incorporates local culture and practices. The importance of contextualization is that it considers learners' geography, cultural diversity, and individuality. Teachers can contextualize by relating lessons to students' prior knowledge and experiences.
Uploaded by
charles stone panuncilloCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd