100% found this document useful (1 vote)
783 views25 pagesOperations on Rational Numbers for Class 7
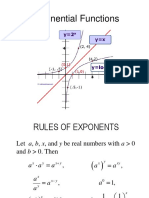
This document discusses operations on rational numbers including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It provides examples and properties of each operation. For addition and subtraction, it discusses how to combine rational numbers with the same or different denominators. It then outlines properties like closure, commutativity, associativity, identity, and inverses that apply to rational number operations.
Uploaded by
Abhijit PatraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
783 views25 pagesOperations on Rational Numbers for Class 7
This document discusses operations on rational numbers including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It provides examples and properties of each operation. For addition and subtraction, it discusses how to combine rational numbers with the same or different denominators. It then outlines properties like closure, commutativity, associativity, identity, and inverses that apply to rational number operations.
Uploaded by
Abhijit PatraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd