Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Green Computing Presentation Maragatham
Uploaded by
ABHILASH C N0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesEnergy efficient computing in grids and clouds is important for three reasons: 1) traditional HPC focuses on performance not efficiency, 2) datacenters consume large amounts of power threatening the environment, and 3) the largest supercomputers consume megawatts of power equivalent to small cities. Software solutions can improve efficiency through power-aware scheduling of tasks, data, and network communication. Researchers are estimating energy consumption of parallel applications, modeling energy requirements, and developing power-aware file systems to address this important issue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnergy efficient computing in grids and clouds is important for three reasons: 1) traditional HPC focuses on performance not efficiency, 2) datacenters consume large amounts of power threatening the environment, and 3) the largest supercomputers consume megawatts of power equivalent to small cities. Software solutions can improve efficiency through power-aware scheduling of tasks, data, and network communication. Researchers are estimating energy consumption of parallel applications, modeling energy requirements, and developing power-aware file systems to address this important issue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesGreen Computing Presentation Maragatham
Uploaded by
ABHILASH C NEnergy efficient computing in grids and clouds is important for three reasons: 1) traditional HPC focuses on performance not efficiency, 2) datacenters consume large amounts of power threatening the environment, and 3) the largest supercomputers consume megawatts of power equivalent to small cities. Software solutions can improve efficiency through power-aware scheduling of tasks, data, and network communication. Researchers are estimating energy consumption of parallel applications, modeling energy requirements, and developing power-aware file systems to address this important issue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Energy Efficient Computing
in Grid & Cloud
Presented by presented To
Ghouse Pasha VII ‘A’ & ‘B’ ISE
Lecturer
Dept. of Information Science & Engg.
SJB Institute of Technology
Bangalore
Motivation
Traditional research interest in cluster systems has been high
performance, such as
high throughput
low turnaround time,
load balancing
Computational tasks are being created to serve the
requirements of scientific community.
Computational grids gives experts immediate access
Comprises of geographically distributed MPPs or Clusters
Largest supercomputers can consume megawatts
Earth Simulator on Japan’s 5120-processor consumes 11.9 MW
Enough for a city of 40,000 population
Only a fraction of power consumed is used for actual
computations
According to Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, for
every watt of power consumed by IBM BlueGene , 0.7W
of power is required to cool it.
Datacenters poses great threat to environment
Carbon Dioxide Emission
Exponential rise in power consumption
At Node level
Processors are major consumers
Solution for Addressing
HPC suppliers are addressing this problem on
a number of fronts
at the chip level
at the blade/box level
in computing infrastructure
with software
Software level
Solution can be power aware scheduling
Task
Data Blocks
Communication Network
Objective
to improve power management and consumption
using power aware ability of system devices, such
as processors, disks, and communication links.
Green Computing@NMIT
Estimating Energy Consumed by the Parallel
Application
Mohan & Friends
Modeling & Predicting Energy required by the
parallel application
Power Aware File Systems
Sachin & Friends
Energy Estimation
E=P X N X T
E: energy consumed by a program
N: the number of clock cycles taken by the program
T: Clock Period
P: Average power consumed by a microprocessor
P=I X Vcc
I:Average current
Vcc: Supply voltage
Linux Packages (Sensors)
Energy Estimation Cont..
T=1/f
N:
RDTSC ("read time stamp counter") instruction
instruction available on recent processors
Great tool for accurate timing
It stores the number of elapsed clock-cycles since
power-on as 64 bit integer with high 32 bits in
register edx and low 32 bits in register eax.
RDTSC before and after task
Modelling & Prediction
Predicted Energy in terms of
Different No of clock cycles
Different clock period
Different Average power consumption
Ax=E
X: unknown coeffcients
A is a matrix
Curve-fitting technique
History
VM Reallocation Problem
The VM reallocation problem can be divided in
two:
Selection of VMs to migrate
Determining new placement of these VMs on
physical hosts.
11 02/21/2023
You might also like
- Embedded Deep Learning: Algorithms, Architectures and Circuits for Always-on Neural Network ProcessingFrom EverandEmbedded Deep Learning: Algorithms, Architectures and Circuits for Always-on Neural Network ProcessingNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V10I2P11) :sarvottam Dixit, Neerja JainDocument7 pages(IJCST-V10I2P11) :sarvottam Dixit, Neerja JainEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Reducing Dynamic Energy in Networks On Chip: 1 Arley Villa Salazar 2 Gustavo Pati NoDocument6 pagesReducing Dynamic Energy in Networks On Chip: 1 Arley Villa Salazar 2 Gustavo Pati NoARLEY FERNANDO VILLA SALAZARNo ratings yet
- Computer Performance Enhancing Techniques - Session-2Document36 pagesComputer Performance Enhancing Techniques - Session-2LathaNo ratings yet
- Quanto: Tracking Energy in Networked Embedded SystemsDocument16 pagesQuanto: Tracking Energy in Networked Embedded SystemsNarasimha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Predictive Power Consumption Model For Compute Intensive Applications in Clustered ARM A53 Embedded SystemsDocument4 pagesPredictive Power Consumption Model For Compute Intensive Applications in Clustered ARM A53 Embedded SystemsEl ProfesorNo ratings yet
- Wattch: Framework For Architectural-Level Power Analysis and OptimizationsDocument12 pagesWattch: Framework For Architectural-Level Power Analysis and OptimizationsUmekalsoomNo ratings yet
- Operating System Support For Mobile Devices: 4/5/2004 Richard YangDocument38 pagesOperating System Support For Mobile Devices: 4/5/2004 Richard YangTMDODNo ratings yet
- Khan2019 Article AnalyzingThePowerConsumptionBeDocument10 pagesKhan2019 Article AnalyzingThePowerConsumptionBeSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- BASE PAEER Application Driven Voltage Island Partitioning For Low Power SoCDocument11 pagesBASE PAEER Application Driven Voltage Island Partitioning For Low Power SoCshaNo ratings yet
- Manu 2019Document6 pagesManu 2019venkat301485No ratings yet
- 00) TD-SRAM - Time-Domain-Based - In-Memory - Computing - Macro - For - Binary - Neural - NetworksDocument11 pages00) TD-SRAM - Time-Domain-Based - In-Memory - Computing - Macro - For - Binary - Neural - NetworksAMANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- A Review of Low Power Processor DesignDocument10 pagesA Review of Low Power Processor DesignNalini RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Column Bypassing Multiplier Implementation On FPGADocument17 pagesColumn Bypassing Multiplier Implementation On FPGAIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ediol 2009mar25 MCP Ta 01Document2 pagesEdiol 2009mar25 MCP Ta 01prajneshNo ratings yet
- A Review of Low Power Processor DesignDocument9 pagesA Review of Low Power Processor DesignNalini RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Thermal and IR Drop Analysis Using Convolutional Encoder-Decoder NetworksDocument7 pagesThermal and IR Drop Analysis Using Convolutional Encoder-Decoder NetworksyutuohangNo ratings yet
- A Novel Design and Analysis of 4: 2 Compressors With Reduced Area Delay and PowerDocument15 pagesA Novel Design and Analysis of 4: 2 Compressors With Reduced Area Delay and PowerraghavNo ratings yet
- Deep Reinforcement Learning Enabled Self Configurable Networks On Chip For High Performance and Energy Efficient ComputiDocument16 pagesDeep Reinforcement Learning Enabled Self Configurable Networks On Chip For High Performance and Energy Efficient ComputiFazrul FaizNo ratings yet
- Eui Seong 2008Document13 pagesEui Seong 2008Armin AhmadzadehNo ratings yet
- PubDat 188476Document15 pagesPubDat 188476Mohamed AlmortadaNo ratings yet
- Power Consumption and Energy Management For Edge Computing: State of The ArtDocument10 pagesPower Consumption and Energy Management For Edge Computing: State of The ArtTELKOMNIKANo ratings yet
- Topological Properties of Multiprocessor Interconnection NetworkDocument8 pagesTopological Properties of Multiprocessor Interconnection NetworkSamita Prava JenaNo ratings yet
- S. Narayanamoorthy, H.A. Moghaddam, Z. Liu, T. Park, N.S. Kim, InIEEE Transactions On VeryLarge Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems23 (6), 1180 (2015)Document5 pagesS. Narayanamoorthy, H.A. Moghaddam, Z. Liu, T. Park, N.S. Kim, InIEEE Transactions On VeryLarge Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems23 (6), 1180 (2015)VipinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24Document21 pagesLecture 24Mohan Kumar MNo ratings yet
- 07) A Time-Domain Binary CNN Engine With Error-Detection-Based Resilience in 28nm CMOSDocument5 pages07) A Time-Domain Binary CNN Engine With Error-Detection-Based Resilience in 28nm CMOSAMANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Review On High Performance Energy Efficient Multicore Embedded Computing 1Document7 pagesWeek 6 - Review On High Performance Energy Efficient Multicore Embedded Computing 1Game AccountNo ratings yet
- GreenEdge - Joint Green Energy Scheduling and Dynamic Task Offloading in Multi - Tier Edge Computing SystemsDocument14 pagesGreenEdge - Joint Green Energy Scheduling and Dynamic Task Offloading in Multi - Tier Edge Computing SystemsJesus RNo ratings yet
- Aalborg Universitet: Dragicevic, Tomislav Wheeler, Patrick Blaabjerg, FredeDocument12 pagesAalborg Universitet: Dragicevic, Tomislav Wheeler, Patrick Blaabjerg, FredeHajmunnisaNo ratings yet
- Design Optimization and Implementation of RF Energy Harvesting CircuitsDocument10 pagesDesign Optimization and Implementation of RF Energy Harvesting CircuitsMohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Computer Applications in Power SystemDocument15 pagesChapter-1: Computer Applications in Power SystembrukNo ratings yet
- Warehouse-Scale Computers: Request-Level and Data-Level ParallelismDocument16 pagesWarehouse-Scale Computers: Request-Level and Data-Level ParallelismJameem AhamedNo ratings yet
- Calculating Total Power Requirements For Data CentersDocument11 pagesCalculating Total Power Requirements For Data CentersDomingo RuizNo ratings yet
- Low Power DSP 1 TechDocument4 pagesLow Power DSP 1 TechtheobrambaNo ratings yet
- ×32 Bit Multiprecision Razor-Based Dynamic: 32 Bit Voltage Scaling Multiplier With Operands SchedulerDocument12 pages×32 Bit Multiprecision Razor-Based Dynamic: 32 Bit Voltage Scaling Multiplier With Operands SchedulerSenthilkumar KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Low-Power Digital Signal Processor Architecture For Wireless Sensor NodesDocument9 pagesLow-Power Digital Signal Processor Architecture For Wireless Sensor NodesGayathri K MNo ratings yet
- Efficient Design of 1Document7 pagesEfficient Design of 1sumathiNo ratings yet
- 0710ijcnc04 PDFDocument10 pages0710ijcnc04 PDFJam 234No ratings yet
- Approximate NoC and Memory Controller Architectures for GPGPU AcceleratorsDocument15 pagesApproximate NoC and Memory Controller Architectures for GPGPU AcceleratorsMiguel Ramírez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- A Fully Hardware-Based Memristive Multilayer Neural Network: Research ArticleDocument9 pagesA Fully Hardware-Based Memristive Multilayer Neural Network: Research ArticleZhanzhi LiuNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Multi-Core Processing: Electronics June 2014Document9 pagesEnergy Efficient Multi-Core Processing: Electronics June 2014Engr. Hamayun khanNo ratings yet
- Workload-Aware Neuromorphic Power Controller DesignDocument8 pagesWorkload-Aware Neuromorphic Power Controller Designವಿಶ್ವನಾಥ ಸಿNo ratings yet
- 2.06095515-Compiler-Directed Energy Reduction Using Dynamic Voltage Scaling and Voltage Islands For Embedded SystemsDocument11 pages2.06095515-Compiler-Directed Energy Reduction Using Dynamic Voltage Scaling and Voltage Islands For Embedded SystemsPhan Giang ChâuNo ratings yet
- Low Power Vlsi ThesisDocument5 pagesLow Power Vlsi Thesismariapadillaomaha100% (2)
- Energy Efficiency of Data Networks Through Rate AdaptationDocument6 pagesEnergy Efficiency of Data Networks Through Rate AdaptationLeen AzlanNo ratings yet
- LjusevDocument6 pagesLjusevrute silvaNo ratings yet
- A Heterogeneous RISC-V Processor For Efficient DNN Application in Smart Sensing SystemDocument19 pagesA Heterogeneous RISC-V Processor For Efficient DNN Application in Smart Sensing SystemUmair AhmadhNo ratings yet
- Algorithmic Level Power Analysis and Architectural Level EstimationDocument35 pagesAlgorithmic Level Power Analysis and Architectural Level EstimationPrabhavathi PNo ratings yet
- Fast Newton-Raphson Power Flow Analysis Based On Sparse Techniques and Parallel ProcessingDocument11 pagesFast Newton-Raphson Power Flow Analysis Based On Sparse Techniques and Parallel ProcessingMuhammad Kamran MustafaNo ratings yet
- Low-Loss Photonic Reservoir Computing With Multimode Photonic Integrated CircuitsDocument10 pagesLow-Loss Photonic Reservoir Computing With Multimode Photonic Integrated CircuitsprajneshNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Wireless Noc With Congestion-Aware Routing For Multicore ChipsDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Wireless Noc With Congestion-Aware Routing For Multicore ChipsHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Design and Operation of Energy-Aware Wireless Sensor Networks Through Scheduling and RoutingDocument3 pagesDesign and Operation of Energy-Aware Wireless Sensor Networks Through Scheduling and RoutingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Hohlt 2004Document10 pagesHohlt 2004Eko PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Model Predictive Control Using Artificial Neural Network For Power ConvertersDocument10 pagesModel Predictive Control Using Artificial Neural Network For Power ConvertersDick CarlNo ratings yet
- Ijesrt: Performance Analysis of An Noc For Multiprocessor SocDocument5 pagesIjesrt: Performance Analysis of An Noc For Multiprocessor SocRajesh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient Techniques for 5G and IoTDocument22 pagesEnergy-Efficient Techniques for 5G and IoTRitvik RaiNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Implementation On Full Adder Circuits: R.Swapna, Shoban MudeDocument5 pagesAdiabatic Implementation On Full Adder Circuits: R.Swapna, Shoban MudeshrivathsavsNo ratings yet
- A Logic-Compatible EDRAM Compute-In-Memory With Embedded ADCs For Processing Neural NetworksDocument13 pagesA Logic-Compatible EDRAM Compute-In-Memory With Embedded ADCs For Processing Neural NetworksHelloNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Parallel Computing Algorithm For Shared Memory MpsocDocument3 pagesOptimization of Parallel Computing Algorithm For Shared Memory MpsocerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Low Power DSP Using Approximate AddersDocument14 pagesLow Power DSP Using Approximate AddersNMANo ratings yet
- UNIX Processes Programming GuideDocument45 pagesUNIX Processes Programming GuideABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document117 pagesUnit 3ABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document35 pagesUnit 2ABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document86 pagesUnit 7ABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Mobile Help GuideDocument6 pagesMobile Help GuideABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Localization for WSNs with Obstacles Using Convex OptimizationDocument6 pagesCooperative Localization for WSNs with Obstacles Using Convex OptimizationABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Store Room System DetailsDocument2 pagesStore Room System DetailsABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Anti VirusDocument6 pagesAnti VirusABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Abhi IeeeDocument4 pagesAbhi IeeeABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Cosmetics ShopDocument7 pagesCosmetics ShopSanjay RajputNo ratings yet
- Android Lab ManualDocument63 pagesAndroid Lab ManualGarv BhattNo ratings yet
- Control/Repeater Panel M 4.3: General Description DataDocument28 pagesControl/Repeater Panel M 4.3: General Description DatadangthutqmNo ratings yet
- TOPIC IMO Performance Standards ECDIS MSC 232 (Document6 pagesTOPIC IMO Performance Standards ECDIS MSC 232 (lorraine atienzaNo ratings yet
- 3.7 AI - DS Assignment2-1Document4 pages3.7 AI - DS Assignment2-1Anurag SinghNo ratings yet
- Product-Tracking-Tracing IoT BlockchainDocument8 pagesProduct-Tracking-Tracing IoT Blockchainanshu_foruNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Equation - ME17 - 36Document6 pagesReynolds Equation - ME17 - 36parth bhala0% (1)
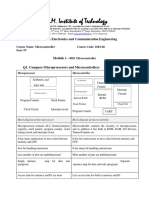
- B.N.M. Institute of Technology Microcontroller CourseDocument19 pagesB.N.M. Institute of Technology Microcontroller Coursekirthi bharadwajNo ratings yet
- ICT Action Plan 2019 2020Document4 pagesICT Action Plan 2019 2020Marjorie RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Bse Star MF User Manual For MFDDocument26 pagesBse Star MF User Manual For MFDSUSHANT YEJARENo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet 1Document40 pagesSpreadsheet 1Alexandra ShaneNo ratings yet
- Makerere Report and Proposal FormatDocument20 pagesMakerere Report and Proposal FormatRicky Okwir Okello100% (6)
- APP ConnectorDocument233 pagesAPP ConnectorTasha RozsokhaNo ratings yet
- Redline VF DS - RDL-3000 XP EllipseDocument2 pagesRedline VF DS - RDL-3000 XP EllipseTommy AsselinNo ratings yet
- Spatial Soil Erosion Estimation Using An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) andDocument10 pagesSpatial Soil Erosion Estimation Using An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) andhabtamu tamiruNo ratings yet
- 6880309T87 AMobileDSMDocument265 pages6880309T87 AMobileDSMAyon BaxterNo ratings yet
- CTERA 5.0 End User Portal Quick Start GuideDocument33 pagesCTERA 5.0 End User Portal Quick Start GuideAlberto DonolatoNo ratings yet
- CEN ISO TR 12489 (2016) (E) CodifiedDocument7 pagesCEN ISO TR 12489 (2016) (E) CodifiedJHNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesNarrative ReportMelody DacuyaNo ratings yet
- Gems Choice Board SlidesManiaDocument10 pagesGems Choice Board SlidesManiaNikka CamannongNo ratings yet
- Robot state and safety mode dataDocument11 pagesRobot state and safety mode dataElie SidnawyNo ratings yet
- Practical Exam in Empowerment TechnologiesDocument5 pagesPractical Exam in Empowerment TechnologiesROMMEL LAGATICNo ratings yet
- Colour Code Chart For Welding ConsumablesDocument1 pageColour Code Chart For Welding ConsumablesJayan VKNo ratings yet
- S5735-S8P2X-IA200H1 Quick Start GuideDocument16 pagesS5735-S8P2X-IA200H1 Quick Start GuideChristian Javier Lopez DuranNo ratings yet
- Ae - Lab 6Document6 pagesAe - Lab 6Usman KhalilNo ratings yet
- HCOM117 Student Number 48082627 Assignment 1 Internet ExplorerDocument5 pagesHCOM117 Student Number 48082627 Assignment 1 Internet ExplorerKeabetsweNo ratings yet
- KAWAI R-ROM Switcher InstallDocument3 pagesKAWAI R-ROM Switcher InstallMiguel ViscarraNo ratings yet
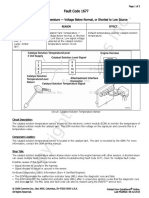
- 06-fc1677 Catalyst Tank Temperature - Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted To Low Source PDFDocument3 pages06-fc1677 Catalyst Tank Temperature - Voltage Below Normal, or Shorted To Low Source PDFSuryadiNo ratings yet
- Digital Learning ObjectDocument60 pagesDigital Learning Objectust hafedz100% (3)
- 7 Things You Should Know About Augmented Reality PDFDocument2 pages7 Things You Should Know About Augmented Reality PDFKartika LesmanaNo ratings yet