Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distribution Systems
Uploaded by
Cameout0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesDistribution Systems
Uploaded by
CameoutCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
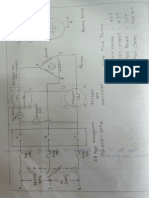
Distribution systems
Types of distribution systems
• An electrical power distribution system can be
classified according to its feeder connection
schemes or topologies as follows -
• Radial distribution system
• Parallel feeders distribution
• Ring main distribution system
• Interconnected distribution
Radial Distribution System
• only when substation or generating stations is located
at the center of the consumers.
• different feeders radiate from a substation or a
generating station and feed the distributors at one end.
• power flow is in only one direction.
• simplest system and has the lowest initial cost.
• Not highly reliable.
• major drawback - result in supply failure -no
alternative feeder to feed distributors.
Radial Distribution System
Single line diagram of a typical radial
distribution system
Parallel Feeders Distribution System
• Number of feeders is doubled.
• Reliability of the supply is important
• For load sharing where the load is higher.
Parallel Feeders Distribution System
Ring Main Distribution System
• Each distribution transformer is fed with two
feeders but in different paths.
• The feeders in this system form a loop
• starts from the substation bus-bars, runs
through the load area feeding distribution
transformers and returns to the substation
bus-bars.
Single line diagram of a ring main distribution
system.
Advantages Of Ring Main Distribution System
• Fewer voltage fluctuations at consumer's
terminal.
• Very reliable as each distribution transformer
is fed with two feeders.
• On event of a fault in any section of the
feeder, the continuity of the supply is ensured
from the alternative path.
Single Line Diagram of an
Electrical Substation
Single Busbar Substation
• There is a circuit breaker for protection of each circuit, - no loss of
supply in outages.
• In case of fault on the transformer of a feeder, circuit breaker results
in loss of feeder or transformer circuit which is restored after
isolation of faulty circuit breaker.
• Loss of circuit is involved in the maintenance of the circuit breaker
of the transformer of the feeder.
• There are bypass isolators amid circuit isolator and busbar hence
allowing maintenance of circuit breaker without any loss to the
circuit.
• Any fault in busbar is causing loss of a transformer or feeder. Hence,
maintenance of a busbar will result in an outage of 2 circuits.
Mesh Busbar Substation
• There is a requirement of two circuit breakers
for disconnecting or connecting of a circuit and
disconnection is also requiring opening up of
mesh.
• There is an option of maintenance of circuit
breakers without loss of supply.
• One circuit breaker loss occurs when busbar is
faulty while fault in breaker involves loss of two
circuits.
You might also like
- Electrical ServicesDocument62 pagesElectrical ServicesAshmita AryalNo ratings yet
- Design of Subtransmission LinesDocument45 pagesDesign of Subtransmission LinesBvijaya krishnaNo ratings yet
- Busbar ProtectionDocument23 pagesBusbar ProtectionJayamkondanNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission, Distribution and UtilizationDocument19 pagesPower Transmission, Distribution and UtilizationPhD EENo ratings yet
- 21EEE - 2023 - Distribution SystemsDocument17 pages21EEE - 2023 - Distribution SystemsAmbadiNo ratings yet
- Distribution System and Design: Presented By: Renz Modalez Florencio Bacani Jhon Glen Donato Cleo BegasoDocument30 pagesDistribution System and Design: Presented By: Renz Modalez Florencio Bacani Jhon Glen Donato Cleo BegasoKennethNo ratings yet
- 12 Distribution SystemDocument27 pages12 Distribution SystemPao Castillon100% (1)
- Module II - Electrical ServicesDocument109 pagesModule II - Electrical ServicesBadarul MuneerNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar SchemesDocument26 pagesBus Bar SchemesSoorya Priya GopalakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Substation Bus Bar Configuration: Electrical Maintenance TeamDocument18 pagesSubstation Bus Bar Configuration: Electrical Maintenance TeamFaisalNo ratings yet
- Distributionsystems 150204040603 Conversion Gate01Document18 pagesDistributionsystems 150204040603 Conversion Gate01Mukesh ParewaNo ratings yet
- Substation Components and Bus SchemesDocument32 pagesSubstation Components and Bus Schemesvenki249No ratings yet
- A350369487 - 11012 - 1 - 2017 - Electric Traction1Document40 pagesA350369487 - 11012 - 1 - 2017 - Electric Traction1GARIMA RANJAN ANANDNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar ArrangementsDocument23 pagesBus Bar ArrangementsKarthik SsnongoleNo ratings yet
- Design of Subtransmission Lines and Distribution SubstationsDocument80 pagesDesign of Subtransmission Lines and Distribution SubstationsOmerAbdulRazzaq40% (5)
- Power System 2Document103 pagesPower System 2msathish_eeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Study and Design of Primary and Secondary DistributionDocument74 pagesLecture 1 Study and Design of Primary and Secondary DistributionJade Albert G. FalladoNo ratings yet
- Introduction PPTDocument28 pagesIntroduction PPTAbhimanyu MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Substation Layout and Accessories Busbar Arrangement: A Report ONDocument38 pagesSubstation Layout and Accessories Busbar Arrangement: A Report ONAdhiatma M. Nur Hadi100% (1)
- BE Distribution-2070Document41 pagesBE Distribution-2070Wanted SarojNo ratings yet
- Busbar ArrangementsDocument6 pagesBusbar ArrangementsUmair KhanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution SystemDocument3 pagesElectrical Power Distribution SystemmshahidshaukatNo ratings yet
- Substation ComponentsDocument44 pagesSubstation Componentsvenki249100% (1)
- Powersystemstructure 220719130337 978a2bfdDocument12 pagesPowersystemstructure 220719130337 978a2bfdJosee MusabyimanaNo ratings yet
- Distirbution SystemsDocument8 pagesDistirbution Systemsdennisnyala02No ratings yet
- AC Distribution SystemsDocument42 pagesAC Distribution SystemsAnant AjithkumarNo ratings yet
- Distribution System 2Document12 pagesDistribution System 2ismiNo ratings yet
- Power Distribution and Utilization: B.Sc. Electrical EngineeringDocument17 pagesPower Distribution and Utilization: B.Sc. Electrical EngineeringJawad HyderNo ratings yet
- Substation ComponentsDocument44 pagesSubstation Componentsgurkirat1108No ratings yet
- Lecture 7-1Document44 pagesLecture 7-1Shahab HassanNo ratings yet
- Substations: Nauman Ahmad Assistant Professor Ee Sen UMT LahoreDocument25 pagesSubstations: Nauman Ahmad Assistant Professor Ee Sen UMT Lahorezakir abbasNo ratings yet
- EE17 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesEE17 Lecture NotesRoselyn MatienzoNo ratings yet
- 400kv SubstationDocument38 pages400kv SubstationVenkata Suresh Mandava75% (4)
- MOD 2.4 Distribution Systems 2Document9 pagesMOD 2.4 Distribution Systems 2Nandhu SachinNo ratings yet
- What Is Electrical Bus-Bar? - Definition & Types of Electrical Bus Bar - Circuit GlobeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Electrical Bus-Bar? - Definition & Types of Electrical Bus Bar - Circuit GlobeRazu AhmmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives LEC # 1Document50 pagesElectrical Drives LEC # 1Muhammad Ali ImranNo ratings yet
- Transmission and DistributionDocument14 pagesTransmission and DistributionIan LujeroNo ratings yet
- Study of A 22013233kv SubstationDocument19 pagesStudy of A 22013233kv SubstationARVINDNo ratings yet
- Balanced Faults Part 2Document20 pagesBalanced Faults Part 2Faiza Tabassam 546-FET/BSEE/F19No ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring SystemDocument48 pagesElectrical Wiring SystemHimalya KaimNo ratings yet
- DC Power DistributionDocument24 pagesDC Power DistributionZay YarNo ratings yet
- Distribution SystemDocument22 pagesDistribution SystemMuhammad HaikalNo ratings yet
- Department of Mirpur Institute of TechnologyDocument40 pagesDepartment of Mirpur Institute of TechnologySEARCH GBNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation: Electricity Distribution System AT 220 KV Sub-Station, SahibabadDocument23 pagesSummer Training Presentation: Electricity Distribution System AT 220 KV Sub-Station, SahibabadMarut Awasthi100% (1)
- Power Distribution Systems and Its CharacteristicsDocument50 pagesPower Distribution Systems and Its CharacteristicsquangspktNo ratings yet
- Department of Mirpur Institute of TechnologyDocument25 pagesDepartment of Mirpur Institute of TechnologySEARCH GBNo ratings yet
- 3 Skema HVDCDocument18 pages3 Skema HVDCMuhammad YogiNo ratings yet
- Application of Power Electronics in HVDC: Snehal V. Purani Lukhdhirji Engineering College M.E. (Power Systems)Document20 pagesApplication of Power Electronics in HVDC: Snehal V. Purani Lukhdhirji Engineering College M.E. (Power Systems)doud98No ratings yet
- Distribution Planning.1 1Document17 pagesDistribution Planning.1 1Arif HassenNo ratings yet
- Intro To SubstationsDocument30 pagesIntro To SubstationsMonabrent GbofNo ratings yet
- Distribution System: Topic 3Document54 pagesDistribution System: Topic 3hashim_mokhtar9286No ratings yet
- Radial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsDocument29 pagesRadial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsHamid RazaNo ratings yet
- DistributionDocument29 pagesDistributionvenki249No ratings yet
- Distribution FedersDocument21 pagesDistribution FedersKVRamananNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Fundamentals of Distribution SystemsDocument39 pagesWeek 11 - Fundamentals of Distribution SystemsEstika Vriscilla GintingNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Teachnook MINOR PROJECT - PYDocument9 pagesTeachnook MINOR PROJECT - PYCameoutNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledCameoutNo ratings yet
- Department: Program Name/Code: B TECH/ Course Name/Code:: Question BankDocument16 pagesDepartment: Program Name/Code: B TECH/ Course Name/Code:: Question BankCameoutNo ratings yet
- Digital Control SystemDocument15 pagesDigital Control SystemCameoutNo ratings yet
- U20CYHT01 - Social and Environmental EngineeringDocument1 pageU20CYHT01 - Social and Environmental EngineeringCameoutNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledCameoutNo ratings yet
- Be - Cells The Basic UnitDocument41 pagesBe - Cells The Basic UnitCameoutNo ratings yet
- 75.schrödinger's Wave Equation For Particle in A BoxDocument15 pages75.schrödinger's Wave Equation For Particle in A BoxCameoutNo ratings yet
- Cells Maintain Their Internal EnvironmentDocument29 pagesCells Maintain Their Internal EnvironmentCameoutNo ratings yet
- Musku TharunDocument9 pagesMusku TharunCameoutNo ratings yet
- Musku TharunDocument9 pagesMusku TharunCameoutNo ratings yet
- Huawei Charger English Cargador Litio HeliDocument17 pagesHuawei Charger English Cargador Litio HeliEdwin calderon romero100% (1)
- PES TP TR71 PSRC Microgrid 082019Document58 pagesPES TP TR71 PSRC Microgrid 082019A guitar la tocarraNo ratings yet
- NV3000 14Document233 pagesNV3000 14Gustavo Castillo100% (1)
- High Voltage TestingDocument41 pagesHigh Voltage Testingpvrk123No ratings yet
- KEI" Single Core Compacted Aluminium & Copper Conductor, XLPE Insulated, Unarmoured & Armoured Cable AL & CU / XLPE / AL Wire / PVC Conforming To IS 7098 Part-2/1985Document2 pagesKEI" Single Core Compacted Aluminium & Copper Conductor, XLPE Insulated, Unarmoured & Armoured Cable AL & CU / XLPE / AL Wire / PVC Conforming To IS 7098 Part-2/1985Wires Cable0% (1)
- Mariner 560 S - EngDocument2 pagesMariner 560 S - EngPablo CañaNo ratings yet
- Statcom DocumentationDocument9 pagesStatcom Documentationbalu_33babuNo ratings yet
- Visio-SWCS - Control Block Diagram Rev.02Document2 pagesVisio-SWCS - Control Block Diagram Rev.02nautelNo ratings yet
- MGK Guide To Reciprocating Engine Generators and Microgrids v4Document13 pagesMGK Guide To Reciprocating Engine Generators and Microgrids v4Jeff LNo ratings yet
- Embracing Energy Efficiency: A Davao Light Experience: Engr. Rodger S. Velasco President and COODocument31 pagesEmbracing Energy Efficiency: A Davao Light Experience: Engr. Rodger S. Velasco President and COOSun TzuNo ratings yet
- 3&4 Microgrids2020Document163 pages3&4 Microgrids2020NamiraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Transmission and DistributionDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Transmission and DistributionKyla Belgado100% (1)
- Pnoz X13 GBDocument4 pagesPnoz X13 GByus11No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction of Calculation Short CircuitDocument15 pages1 Introduction of Calculation Short CircuitChakraphorp KhmerNo ratings yet
- TRENCHDocument13 pagesTRENCHSimon Caceres100% (1)
- Multisim Unsolved Questions BITS PilaniDocument2 pagesMultisim Unsolved Questions BITS Pilanimanish_genus100% (1)
- How To Coordinate Transformer Primary-Side Fuses With Feeder ReclosersDocument3 pagesHow To Coordinate Transformer Primary-Side Fuses With Feeder ReclosersvoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Synchronisation of AlternatorDocument2 pagesAutomatic Synchronisation of AlternatorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 250 Kva Himoinsa PDFDocument12 pages250 Kva Himoinsa PDFwassimNo ratings yet
- RT01 - F650 - BCU - TRAFO 132kV - NDHIWADocument8 pagesRT01 - F650 - BCU - TRAFO 132kV - NDHIWANgigiDanielNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications of The Following Test EquipmentDocument8 pagesTechnical Specifications of The Following Test EquipmentPaul Huallparimachi ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- CARLA System: Cargo Tank High and Overflow ProtectionDocument2 pagesCARLA System: Cargo Tank High and Overflow Protectionlopejo lopejoNo ratings yet
- Formation of Bus Admittance Matrix UsingDocument24 pagesFormation of Bus Admittance Matrix UsingQuazi Mosaddequl Haque100% (1)
- Krishna+Mohan+Dwivedi+Document4 pagesKrishna+Mohan+Dwivedi+abhishekatupesNo ratings yet
- EEE 315 ELECTRICAL MACHINES III Supplementary EXAM - 2017Document5 pagesEEE 315 ELECTRICAL MACHINES III Supplementary EXAM - 2017Abkul KunniNo ratings yet
- # 3 PH Ac Input - Phase Current in Inputs N Putputs Mntned - 3 PH Inductive Load - Both LC Filters Used For Current and VoltageDocument3 pages# 3 PH Ac Input - Phase Current in Inputs N Putputs Mntned - 3 PH Inductive Load - Both LC Filters Used For Current and VoltageTeenaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Tips and Tricks Power Supply STR 6701Document2 pagesAdvanced Tips and Tricks Power Supply STR 6701Kiray VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- List of Power Stations in Bangladesh - WikipediaDocument5 pagesList of Power Stations in Bangladesh - WikipediaAvisheak PalNo ratings yet
- Voltage Drop Calculations by Bill BamfordDocument7 pagesVoltage Drop Calculations by Bill Bamfordankit jainNo ratings yet
- PowerPlus-SA-10KVA-3x400V UPS GamatronicDocument107 pagesPowerPlus-SA-10KVA-3x400V UPS GamatronicFernando Alexander SarmientoNo ratings yet