Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perdev Reporting
Uploaded by
Igrid Kyla Layesa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views30 pagesOriginal Title
Perdev Reporting.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views30 pagesPerdev Reporting
Uploaded by
Igrid Kyla LayesaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
GOOD MORNING
Presented by: Group 4
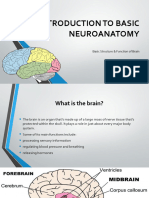
BRAIN
It is a complex organ that controls
thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor
skills, vision, breathing, temperature,
hunger and every process that regulates
our body.
PERSONAL
DEVELOPMENT
M o d u l e 1 1 : B r a i n s : P a r t s ,
P r o c e s s e s a n d F u n c t i o n s
Presented by: Group 4
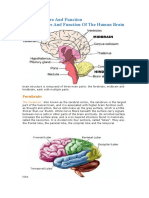
Brain
The brain is the most complex part of the human body.
This three-pound organ is the seat of intelligence,
interpreter of the senses, initiator of body movement,
and controller of behavior. Lying in its bony shell and
washed by protective fluid, the brain is the source of all
the qualities that define our humanity.
Parts
of
the
Brain
1. Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and
coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other
areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and
reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other
functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
2. Cerebellum
The cerebellum is important for making postural adjustments
in order to maintain balance. Through its input from
vestibular receptors and proprioceptors, it modulates
commands to motor neurons to compensate for shifts in body
position or changes in load upon muscles.
3. Brain Stem
It is responsible for many vital functions of life, such
as breathing, consciousness, blood pressure, heart rate, and
sleep. The brainstem contains many critical collections of
white and grey matter. The grey matter within the brainstem
consists of nerve cell bodies and forms many important
brainstem nuclei.
4. Limbic System
The limbic system is the part of the brain involved
in our behavioral and emotional responses,
especially when it comes to behaviors we need for
survival: feeding, reproduction and caring for our
young, and fight or flight responses.
5. Thalamus
Thalamus is your body's information relay station. All
information from your body's senses (except smell) must be
processed through your thalamus before being sent to your
brain's cerebral cortex for interpretation. Your thalamus also
plays a role in sleep, wakefulness, consciousness, learning
and memory.
6. Hypothalamus
A structure deep in your brain, acts as your body's
smart control coordinating center. Its main function is
to keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis.
It does its job by directly influencing your autonomic
nervous system or by managing hormones.
7. Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral cortex is responsible for the higher-level
processes of the human brain, including language,
memory, reasoning, thought, learning, decision-
making, emotion, intelligence and personality.
Lobes of Cerebrum
Frontal Lobe
The largest lobes in the human brain and they
are also the most common region of injury in
traumatic brain injury. The frontal lobes are
important for voluntary movement, expressive
language and for managing higher level
executive functions.
Function: “Action”
Mental and Physical
Executive functioning includes:
• Planning • Memory
• Problem Solving
• Learning
• Motivation
• Reward
• Judgement
• Attention
• Decision Making
• Impulse Control
• Social Behavior
• Personality
Parietal Lobe
Parietal lobe is a key part of your understanding of the world
around you. It processes your sense of touch and assembles
input from your other senses into a form you can use. Your
parietal lobe also helps you understand where you are in
relation to other things that your senses are picking up
around you.
Function: “Somatosensory”
Processing
Awareness of Somatic Proprioception
Sensation Somatic
• Touch Sensation
• Analyzing • Coordination of
• Pain • Recognizing Visual, Auditory
• Temperature • Memory of and Somatosensory
• Pressure Somatic Stimuli
Sensation • Spacial and Body
• Vibration Awareness
Temporal Lobe
Temporal lobe is the most commonly associated
with processing auditory information and with the
encoding of memory. The temporal lobes are also
believed to play an important role in processing
affect/emotions, language, and certain aspects of visual
perception.
Function: “Auditory”
Awareness of Auditory Processing Auditory
Stimuli
Stimuli
• Analyzing
• Hearing sounds • Recognizing
• Memory of
• Pitch, Frequency Auditory Stimuli
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobes sit at the back of the head and
are responsible for visual perception, including color,
form and motion. Damage to the occipital lobe can
include: Difficulty with locating objects in
environment. Difficulty with identifying colors (Color
Agnosia)
Function: “Visual”
Awareness of Visual Stimuli
• Seeing objects/stimuli
Processing Visual Stimuli
• Analyzing
• Recognizing
• Memory of Visual Stimuli
• Shapes, Colors, Sizes
QUIZ
Identify:
1. This three-pound organ is the
seat of intelligence, interpreter
of the senses, initiator of body
movement, and controller of
behavior.
Identify:
2. It plays a role in sleep,
wakefulness, consciousness,
learning and memory.
Identify:
3. It plays an important role in
processing affect/emotions,
language, and certain aspects of
visual perception.
Identify
4. The inability to
recognize colors or
difficulty with identifying
colors.
Enumerate:
5. Enumerate the parts of the Brain.
Answer:
1. Brain
2. Thalamus
3. Temporal Lobe
4. Color Agnosia
5. Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem, Limbic System,
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Cerebral Cortex
Thank you!!!
You might also like
- CognitiveDocument6 pagesCognitivesanika kadamNo ratings yet
- Brain Parts and Their Functions in LearningDocument6 pagesBrain Parts and Their Functions in LearningChabbigillNo ratings yet
- POWERS OF THE MIND: IMPROVING BRAIN FUNCTIONS THROUGH EXERCISESDocument41 pagesPOWERS OF THE MIND: IMPROVING BRAIN FUNCTIONS THROUGH EXERCISESGemma Rose LaquioNo ratings yet
- Personal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)Document5 pagesPersonal-Development-2 (3RD Quarter)karilesbackupaccNo ratings yet
- The World We Have Created Is A Product of Our Thinking, It Cannot Be Changed Without Changing Our ThinkingDocument41 pagesThe World We Have Created Is A Product of Our Thinking, It Cannot Be Changed Without Changing Our ThinkingGemma Rose LaquioNo ratings yet
- PERDEV Group 4 Power of MindDocument28 pagesPERDEV Group 4 Power of MindAhron SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Guide to Emotional Intelligence and Active Listening for More Satisfying RelationshipsFrom EverandThe Guide to Emotional Intelligence and Active Listening for More Satisfying RelationshipsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document34 pagesLesson 11Jeddah Lynn AbellonNo ratings yet
- Transcript Public SpeakingDocument2 pagesTranscript Public SpeakingPivvkyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemVenkatesh MNo ratings yet
- The Power of Emotional Intelligence: How To Build A Powerful Emotional Intelligence And Change Your Life With The Best TechniquesFrom EverandThe Power of Emotional Intelligence: How To Build A Powerful Emotional Intelligence And Change Your Life With The Best TechniquesNo ratings yet
- External Parts of The BrainDocument2 pagesExternal Parts of The BrainLemonTree AUNo ratings yet
- Power of The Mind - PerDev PDFDocument14 pagesPower of The Mind - PerDev PDFHannah RodelasNo ratings yet
- Lobes of The BrainDocument5 pagesLobes of The BrainEnforcement SectionNo ratings yet
- Understanding the BrainDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the BrainKeir ShattNo ratings yet
- Brain PowerDocument33 pagesBrain PowerMary Celestine GolongNo ratings yet
- PerDev_reviewer-Pre-fi_2nd semDocument8 pagesPerDev_reviewer-Pre-fi_2nd semMhonabelle SalomonNo ratings yet
- 2lecture HBDocument353 pages2lecture HBMariettaNo ratings yet
- NEURAL NETWORK How the Brain Works: An Overview of Brain Anatomy and FunctionDocument37 pagesNEURAL NETWORK How the Brain Works: An Overview of Brain Anatomy and FunctionAmirh AfunayNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Q1 M11Document17 pagesPersonal Development Q1 M11Joshua Laurence PalconNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesBrain Structure and Functionmademoiselle in transitNo ratings yet
- The Powers of the Mind RevealedDocument2 pagesThe Powers of the Mind RevealedErron Francisco NicolNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 17102022 034332pmDocument13 pagesLec 2 17102022 034332pmMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument4 pagesBrainKrizzel Anne MoralesNo ratings yet
- The Complexity of the BrainDocument20 pagesThe Complexity of the BrainMansa FontanosaNo ratings yet
- Mind and Behavior 1Document23 pagesMind and Behavior 1Yara El-GhadbanNo ratings yet
- Brain Parts, Processes and FunctionsDocument15 pagesBrain Parts, Processes and FunctionsDarlyn Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 POWERS of The MINDDocument25 pagesLesson 6 POWERS of The MINDRham RhumNo ratings yet
- SubjectDocument11 pagesSubjectRoshni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument27 pagesHuman BrainSuhail KhanNo ratings yet
- YihalemDocument16 pagesYihalemyihalemasmamawNo ratings yet
- The Four Lobes of the Brain and Its FunctionsDocument40 pagesThe Four Lobes of the Brain and Its FunctionsMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Bab4 NeuroscienceDocument28 pagesBab4 NeuroscienceRatno Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Biological Foundation of PsychologyDocument5 pagesUnit 2-Biological Foundation of PsychologyassmmNo ratings yet
- Brain Final PPTDocument27 pagesBrain Final PPT8898000884No ratings yet
- The Power of MindDocument41 pagesThe Power of Mindalliahdane valenciaNo ratings yet
- Brain Blaster: Everything you need to know about Focus, attention and Boost Your Brain.From EverandBrain Blaster: Everything you need to know about Focus, attention and Boost Your Brain.No ratings yet
- PL PT CogpsyDocument3 pagesPL PT CogpsyArsela MaeNo ratings yet
- Brain Enhancement. How to Optimize Your Brain for a Fuller Life.From EverandBrain Enhancement. How to Optimize Your Brain for a Fuller Life.No ratings yet
- The Powers of MindDocument2 pagesThe Powers of MindRachelle Joy Fronda RasulaNo ratings yet
- PerDev Q1W6 The Power of MindDocument36 pagesPerDev Q1W6 The Power of Mindjzwf8m82gjNo ratings yet
- All About The Brain The Human Body QuizDocument33 pagesAll About The Brain The Human Body QuizmariuzanguscustodioNo ratings yet
- 15 Areas of The Brain and Their FunctionsDocument6 pages15 Areas of The Brain and Their Functionslaurahermoza1995No ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesCentral Nervous SystemTahir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Personality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteDocument8 pagesPersonality Development Weeks 7-8 Lecture NoteCzarina Ciara AndresNo ratings yet
- PerdevDocument20 pagesPerdevAngeilo Salmasan PaitNo ratings yet
- MasterMind 101 Learn to Control Your Emotional Thoughts And Free Yourself From Your Own Prison.From EverandMasterMind 101 Learn to Control Your Emotional Thoughts And Free Yourself From Your Own Prison.No ratings yet
- Perdev HW2Document6 pagesPerdev HW2rianne margaretNo ratings yet
- FCE 3204 Thinking SkillsDocument23 pagesFCE 3204 Thinking SkillsTey Boon KiatNo ratings yet
- Dementia and The BrainDocument13 pagesDementia and The BrainLuminita AndreiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3Document31 pagesTOPIC 3Fatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- 6 Q1-PerDev - ForstudentsDocument16 pages6 Q1-PerDev - ForstudentsBoyet CatalanNo ratings yet
- Empath survival guide: The Complete Survival Manual for Healing, Self-Discovery, and Avoiding AbusersFrom EverandEmpath survival guide: The Complete Survival Manual for Healing, Self-Discovery, and Avoiding AbusersNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document53 pagesUnit 4saima mubarakNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience in the workplace How understanding the brain can transform your business e bookDocument34 pagesNeuroscience in the workplace How understanding the brain can transform your business e bookHarish C NNo ratings yet
- THC3106 Module 2Document2 pagesTHC3106 Module 2Hope OLPINDANo ratings yet
- Flora of KeralaDocument89 pagesFlora of KeralaArsmagneticaNo ratings yet
- CAMPBELL Biology-10ed Chapter Changed (US-Globe) - 1Document5 pagesCAMPBELL Biology-10ed Chapter Changed (US-Globe) - 1詹昀婷No ratings yet
- Protein Purificiation Formal Lab Write UpDocument12 pagesProtein Purificiation Formal Lab Write Upgraum1090% (20)
- HSG Lop 9 - 2023Document6 pagesHSG Lop 9 - 2023Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF BIOLOGY LAB MANUALDocument43 pagesCONCEPTS OF BIOLOGY LAB MANUALUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- San Juan National High School Science Test ReviewDocument3 pagesSan Juan National High School Science Test ReviewtolisNo ratings yet
- Genetics Terms ExplainedDocument9 pagesGenetics Terms ExplainedJan IceNo ratings yet
- Issue 02 Research Horizons - Novel Sensor Technologies and ApplicationsDocument36 pagesIssue 02 Research Horizons - Novel Sensor Technologies and ApplicationsAlmir TellesNo ratings yet
- Ii SemDocument2 pagesIi SemAnnaNo ratings yet
- Science News - December 17, 2022 USADocument44 pagesScience News - December 17, 2022 USAC0D3R4 T34MNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 3: Teen Stress, Pressures and Finding Different SoundsDocument7 pagesUnit 1 and 3: Teen Stress, Pressures and Finding Different Soundsngọc chinh maiNo ratings yet
- Summary 7ADocument2 pagesSummary 7ATHJNo ratings yet
- Willette Et Al. Sardines ReviewNzjJJDocument22 pagesWillette Et Al. Sardines ReviewNzjJJAlgeneNo ratings yet
- Mitosis QuizDocument3 pagesMitosis QuizclaireNo ratings yet
- Bo de Thi Thu THPT Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2018 Co Dap An 1Document152 pagesBo de Thi Thu THPT Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2018 Co Dap An 1Phong PogNo ratings yet
- The Cold and The Dark The World After Nuclear War Illustrated 0393302415 9780393302417 CompressDocument266 pagesThe Cold and The Dark The World After Nuclear War Illustrated 0393302415 9780393302417 CompressAlex DavilaNo ratings yet
- Exchange of Substances - Questions by Topic: Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelDocument9 pagesExchange of Substances - Questions by Topic: Edexcel (A) Biology A-Levelhamda yNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela: End Semester Examination Programme (2020-21 / Autumn) 24 JUN 2021 21:26Document11 pagesNational Institute of Technology Rourkela: End Semester Examination Programme (2020-21 / Autumn) 24 JUN 2021 21:26Veda SherlaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormone SummaryDocument11 pagesThyroid Hormone SummaryAishwarya SinghNo ratings yet
- Laboratory-exercise-No.1 MicrobioDocument9 pagesLaboratory-exercise-No.1 MicrobioMarvin TalahibanNo ratings yet
- CORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Document22 pagesCORONA-SARS Detection BASED ON SPOT-CHECK PCR - PSA-PASTEUR TEST - V.0120Thanh DoNo ratings yet
- GMO FOOD 2nd Edition (Contemporary World Issues) David E. Newton - GMO Food - A Reference Handbook (2021)Document396 pagesGMO FOOD 2nd Edition (Contemporary World Issues) David E. Newton - GMO Food - A Reference Handbook (2021)SkittlessmannNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Cat Version 10th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Cat Version 10th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualWilliamCartersafg100% (60)
- Biochem CfeDocument5 pagesBiochem CfeJulius MatroNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's School Nevta PT 1 Exams Syllabus Classes XI & XII 2023-24Document5 pagesSt. Xavier's School Nevta PT 1 Exams Syllabus Classes XI & XII 2023-24AdaNo ratings yet
- SGE HPLC ProtecolDocument8 pagesSGE HPLC ProtecolMarcela Robayo BarragánNo ratings yet
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology-1988-Kobayashi-693.fullDocument6 pagesApplied and Environmental Microbiology-1988-Kobayashi-693.fullToo FASTNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post Mendelian Concepts of HeredityDocument25 pagesPre and Post Mendelian Concepts of HeredityAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- 1.6, 1.7 Circulatory System Structure and Function Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages1.6, 1.7 Circulatory System Structure and Function Exam QuestionsAhmad LuqmanNo ratings yet